begin quote from:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nord_Stream
Nord Stream
| Nord Stream 1 | |
|---|---|
 Location of Nord Stream 1 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Russia Germany |
| Coordinates | 60°31′44″N 28°4′21″E 54°8′24″N 13°38′23″E |
| General direction | east–west–south |
| From | Vyborg, The Russian Federation |
| Passes through | Baltic Sea |
| To | Lubmin near Greifswald, Germany |
| General information | |
| Type | Natural gas |
| Partners | Gazprom Uniper Wintershall Dea Gasunie Engie |
| Operator | Nord Stream AG |
| Manufacturer of pipes | EUROPIPE OMK Sumitomo |
| Installer of pipes | Saipem |
| Pipe layer | Castoro Sei |
| Contractors | Rambøll Environmental Resource Management Marin Mätteknik IfAÖ PeterGaz DOF Subsea Intec Engineering Tideway BV Royal Boskalis Westminster EUPEC PipeCoatings Rolls-Royce plc Dresser-Rand Group Siirtec Nigi SPA |
| Commissioned | 8 November 2011 (1st line) 8 October 2012 (2nd line) |
| Technical information | |
| Length | 1,222 km (759 mi) |
| Maximum discharge | 55 billion m3/a (1.9 trillion cu ft/a) |
| Diameter | 1,220 mm (48 in) |
| No. of compressor stations | 1 |
| Compressor stations | Portovaya |
| Nord Stream 2 | |
|---|---|
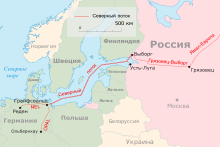 Map of Nord Stream 2 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Russia Germany |
| Coordinates | 60°33′24″N 28°3′59″E 54°8′24″N 13°38′23″E |
| General direction | east–west–south |
| From | Ust-Luga, Russia |
| Passes through | Baltic Sea |
| To | Lubmin near Greifswald, Germany |
| General information | |
| Type | Natural gas |
| Partners | Gazprom Uniper Wintershall Dea OMV Engie Royal Dutch Shell |
| Operator | Nord Stream 2 AG |
| Manufacturer of pipes | EUROPIPE OMK Chelyabinsk Pipe-Rolling Plant (Chelpipe) |
| Installer of pipes | Allseas (Until 21 December 2019) |
| Pipe layer | Pioneering Spirit Solitaire C10 Akademik Cherskiy Fortuna |
| Expected | 2022 |
| Technical information | |
| Length | 1,230 km (760 mi) |
| Maximum discharge | 55 billion m3/a (1.9 trillion cu ft/a) |
| Diameter | 1,220 mm (48 in) |
| No. of compressor stations | 1 |
| Compressor stations | Slavyanskaya |
Nord Stream (Russian: Северный поток, Severny potok) is a system of offshore natural gas pipelines in Europe, running under the Baltic Sea from Russia to Germany. It includes two pipelines running from Vyborg to Lubmin near Greifswald forming the original Nord Stream (also known as Nord Stream 1;[1] former names: North Transgas and North European Gas Pipeline), and two further pipelines running from Ust-Luga to Lubmin termed Nord Stream 2. In Lubmin Nord Stream 1 is connected to the OPAL pipeline to Olbernhau on the Czech border and to the NEL pipeline to Rehden near Bremen.
Nord Stream 1 is owned and operated by Nord Stream AG, whose majority shareholder is the Russian state company Gazprom. Nord Stream 2 is owned and planned to be operated by Nord Stream 2 AG, which is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Gazprom.
The first line of Nord Stream 1 was laid by May 2011 and was inaugurated on 8 November 2011.[2][3] The second line of Nord Stream 1 was laid in 2011–2012 and was inaugurated on 8 October 2012. At 1,222 km (759 mi) in length, Nord Stream 1 is the longest sub-sea pipeline in the world, surpassing the Langeled pipeline.[4][5]
The laying of Nord Stream 2 was carried out in 2018–2021.[6] The first line of Nord Stream 2 was completed in June 2021, and the second line was completed in September 2021.
Nord Stream 1 has a total annual capacity of 55 billion m3 (1.9 trillion cu ft) of gas, and the construction of Nord Stream 2 is expected to double this capacity to a total of 110 billion m3 (3.9 trillion cu ft).[7][8][9]
The Nord Stream projects have been fiercely opposed by the United States and Ukraine, as well as by other Central and Eastern European countries, because of concerns that the pipelines would increase Russia's influence in Europe, and because of the knock-on reduction of transit fees for use of the existing pipelines in Central and Eastern European countries.
The name "Nord Stream" occasionally refers to a wider pipeline network, including the feeding onshore pipeline in Russia, and further connections in Western Europe.[10]
History[edit]
Nord Stream 1[edit]
The pipeline project started in 1997 when Gazprom and the Finnish oil company Neste (in 1998 merged with Imatran Voima to form Fortum, which in 2004 separated again into Fortum and Neste) formed the joint company North Transgas Oy for construction and operation of a gas pipeline from Russia to Northern Germany across the Baltic Sea.[11] North Transgas cooperated with the German gas company Ruhrgas (which later became part of E.ON, which was split still later into E.ON and Uniper). A route survey in the Exclusive Economic Zones of Finland, Sweden, Denmark and Germany, and a feasibility study of the pipeline was conducted in 1998. Several routes were considered including routes with onshore segments through Finland and Sweden.[12]
On 24 April 2001, Gazprom, Fortum, Ruhrgas and Wintershall adopted a statement regarding a joint feasibility study for construction of the pipeline.[13] On 18 November 2002, the Management Committee of Gazprom approved a schedule of project implementation. In May 2005, Fortum withdrew from the project and sold its stake in North Transgas to Gazprom. As a result, Gazprom became the only shareholder of North Transgas Oy.[11][14]
On 8 September 2005, Gazprom, BASF and E.ON signed a basic agreement on the construction of a North European Gas Pipeline. On 30 November 2005, the North European Gas Pipeline Company (later renamed Nord Stream AG) was incorporated in Zug, Switzerland. On 9 December 2005, Gazprom started construction of the Russian onshore feeding pipeline (Gryazovets–Vyborg gas pipeline) in the town of Babayevo in Vologda Oblast.[15] The feeding pipeline was completed in 2010.
On 4 October 2006, the pipeline and the operating company were officially renamed Nord Stream AG.[16] After establishment of Nord Stream AG, all information related to the pipeline project, including results of the seabed survey of 1998, were transferred from North Transgas to the new company, and on 2 November 2006, North Transgas was officially dissolved.[17]
The environmental impact assessment started on 16 November 2006 with notification sent to Russia, Finland, Sweden, Denmark and Germany, as parties of origin (the countries whose exclusive economic zones and/or territorial waters the pipeline is planned to pass through), as well as to Poland, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia as affected parties.[18] The final report on transboundary environmental impact assessment was delivered on 9 March 2009.[19]
On 19 March 2007, Nord Stream AG hired Italian company Snamprogetti, a subsidiary of Saipem, for detailed design engineering of the pipeline.[20] A letter of intent for construction works was signed with Saipem on 17 September 2007 and the contract was concluded on 24 June 2008.[21][22] On 25 September 2007, the pipe supply contracts were awarded to the pipe producers EUROPIPE and OMK, and on 18 February 2008, the concrete weight coating and logistics services agreement was awarded to EUPEC PipeCoatings S.A.[23][24] The supply contracts for the second line were awarded to OMK, Europipe and Sumitomo Heavy Industries on 22 January 2010.[25] On 30 December 2008 Rolls-Royce plc was awarded a contract to supply turbines for the compressor, and on 8 January 2009, Royal Boskalis Westminster and Danish Dredging Contractor Rohde Nielsen A/S. were awarded a joint venture seabed dredging contract.[26][27]
The agreement to take Gasunie to the consortium as the fourth partner, was signed on 6 November 2007.[28] On 10 June 2008, Gasunie was included in the register of shareholders.[29] On 1 March 2010, French energy company GDF Suez signed with Gazprom a memorandum of understanding to acquire 9% stake in the project.[30] The transaction was closed in July 2010.[31]
In August 2008, Nord Stream AG hired former Finnish prime minister Paavo Lipponen as a consultant to help speed up the application process in Finland and to serve as a link between Nord Stream and Finnish authorities.[32]
On 21 December 2007, Nord Stream AG submitted application documents to the Swedish government for the pipeline construction in the Swedish Exclusive Economic Zone.[33] On 12 February 2008, the Swedish government rejected the consortium's application which it had found incomplete.[34][35] New application was filed later. On 20 October 2009, Nord Stream received a construction permit to build the pipeline in the Danish waters.[36] On 5 November 2009, the Swedish and Finnish authorities gave a permit to lay the pipeline in their exclusive economic zones.[37] On 22 February 2010, the Regional State Administrative Agency for Southern Finland issued the final environmental permit allowing construction of the Finnish section of the pipeline.[38][39]
On 15 January 2010 construction of the Portovaya compressor station in Vyborg near the Gulf of Finland began. [40] [41] The first pipe of the pipeline was laid on 6 April 2010 in the Swedish exclusive economic zone by the Castoro Sei vessel. In addition to Castoro Sei, also Castoro 10 and Solitaire were contracted for pipe-laying works.[42] Construction of the pipeline was officially launched on 9 April 2010 at Portovaya Bay.[43]
The laying of the first line was completed on 4 May 2011 (the last pipe put in place), while all underwater works on the first line were completed on 21 June 2011.[5] In August 2011, Nord Stream was connected with the OPAL pipeline.[44] First gas was pumped into the first line on 6 September 2011.[45]
The pipeline was officially inaugurated by the German Chancellor Angela Merkel, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev, French Prime Minister François Fillon, and Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte on 8 November 2011 at the ceremony held in Lubmin.[2][3][46] Construction of the second line was completed in August 2012 and it was inaugurated on 8 October 2012.[47]
Nord Stream 2[edit]
In 2011, Nord Stream AG started evaluation of an expansion project consisting of two additional lines (later named Nord Stream 2) to double the annual capacity up to 110 billion m3 (3.9 trillion cu ft). In August 2012, Nord Stream AG applied to the Finnish and Estonian governments for route studies in their underwater exclusive economic zones for the third and fourth lines.[48] A plan to route an additional pipeline to the United Kingdom was considered but abandoned.[49][50]
In January 2015, Gazprom announced that the expansion project had been put on hold since the existing lines were running at only half capacity, due to EU sanctions on Russia,[51] following its annexation of Crimea.
In June 2015, an agreement to build Nord Stream 2 was signed between Gazprom, Royal Dutch Shell, E.ON, OMV, and Engie.[52] As the creation of a joint venture was blocked by Poland,[clarification needed] on 24 April 2017, Uniper, Wintershall, Engie, OMV and Royal Dutch Shell signed a financing agreement with Nord Stream 2 AG, a subsidiary of Gazprom responsible for the development of the Nord Stream 2 project.[53]
On 31 January 2018, Germany granted Nord Stream 2 a permit for construction and operation in German waters and for landfall areas near Lubmin.[54]
In May 2018 construction started at the Greifswald end point.[55]
In January 2019, the US ambassador in Germany, Richard Grenell, sent letters to companies involved in the construction of Nord Stream 2 urging them to stop working on the project and threatening them with the possibility of sanctions.[56] In December 2019, the Republican Senators Ted Cruz and Ron Johnson have also urged Allseas owner Edward Heerema to suspend the works on the pipeline, warning him that otherwise the United States would impose sanctions.[57] Cruz formally proposed such a bill to enable sanctions on 8 November 2021.[58]
On 21 December 2019, Allseas announced that the company had suspended its Nord Stream 2 pipelaying activities, anticipating enactment of the U.S. National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020 containing sanctions.[59][60]
In May 2020, the German energy regulator refused an exception from competition rules that require Nord Stream 2 to separate gas ownership from transmission.[61] In August 2020, Poland fined Gazprom €50 million due to the latter's lack of cooperation with an investigation launched by UOKiK, the Polish anti-monopoly watchdog. UOKiK cited competition rules against Gazprom and companies that are financing the project, suspecting that they have continued to work on the pipeline without permission from the government of Poland.[62]
In December 2020, the Russian pipelaying ship Akademik Cherskiy continued pipe-laying.[63] In January, Fortuna, another pipe-layer joined forces with the Akademik Cherskiy to complete the pipeline.[64] On 4 June 2021, President Putin announced that the pipe-laying for first line of the Nord Stream 2 has been fully completed. On 10 June, the sections of the pipeline were connected.[65] The laying of the second line was completed in September 2021.[66]
In June 2021, U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken said that Nord Stream 2 completion was inevitable. In July 2021, the U.S. urged Ukraine not to criticise a forthcoming agreement with Germany over the pipeline.[67][68] On July 20, Joe Biden and Angela Merkel reached a conclusive deal that the U.S. may trigger sanctions if Russia uses Nord Stream as a "political weapon". The deal aims to prevent Poland and Ukraine from being cut off from Russian gas supplies. Ukraine will get a $50 million loan for green technology until 2024 and Germany will set up a billion dollar fund to promote Ukraine's transition to green energy to compensate the loss of the gas transit fees. The contract for transiting Russian gas through Ukraine will be prolonged until 2034, if the Russian government agrees.[69][70][71]
On 16 November 2021, European natural gas prices rose by 17% after Germany's energy regulator suspended approval of the Nord Stream 2.[72][73]
On 9 December 2021, Polish Prime Minister, Mateusz Morawiecki, called on Germany’s newly appointed Chancellor Olaf Scholz, to oppose the start-up of Nord Stream 2 and not to give in to pressure from Russia. On a visit to Rome, Morawiecki said: "I will call on Chancellor Scholz not to give in to pressure from Russia and not to allow Nord Stream 2 to be used as an instrument for blackmail against Ukraine, an instrument for blackmail against Poland, an instrument for blackmail against the European Union."[74]
Technical features[edit]
Russian onshore pipeline[edit]
Nord Stream is fed by the Gryazovets–Vyborg gas pipeline. It is a part of the integrated gas transport network of Russia connecting existing grid in Gryazovets with the coastal compressor station at Vyborg.[75] The length of this pipeline is 917 km (570 mi), the diameter of the pipe is 1,420 mm (56 in), and working pressure is 100 atm (10 MPa), which is secured by six compressor stations. The Gryazovets-Vyborg pipeline, parallel to the branch of the Northern Lights pipeline (Gryazovets–Leningrad and Leningrad–Vyborg–Russian state border pipelines), also supplies gas to the Northwestern region of Russia (Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast).[10] The pipeline is operated by Gazprom Transgaz Saint Petersburg.[10]
To feed Nord Stream 2 2,866 km (1,781 mi) of new pipeline and three compressor stations were built, and five existing compressor stations were expanded.[76] The feeding pipeline starts in Gryazovets and follows the existing route of the Northern Lights pipeline. In Volkhov, the pipeline turns south and continues to the Slavyanskaya compressor station near Ust-Luga.[77]
Baltic Sea offshore pipeline[edit]
The Nord Stream offshore pipeline is operated by Nord Stream AG.[18][28] It runs from Vyborg compressor station at Portovaya Bay along the bottom of the Baltic Sea to Greifswald in Germany. The length of the subsea pipeline is 1,222 km (759 mi), of which 1.5 km (0.93 mi) in Russian inland, 121.8 km (65.8 nmi) in Russian territorial waters, 1.4 km (0.8 nmi) in the Russian economic zone, 375.3 km (202.6 nmi) in the Finnish economic zone, 506.4 km (273.4 nmi) in the Swedish economic zone, 87.7 km (47.4 nmi) in the Danish territorial waters, 49.4 km (26.7 nmi) in the Danish economic zone, 31.2 km (16.8 nmi) in the German economic zone, 49.9 km (26.9 nmi) in German territorial waters and 0.5 km (0.31 mi) in German inland.[78] The pipeline has two parallel lines, both with capacity of 27.5 billion m3 (970 billion cu ft) of natural gas per year.[7] Pipes have a diameter of 1,220 mm (48 in), a wall thickness of 26.8 to 41 mm (other specification 38 mm (1.50 in)) and a working pressure of 220 bar (22 MPa; 3,200 psi).[18]
Nord Stream 2 starts at the Slavyanskaya compressor station near Ust-Luga port, located 2.8 km (1.7 mi) south-east of the village of Bolshoye Kuzyomkino (Narvusi) in the Kingiseppsky District of the Leningrad Oblast, in the historical Ingria close to the Estonian border. A 3.2 km (2.0 mi) onshore pipeline runs from the compressor station to the landfall at the Kurgalsky Peninsula on the shore of Narva Bay.[79][76] Also the landfall point in Kolganpya (Kolkanpää) at the Soikinsky Peninsula was considered as an alternative.[76] Except the Russian section, the route of Nord Stream 2 follows mainly the route of Nord Stream.[49][76] From the Russian landfall, a 114 km (71 mi) section runs through Russian territorial waters to the Finnish exclusive economic zone. The Finnish section is 374 km (232 mi) and the following section in the Swedish exclusive economic zone is 510 km (320 mi) long.[79] The 147 km (91 mi) Danish sections runs on the Danish continental shelf southeast of Bornholm.[9] The German part of the pipeline consists of 85 km (53 mi) of offshore pipeline and 29 km (18 mi) onshore pipeline connecting the landfall with the Nord Stream 2 receiving terminal.[79] Nord Stream 2 has two parallel lines, both with capacity of 27.5 billion m3 (970 billion cu ft) of natural gas per year.[8][79]
Middle and Western European pipelines[edit]
Nord Stream is connected to two transmission pipelines in Germany. The southern pipeline (OPAL pipeline) runs from Greifswald to Olbernhau near the German-Czech border. It connects Nord Stream with JAGAL (connected to the Yamal-Europe pipeline), and STEGAL (connected to the Russian gas transport route via Czechia and Slovakia) transmission pipelines. The Gazelle pipeline, put into operation in January 2013,[80] links the OPAL pipeline with South-German gas network.
The western pipeline (NEL pipeline) runs from Greifswald to Achim, where it is connected with the Rehden-Hamburg gas pipeline.[81] Together with the MIDAL pipeline it creates the Greifswald–Bunde connection. Further gas delivery to the United Kingdom is made through the connection between Bunde and Den Helder, and from there through the offshore interconnector Balgzand–Bacton (BBL Pipeline).
Nord Stream 2 is connected to the NEL pipeline and European Gas Pipeline Link (EUGAL), which runs largely parallel to the OPAL pipeline.[79][82]
Supply sources[edit]
Yuzhno-Russkoye field, which is located in the Krasnoselkupsky District, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Tyumen Oblast, was designated as the main source of natural gas for the Nord Stream 1 pipeline.[83][84][85] Nord Stream 1 and 2 are also fed from fields in Yamal Peninsula, Ob and Taz bays. It was predicted that also the majority of gas from the Shtokman field would be sold to Europe via the Nord Stream pipeline when it comes on stream and the connecting pipeline via Kola peninsula to Volkhov or Vyborg is built.[86] However, the Shtokman project was postponed indefinitely.
The proposed gas route from Russia's West Siberian petroleum basin to China is known as Power of Siberia 2 pipeline.[87] For Russia, the pipeline allows another economic partnership in the face of resistance to the Nord Stream 2 pipeline.[88]
Costs and financing[edit]
According to Gazprom, the costs of the onshore pipelines in Russia and Germany were around €6 billion.[89] The offshore section of the project cost €8.8 billion.[90] 30% of the financing was raised through equity provided by shareholders in proportion to their stakes in the project, while 70% came from external financing by banks.[91]
There were two tranches.[92][93] The first tranche for a €3.9 billion includes a 3.1 billion, 16-year facility covered by export credit agencies and an €800 million, 10-year uncovered commercial loan to be serviced by earnings from the transportation contracts. A €1.6 billion is covered by French credit insures company Euler Hermes, a €1 billion by the German United Loan Guarantee Programme UFK, and a €500 million Italian Export Credit Agency SACE SpA. Loans to be provided by 26 commercial banks. Crédit Agricole is documentation bank and bank facility agent. Société Générale is intercreditor agent, Sace facility agent, security trustee and model bank. Commerzbank is Hermes facility agent, UniCredit is UFK facility agent, Deutsche Bank is account bank and Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation is technical and environmental bank.[91][92] The financial advisers were Société Générale, Royal Bank of Scotland (ABN Amro), Dresdner Kleinwort (Commerzbank), and Unicredit.[94][95] The legal adviser to Nord Stream was White & Case and legal adviser for the lenders was Clifford Chance.[92]
For Nord Stream 2, the loan from Uniper, Wintershall Dea, OMV, Engie, and Royal Dutch Shell covers 50% of the project costs of €9.5 billion. The rest is being financed by Gazprom.[53]
Contractors[edit]
Nord Stream 1[edit]
The environmental impact assessment of Nord Stream 1 was carried out by Rambøll and Environmental Resource Management. The route and seabed surveys were conducted by Marin Mätteknik, IfAÖ, PeterGaz and DOF Subsea.[96][97]
Work preliminary front-end engineering was done by Intec Engineering.[98] The design engineering of the subsea pipeline was done by Snamprogetti (now part of Saipem) and the pipeline was constructed by Saipem.[20][22] Saipem gave sub-contract to Allseas for laying more than 1/4 of both the pipelines. The seabed was prepared for the laying of the pipeline by a joint venture of Royal Boskalis Westminster and Tideway.[27] The pipes were provided by EUROPIPE, OMK, and Sumitomo.[23][25] Concrete weight coating and logistics services were provided by EUPEC PipeCoatings S.A. For the concrete weight coating new coating plants were constructed in Mukran (Germany) and Kotka (Finland).[24] Rolls-Royce plc supplied eight aeroderivative gas turbines driving centrifugal compressors for front-end gas boosting at the Vyborg (Portovaya) gas compressor station.[26] Dresser-Rand Group supplied DATUM compressors and Siirtec Nigi SPA provided a gas treatment unit for the Portovaya station.[99][100]
For the construction period, Nord Stream AG created a logistic center in Gotland. Other interim stock yards are located in Mukran, in Kotka, in Hanko (Finland) and in Karlskrona (Sweden).[24]
Nord Stream 2[edit]
Nord Stream 2 was laid by Allseas using pipe-laying vessels Pioneering Spirit and Solitaire,[101] except the part of German offshore section which was laid by Saipem's pipe-laying vessel C10.[79] Pipes were manufactured by EUROPIPE, OMK and the Chelyabinsk Pipe-Rolling Plant (Chelpipe), and were coated by Wasco Coatings Europe. Blue Water Shipping handled the transportation and storage of pipeline segments in Germany, Finland and Sweden for Wasco. A joint venture of Boskalis and Van Oord did rock placement at the preparatory stage of construction. Kvaerner did the civil and mechanical engineering of the onshore facilities in Russia.[79]
Project companies[edit]
Nord Stream 1 is operated by the special-purpose company Nord Stream AG, incorporated in Zug, Switzerland on 30 November 2005. Shareholders of the company are the Russian gas company Gazprom (51% of shares), German companies Wintershall Dea and PEG Infrastruktur AG (E.ON) (both 15.5%), the Dutch gas company Gasunie (9%), and the French gas company Engie (9%).[18][28] The managing director is Matthias Warnig and the chairman of the shareholders' committee is German ex-chancellor Gerhard Schröder.
Nord Stream 2 is developed and planned to be operated by Nord Stream 2 AG, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of Gazprom.[53] It is registered at the same place and has the same management as Nord Stream AG.
Transportation contracts[edit]
On 13 October 2005 Gazprom signed a contract with German gas company Wingas, then a joint venture of Gazprom and Wintershall (subsidiary of BASF), to supply 9 billion cubic metres (320 billion cubic feet) of natural gas per year for 25 years.[102] On 16 June 2006 Gazprom and Danish Ørsted A/S (then named DONG Energy) signed a 20-year contract for delivery of 1 billion m3 (35 billion cu ft) Russian gas per year to Denmark, while Ørsted will supply 600 million m3 (21 billion cu ft) natural gas per year to the Gazprom's subsidiary, Gazprom Marketing and Trading, in the United Kingdom.[103] 1 October 2009 the companies signed a contract to double the delivery to Denmark.[104]
On 29 August 2006 Gazprom and E.ON Ruhrgas signed an agreement to extend current contracts on natural gas supplies and have signed a contract for an additional 4 billion m3 (140 billion cu ft) per year through the Nord Stream pipeline.[105] On 19 December 2006, Gazprom and Gaz de France (now GDF Suez) agreed to an additional 2.5 billion m3 (88 billion cu ft) gas supply through the Nord Stream.[106]
Controversies[edit]
Nord Stream 1[edit]
The pipeline projects were criticized by some countries and environmental organizations (such as the World Wide Fund for Nature).[107][108][109][110][111]
Political aspects[edit]
Opponents have seen the pipeline as a move by Russia to bypass traditional transit countries (currently Ukraine, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Belarus and Poland).[112] Some transit countries are concerned that a long-term plan of the Kremlin is to attempt to exert political influence on them by threatening their gas supply without affecting supplies to Western Europe.[113][114] The fears are strengthened by the fact that Russia has refused to ratify the Energy Charter Treaty. Critics of Nord Stream say that Europe could become dangerously dependent on Russian natural gas, particularly since Russia could face problems meeting a surge in domestic as well as foreign demand.[115][116][117] Following several Russia–Ukraine gas disputes over gas prices, as well as foreign policy towards Eastern Europe, it has been noted that the gas supplies by Russia can be used as a political tool.[118]
A Swedish Defence Research Agency study, finished in March 2007, counted over 55 incidents since 1991, most with "both political and economic underpinnings".[116][117] In April 2006 Radosław Sikorski, then Poland's defence minister, compared the project to the infamous 1939 Nazi-Soviet Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact. [119] In his book The New Cold War: Putin's Russia and the Threat to the West, published 2008, Edward Lucas stated that "though Nord Stream's backers insist that the project is business pure and simple, this would be easier to believe if it were more transparent."[116] In the report published by the Fridtjof Nansen Institute in 2008, Norwegian researcher Bendik Solum Whist noted that Nord Stream AG was incorporated in Switzerland, "whose strict banking secrecy laws makes the project less transparent than it would have been if based within the EU".[116] Secondly, the Russian energy sector "in general lacks transparency" and Gazprom "is no exception".[116]
The Russian response has been that the pipeline increases Europe's energy security, and that the criticism is caused by bitterness about the loss of significant transit revenues, as well as the loss of political influence that stems from the transit countries' ability to hold Russian gas supplies to Western Europe hostage to their local political agendas.[120] It would reduce Russia's dependence on the transit countries as for the first time it would link Russia directly to Western Europe.[115] According to Gazprom, the direct connection to Germany would decrease risks in the gas transit zones, including the political risk of cutting off Russian gas exports to Western Europe.[121]
Security and military aspects[edit]
Swedish military experts and several politicians, including former Minister for Defence Mikael Odenberg, have stated that the pipeline may cause a security policy problem for Sweden.[122] According to Odenberg, the pipeline motivates Russian navy presence in the Swedish economic zone and the Russians can use this for military intelligence should they want to.[123] Finnish military scholar Alpo Juntunen has said that even though the political discussion over Nord Stream in Finland concentrates on the various ecological aspects, there are clearly military implications to the pipeline that are not discussed openly in Finland.[124] More political concerns were raised when Vladimir Putin stated that the ecological safety of the pipeline project will be ensured by using the Baltic Fleet of the Russian Navy.[125] German weekly Stern has reported that the fibre optic cable and repeater stations along the pipeline could theoretically also be used for espionage. Nord Stream AG asserted that a fibre-optic control cable was neither necessary nor technically planned.[126]
Deputy Chairman of the Board of Executive Directors of Gazprom Alexander Medvedev has dismissed these concerns, stating that "some objections are put forward that are laughable—political, military or linked to spying. That is really surprising because in the modern world ... it is laughable to say a gas pipeline is a weapon in a spy war."[127]
German Bundeswehr asked Nord Stream to change the planned route because the pipeline is laid close to a sea testing ground near Rügen, which is actively used for naval exercises.[citation needed]
Economic aspects[edit]
Russian and German officials have claimed that the pipeline leads to economic savings due to the elimination of transit fees (as transit countries would be bypassed), and a higher operating pressure of the offshore pipeline which leads to lower operating costs (by eliminating the necessity for expensive midway compressor stations).[128] According to Ukrtransgaz in 2011, Ukraine alone will lose natural gas transit fees of up to $720 million per year from Nord Stream 1.[129] According to the Naftogaz chairman in 2019, Ukraine will lose $3 billion per year of natural gas transit fees from Nord Stream 2.[130] Gazprom has stated that it will divert 20 billion m3 (710 billion cu ft) of natural gas transported through Ukraine to Nord Stream.[131] Opponents say that the maintenance costs of a submarine pipeline are higher than for an overland route. In 1998, former Gazprom chairman Rem Vyakhirev claimed that the project was economically unfeasible.[132]
As the Nord Stream pipeline crosses the waterway to Polish ports in Szczecin and Świnoujście, there were concerns that it will reduce the depth of the waterway leading to the ports.[133][134][135] However, in 2011, then-prime minister of Poland Donald Tusk, as well as several experts, confirmed that the Nord Stream pipeline does not block the development plans of Świnoujście and Szczecin ports.[135][136]
Environmental aspects[edit]
The greatest environmental impact in connection with the pipeline results from the consumption of the transported gas, if it allows more imports to the EU. That would be in conflict with decarbonization efforts for climate protection. At a nominal capacity of 55 billion m3/a (1.9 trillion cu ft/a), each pipe pair can cause carbon emissions of 110 million tonnes CO2 annually.[137]
For the Portovaya compressor station at the Russian beginning of Nord Stream 1 with a rating of 366 megawatts, CO2 emissions of around 1.5 million tonnes (3.3 billion pounds) per annum are estimated,[138] not including compressor stations for the gas pipelines within Russia.
Since the pressure loss is the square of the flow velocity, dividing an unchanged gas transport volume between two Nord Stream systems could save around 3/4 of the pumping effort and presumably more than 1 million tonnes (2.2 billion pounds) of CO2 emissions could be avoided annually. Using the Umweltbundesamt's discounted CO2 damage costs of 180 euros / tonne,[139] this would, after a rough estimate,[by whom?][citation needed] enable the third tube to be amortized within around 20 years from a global point of view. Possibly also the fourth tube could be amortized in the hypothetical case of an overall optimization of gas flow over various pipelines between Russia and the EU.
The production of over 2 million tonnes (4.4 billion pounds) of steel for the Nord Stream 2 tubes resulted in more than 3 million tonnes (6.6 billion pounds) of CO2 emissions, not including the concrete coating and the associated pipeline sections onshore.[citation needed]
Before construction there were concerns that during construction the sea bed would be disturbed, dislodging World War II-era naval mines and toxic materials including mines, chemical waste, chemical munitions and other items dumped in the Baltic Sea in the past decades, and thereby toxic substances could surface from the seabed, damaging the Baltic's particularly sensitive ecosystem.[140][141][142][143][144] Swedish Environment Minister Andreas Carlgren demanded that the environmental analysis should include alternative ways of taking the pipeline across the Baltic, as the pipeline is projected to be passing through areas considered environmentally problematic and risky.[145] Sweden's three opposition parties called for an examination of the possibility of rerouting the pipeline onto dry land.[143] Finnish environmental groups campaigned to consider the more southern route, claiming that the sea bed is flatter and so construction would be more straightforward, and therefore potentially less disruptive to waste, including dioxins and dioxin-like compounds, littered on the sea bed.[146] Latvian president Valdis Zatlers said that Nord Stream was environmentally hazardous as, unlike the North Sea, there is no such water circulation in the Baltic Sea.[citation needed] Ene Ergma, Speaker of the Riigikogu (Parliament of Estonia), warned that the pipeline work rips a canal in the seabed which will demand leveling the sand that lies along the way, atomizing volcanic formations and disposing of fill along the bottom of the sea, altering sea currents.[147]
The impact on bird and marine life in the Baltic Sea is also a concern, as the Baltic sea is recognized by the International Maritime Organization as a particularly sensitive sea area. The World Wide Fund for Nature requested that countries party to the Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission (HELCOM) safeguard the Baltic marine habitats, which could be altered by the implementation of the Nord Stream project.[110] Its Finnish branch said it might file a court case against Nord Stream AG if the company did not properly assess a potential alternative route on the southern side of Hogland. According to Nord Stream AG, this was not a suitable route for the pipeline because of the planned conservation area near Hogland, subsea cables, and a main shipping route.[109] Russian environmental organizations warned that the ecosystem in the Eastern part of the Gulf of Finland is the most vulnerable part of the Baltic Sea and assumed damage to the island territory of the planned Ingermanland nature preserve as a result of laying the pipeline.[147] Swedish environmental groups are concerned that the pipeline is planned to pass too closely to the border of the marine reserve near Gotland.[148] Greenpeace is also concerned that the pipeline would pass through several sites designated marine conservation areas.[149]
In April 2007, the Young Conservative League (YCL) of Lithuania started an online petition entitled "Protect the Baltic Sea While It’s Still Not Too Late!", translated into all state languages of the countries of the Baltic region.[150] On 29 January 2008 the Petitions Committee of the European Parliament organized a public hearing on the petition introduced by the leader of YCL – Radvile Morkunaite. On 8 July 2008, the European Parliament endorsed, by 542 votes to 60, a non-binding report calling on the European Commission to evaluate the additional impact on the Baltic Sea caused by the Nord Stream project.[151] The Riigikogu made a declaration on 27 October 2009, expressing "concern over the possible environmental impacts of the gas line" and emphasizing that international conventions have deemed "the Baltic Sea in an especially vulnerable environmental status".[111]
Russian officials described these concerns as far-fetched and politically motivated by opponents of the project. They argued that during the construction the seabed will be cleaned, rather than endangered. Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov has claimed that Russia fully respects the desire to provide for the 100% environmental sustainability of the project and that Russia is fully supportive of such an approach, and that all environmental concerns would be addressed in the process of environmental impact assessment.[152]
Concerns were raised, since originally Nord Stream AG planned on rinsing out the pipeline with 2.3 billion liters of a solution containing glutaraldehyde, which would be pumped afterward into the Baltic Sea. Nord Stream AG responded that glutaraldehyde would not be used, and even if the chemical were used, the effects would be brief and localized due to the speed with which the chemical breaks down once it comes in contact with water.[153]
One of the problems raised was that the Baltic Sea and particularly Gulf of Finland was heavily mined during World War I and II, with many mines still in the sea.[149] According to Marin Mätteknik around 85,000 mines were laid during the First and Second World Wars, of which only half have been recovered. A lot of munitions have also been dumped in this sea.[154] Critics of the pipeline voiced fears that the pipeline would disturb ammunition dumps. In November 2008 it was reported that the pipeline will run through old sea mine defense lines and that the Gulf of Finland is considered one of the most heavily mined sea areas in the world.[155] Sunken mines, which have been found on the pipeline route, lay primarily in international waters at a depth of more than 70 m (230 ft). Nord Stream AG detonated the mines underwater.[155]
Ethical issues[edit]
The former Chancellor of Germany, Gerhard Schröder, and the President of Russia, Vladimir Putin, were strong advocates of the pipeline project during the negotiation phase. International media alluded to a past relationship between the managing director of Nord Stream AG, Matthias Warnig, himself a former East German secret police officer, and Vladimir Putin when he was a KGB agent in East Germany.[156][157][158][159] These allegations were denied by Matthias Warnig, who said that he had met Vladimir Putin for the first time in his life in 1991, when Putin was the head of the Committee for External Relations of the Saint Petersburg Mayor's Office.[159][160]
The agreement to build the pipeline was signed ten days before the German parliamentary election. On 24 October 2005, a few weeks before Schröder had stepped down as Chancellor, the German government guaranteed to cover €1 billion of the Nord Stream project cost, should Gazprom default on a loan. However, this guarantee expired at the end of 2006 without ever having been needed.[161] Soon after leaving the post of Chancellor of Germany, Gerhard Schröder agreed to head the shareholders' committee of Nord Stream AG. This has been widely described by German and international media as a conflict of interest,[162][163][164] the implication being that the pipeline project may have been pushed through for personal gain rather than for improving gas supplies to Germany. Information about the German government's guarantee was requested by the European Commission. No formal charges have been filed against any party despite years of exhaustive investigations.[161]
In February 2009, the Swedish prosecutor's office started an investigation based on suspicions of bribery and corruption after a college on the island of Gotland received a donation from Nord Stream. The 5 million Swedish kronor (US$574,000) donation was directed to a professor at Gotland University College who had previously warned that the Nord Stream pipeline would come too close to a sensitive bird zone.[165] The consortium has hired several former high-ranking officials, such as Ulrica Schenström, former undersecretary at the Swedish Prime Minister's office, and Dan Svanell, former press secretary for several politicians in the Swedish Social Democratic Party.[166] In addition, the former Prime Minister of Finland, Paavo Lipponen, had worked for Nord Stream as an adviser since 2008.[167]
Land-based alternatives[edit]
On 11 January 2007, the Ministry of Trade and Industry of Finland made a statement on the environmental impact assessment programme of the Russia-Germany natural gas pipeline, in which it mentioned that alternative routes via the Baltic states, Kaliningrad and/or Poland might theoretically be shorter than the route across the Baltic Sea, would be easier to flexibly increase the capacity of the pipeline, and might have better financial results.[168] There were also calls from Sweden to consider rerouting the pipeline onto dry land.[143] Poland had proposed the construction of a second line of the Yamal–Europe pipeline, as well as the Amber pipeline through the Baltic states and Poland as land-based alternatives to the offshore pipeline. The Amber project foresees laying a natural gas pipeline across the Tver, Novgorod and Pskov oblasts in Russia and then through Latvia and Lithuania to Poland, where it would be re-connected to the Yamal–Europe pipeline.[12] Latvia has proposed using its underground gas storage facilities if the onshore route were to be used.[citation needed] Proponents have claimed that the Amber pipeline would cost half as much as an underwater pipeline, would be shorter, and would have less environmental impact.[169] Critics of this proposal say that in this case it would be more expensive for the suppliers over the long-term perspective, because the main aim of the project is to reduce transit costs.[170] Nord Stream AG has responded that the Baltic Sea would be the only route for the pipeline and it will not consider an overland alternative.[171]
World War II graves[edit]
A former member of the European Parliament from Estonia, Andres Tarand has raised the issue that the Nord Stream pipeline could disturb World War II graves dating from naval battles in 1941. A Nord Stream spokesman has stated that only one sunken ship is in the vicinity of the planned pipeline and added that it would not be disturbed.[172] However, on 16 July 2008 it was announced that one of DOF Subsea's seismic vessels had discovered during a survey for the planned Nord Stream pipeline, in Finland's exclusive economic zone in the Gulf of Finland, the wreck of a submarine with Soviet markings, believed to have sunk during World War II.[96]
In addition to the wreck of the Soviet submarine, there are sunken ships on the route of Nord Stream in the Bay of Greifswald and in the Gulf of Finland. The ship in the Bay of Greifswald is one of 20 sunk in 1715 by the Swedish navy to create a physical barrier across the shallow entrance to the Bay of Greifswald coastal lagoon.[173] Russian archaeologists claimed that the ship in the Gulf of Finland "was probably built in 1710 and sank during a raid aimed at conquering Finland" in 1713 during the reign of Peter the Great.[174]
Nord Stream 2[edit]
Political aspects[edit]
In January 2018, United States Secretary of State Rex Tillerson stated that the U.S. and Poland opposed the Nord Stream 2 pipeline, seeing it as undermining Europe's energy security and stability.[175] The Nord Stream 2 pipeline was also opposed by former Ukrainian President Petro Poroshenko, Polish Prime Minister Mateusz Morawiecki, former U.S. President Donald Trump, the European Council President Donald Tusk and British foreign minister Boris Johnson.[176][177] Tusk has said that Nord Stream 2 is not in the EU's interests.[178] Former Italian Prime Minister Matteo Renzi and Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orbán have questioned the different treatment of Nord Stream 2 and South Stream projects.[178][179] Some claim that the project violates the long-term declared strategy of the EU to diversify its gas supplies.[180] A letter, signed by the leaders of nine EU countries, was sent to the EC in March 2016, warning that the Nord Stream 2 project contradicts the European energy policy requirements that suppliers to the EU should not control the energy transmission assets, and that access to the energy infrastructure must be secured for non-consortium companies.[181][182] A letter by American lawmakers John McCain and Marco Rubio to the EU also criticized the project in July 2016.[183]
An anti-trust investigation against Gazprom started in 2011 revealed a number of "abusive practices" the company applied against various recipients in the EU and Nord Stream 2 was criticized from this angle as strengthening Gazprom's position in the EU even more. European Commission officials expressed the view that "Nord Stream 2 does not enhance [EU] energy security".[184]
Sberbank's investment research division in 2018 voiced concerns from Russian stakeholders' perspective, specifically that the project's goals are exclusively political and corruption-related:[185]
Sanctions[edit]
On January 1, 2021, an annual defense policy bill passed by the US Congress included sanctions for companies who worked on or insured the pipeline.[60][187] On 26 January 2021, the White House said that Joe Biden "continues to believe that Nord Stream 2 is a bad deal for Europe" and that his administration "will be reviewing" the new sanctions. According to congressional aides cited in a February report by NBC News, the sanctions enjoy "strong bipartisan support" on Capitol Hill.[188][189][190]
In June 2017, Germany, France, Austria and European Commission criticized the United States Senate over new sanctions against Russia targeting the pipeline,[191][192][193] stating that the United States was threatening Europe's energy supplies.[194] In a joint statement, Austrian Chancellor Christian Kern and German Foreign Minister Sigmar Gabriel said, "Europe's energy supply is a matter for Europe, and not for the United States of America."[195] They also said: "To threaten companies from Germany, Austria and other European states with penalties on the U.S. market if they participate in natural gas projects such as Nord Stream 2 with Russia or finance them introduces a completely new and very negative quality into European-American relations."[196] Isabelle Kocher, chief executive officer of Engie, criticised American sanctions targeting the projects, and said they were an attempt to promote American gas in Europe.[197] German Finance Minister Olaf Scholz called the sanctions "a severe intervention in German and European internal affairs", while the EU spokesman criticized "the imposition of sanctions against EU companies conducting legitimate business."[198] German Foreign Minister Heiko Maas tweeted that "European energy policy is decided in Europe, not in the United States". Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov also criticized sanctions, saying that United States Congress "is literally overwhelmed with the desire to do everything to destroy" Russia–United States relations.[199] The German Eastern Business Association said in a statement that "America wants to sell its liquefied gas in Europe, for which Germany is building terminals. Should we arrive at the conclusion that U.S. sanctions are intended to push competitors out of the European market, our enthusiasm for bilateral projects with the U.S. will significantly cool."[200]
On 19 May 2021, the US government waived sanctions against the main company involved in the project, Nord Stream 2 AG, while imposing sanctions on four Russian ships and five other Russian entities.[201][202][203] Russian Deputy Foreign Minister Sergei Ryabkov welcomed the move as "a chance for a gradual transition toward the normalisation of our bilateral ties".[204] Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky said he was "surprised" and "disappointed" by Biden's decision.[205] Biden also waived sanctions on the Nordstream CEO, Matthias Warnig, an ally of Russian President Vladimir Putin.[206] On 22 November 2021, the US State Department announced that it had imposed further sanctions on a Russian vessel and a "Russian-linked entity".[207]
Public opinion[edit]
A representative Forsa study conducted in May 2021 found that 75% of Germans are in favour of the construction of Nord Stream 2, while only 17% are against it.[208] The survey found that broad support for the completion of the project can be found in all voter groups.[208] The Ost-Ausschuss der Deutschen Wirtschaft (Committee on Eastern European Economic Relations) criticised that US sanctions and obstruction efforts are thus threatening democratic processes in Germany and Europe, endangering Germany's interests, and causing damages estimated to be several billion euros at the expense of European taxpayers and businesses.[209]
In March 2021,[210] Germany left nuclear power energy and chose to[clarification needed] move towards a low-carbon economy. Consequently, Germany has begun to compensate its Energiewende with an increased natural gas supply.[211]
Legal aspects[edit]
According to the amended EU gas directive, the EU extends its gas market rules to external pipelines entering to the EU internal gas market. It applies to all pipelines which were completed after 23 May 2019 when amended directive entered into force.[212][213] Additional legal concerns relate to international trade law[214] and to the law of the sea in connection with Nord Stream 2's route through the Danish territorial waters around Bornholm.[215]
Nord Stream 2 AG has started the legal proceeding in the Court of Justice of the European Union to annul the amended directive and has started the arbitration against the EU under the Energy Charter Treaty.[212][216] Although Russia has not ratified the Energy Charter Treaty and has terminated its provisional application, both the EU and Switzerland - a domicile of Nord Stream 2 AG—are contracting parties of it.
Regulatory clearance[edit]
In late October 2021, the approval of the pipeline was still in process as permits were expected from the German regulator (Bundesnetzagentur) and finally from the EU commission later that year. The German agency still awaits the processing of applications by Ukrainian gas company Naftogaz and Ukraine gas grid company GTSOU. Poland also voiced opposition to the approval of the pipeline as it fears a lack of Russian gas transits through its territory. However, spokesperson for the German Ministry of Economy Beate Baron said on 22 October 2021 "all the available capacities for natural gas supplies from Russia to Europe are used".[217][218] Earlier that week, the Swiss-based operator confirmed, it had filled the first line of the pipeline with "technical" gas. On 21 October 2021, Russian President Vladimir Putin stated, the pipeline would start gas delivery the day after Germany approved it. Regulatory clearance for Nord Stream 2 would double Russia's gas exports to the Baltic and Germany to 110 billion cubic metres per year. Economic pressures for its approval in Germany have been mounting, as tight supplies and soaring prices increased costs in transportation and heating fuel markets.[219]
Approvals for gas delivery through the fully constructed pipeline were further delayed in late November 2021, when Germany required part of the Gazprom-owned business entity to be transferred to German ownership. Concurrently, the US Department of State imposed more financial sanctions on Russian companies connected to Nord Stream 2. President Joe Biden earlier waived sanctions on German companies involved in the project.[220] The US and the European Union have accused Russian-owned Gazprom to have not delivered sufficient gas through existing pipelines, while Russia claimed that those pipelines were already delivering natural gas at full capacities. According to energy analysts, the delay of gas deliveries through Nord Stream 2 had significantly exacerbated the 2021 energy crisis.[221]
Others[edit]
The Economist warned that Europe is becoming more dependent on Russia while its own reserves decline.[222]
See also[edit]
- Yamal–Europe pipeline – A natural gas pipeline from Northern Russia through Belarus and Poland to Germany
- South Stream – Proposed natural gas pipeline through south-eastern Europe
- TurkStream – Natural gas pipeline from Russia to Turkey
- Russia–Ukraine gas disputes
- Economy of Germany – National economy of Germany
- Economy of Russia – National economy of Russia
- List of countries by natural gas exports – Wikipedia list article
- List of countries by natural gas imports – Wikipedia list article
- List of countries by natural gas proven reserves – Wikipedia list article









No comments:
Post a Comment