Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human ...
HIV/AIDS
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (
HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by
infection with the
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
[5][6][7] Following initial infection, a person may not notice any symptoms or may experience a brief period of
influenza-like illness.
[8] Typically, this is followed by a prolonged period with no symptoms.
[9] As the infection progresses, it interferes more with the
immune system, increasing the risk of common infections like
tuberculosis, as well as other
opportunistic infections, and
tumors that rarely affect people who have working immune systems.
[8] These late symptoms of infection are referred to as AIDS.
[9] This stage is often also associated with
weight loss.
[9]
HIV is spread primarily by
unprotected sex (including
anal and
oral sex), contaminated
blood transfusions,
hypodermic needles, and
from mother to child during
pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding.
[10] Some bodily fluids, such as saliva and tears, do not transmit HIV.
[11] Methods of prevention include
safe sex,
needle-exchange programs,
treating those who are infected, and
male circumcision.
[8] Disease in a baby can often be prevented by giving both the mother and child
antiretroviral medication.
[8] There is no cure or
vaccine; however, antiretroviral treatment can slow the course of the disease and may lead to a near-normal life expectancy.
[9][12] Treatment is recommended as soon as the diagnosis is made.
[13] Without treatment, the average survival time after infection is 11 years.
[14]
In 2014 about 36.9 million people were living with HIV and it resulted in 1.2 million deaths.
[8] Most of those infected live in
sub-Saharan Africa.
[8] Between its discovery and 2014 AIDS has caused an estimated 39 million deaths worldwide.
[15] HIV/AIDS is considered a
pandemic—a disease outbreak which is present over a large area and is actively spreading.
[16] HIV is believed to have originated in west-central Africa during the late 19th or early 20th century.
[17] AIDS was first recognized by the United States
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in 1981 and its cause—HIV infection—was identified in the early part of the decade.
[18]
HIV/AIDS has had a great impact on society, both as an illness and as a source of
discrimination.
[19] The disease also has large
economic impacts.
[19] There are many
misconceptions about HIV/AIDS such as the belief that it can be transmitted by casual non-sexual contact.
[20] The disease has become subject to many
controversies involving religion including the
Catholic church's decision not to support
condom use as prevention.
[21]
It has attracted international medical and political attention as well
as large-scale funding since it was identified in the 1980s.
[22]
Signs and symptoms
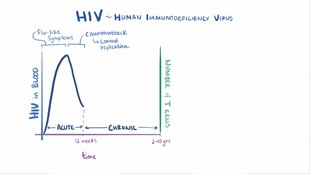
There are three main stages of HIV infection: acute infection, clinical latency and AIDS.
[2]
Acute infection
Main symptoms of acute HIV infection
The initial period following the contraction of HIV is called acute HIV, primary HIV or acute retroviral syndrome.
[3][23] Many individuals develop an
influenza-like illness or a
mononucleosis-like illness 2–4 weeks post exposure while others have no significant symptoms.
[24][25] Symptoms occur in 40–90% of cases and most commonly include
fever,
large tender lymph nodes,
throat inflammation, a
rash, headache, and/or sores of the mouth and genitals.
[23][25] The rash, which occurs in 20–50% of cases, presents itself on the trunk and is
maculopapular, classically.
[26] Some people also develop
opportunistic infections at this stage.
[23] Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting or
diarrhea may occur, as may neurological symptoms of
peripheral neuropathy or
Guillain-Barre syndrome.
[25] The duration of the symptoms varies, but is usually one or two weeks.
[25]
Due to their
nonspecific character, these symptoms are not often
recognized
as signs of HIV infection. Even cases that do get seen by a family
doctor or a hospital are often misdiagnosed as one of the many common
infectious diseases
with overlapping symptoms. Thus, it is recommended that HIV be
considered in people presenting an unexplained fever who may have risk
factors for the infection.
[25]
Clinical latency
The initial symptoms are followed by a stage called clinical latency, asymptomatic HIV, or chronic HIV.
[2] Without treatment, this second stage of the
natural history of HIV infection can last from about three years
[27] to over 20 years
[28] (on average, about eight years).
[29]
While typically there are few or no symptoms at first, near the end of
this stage many people experience fever, weight loss, gastrointestinal
problems and muscle pains.
[2] Between 50 and 70% of people also develop
persistent generalized lymphadenopathy,
characterized by unexplained, non-painful enlargement of more than one
group of lymph nodes (other than in the groin) for over three to six
months.
[3]
Although most
HIV-1
infected individuals have a detectable viral load and in the absence of
treatment will eventually progress to AIDS, a small proportion (about
5%) retain high levels of CD4
+ T cells (
T helper cells) without
antiretroviral therapy for more than 5 years.
[25][30] These individuals are classified as HIV controllers or
long-term nonprogressors (LTNP).
[30]
Another group consists of those who maintain a low or undetectable
viral load without anti-retroviral treatment, known as "elite
controllers" or "elite suppressors". They represent approximately 1 in
300 infected persons.
[31]
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is defined in terms of either a CD4
+ T cell count below 200 cells per µL or the occurrence of specific diseases in association with an HIV infection.
[25] In the absence of specific treatment, around half of people infected with HIV develop AIDS within ten years.
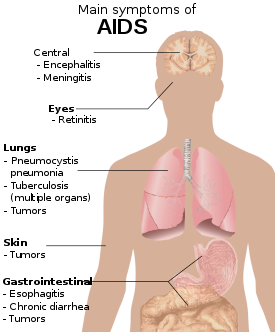
[25] The most common initial conditions that alert to the presence of AIDS are
pneumocystis pneumonia (40%),
cachexia in the form of HIV wasting syndrome (20%), and
esophageal candidiasis.
[25] Other common signs include recurring
respiratory tract infections.
[25]
Opportunistic infections may be caused by
bacteria,
viruses,
fungi, and
parasites that are normally controlled by the immune system.
[32] Which infections occur depends partly on what organisms are common in the person's environment.
[25] These infections may affect nearly every
organ system.
[33]
People with AIDS have an increased risk of developing various viral-induced cancers, including
Kaposi's sarcoma,
Burkitt's lymphoma,
primary central nervous system lymphoma, and
cervical cancer.
[26] Kaposi's sarcoma is the most common cancer occurring in 10 to 20% of people with HIV.
[34]
The second most common cancer is lymphoma, which is the cause of death
of nearly 16% of people with AIDS and is the initial sign of AIDS in 3
to 4%.
[34] Both these cancers are associated with
human herpesvirus 8.
[34] Cervical cancer occurs more frequently in those with AIDS because of its association with
human papillomavirus (HPV).
[34] Conjunctival cancer (of the layer that lines the inner part of eyelids and the white part of the eye) is also more common in those with HIV.
[35]
Additionally, people with AIDS frequently have systemic symptoms such as prolonged fevers,
sweats (particularly at night), swollen lymph nodes, chills, weakness, and
unintended weight loss.
[36] Diarrhea is another common symptom, present in about 90% of people with AIDS.
[37] They can also be affected by diverse psychiatric and neurological symptoms independent of opportunistic infections and cancers.
[38]
Transmission
Average per act risk of getting HIV
by exposure route to an infected source
| Exposure route |
Chance of infection |
| Blood transfusion |
90% [39] |
| Childbirth (to child) |
25%[40] |
| Needle-sharing injection drug use |
0.67%[39] |
| Percutaneous needle stick |
0.30%[41] |
| Receptive anal intercourse* |
0.04–3.0%[42] |
| Insertive anal intercourse* |
0.03%[43] |
| Receptive penile-vaginal intercourse* |
0.05–0.30%[42][44] |
| Insertive penile-vaginal intercourse* |
0.01–0.38% [42][44] |
| Receptive oral intercourse*§ |
0–0.04% [42] |
| Insertive oral intercourse*§ |
0–0.005%[45] |
* assuming no condom use
§ source refers to oral intercourse
performed on a man |
HIV is transmitted by three main routes:
sexual contact,
significant exposure to infected body fluids or tissues, and from
mother to child during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding (known as
vertical transmission).
[10] There is no risk of acquiring HIV if exposed to
feces, nasal secretions, saliva,
sputum, sweat, tears, urine, or vomit unless these are contaminated with blood.
[46] It is possible to be
co-infected by more than one strain of HIV—a condition known as
HIV superinfection.
[47]
Sexual
The most frequent mode of transmission of HIV is through sexual contact with an infected person.
[10] The majority of all transmissions worldwide occur through
heterosexual contacts (i.e. sexual contacts between people of the opposite sex);
[10]
however, the pattern of transmission varies significantly among
countries. In the United States, as of 2010, most transmission occurred
in
men who had sex with men, with this population accounting for 63% of all new cases.
[48]
With regard to
unprotected
heterosexual contacts, estimates of the risk of HIV transmission per
sexual act appear to be four to ten times higher in low-income countries
than in high-income countries.
[49]
In low-income countries, the risk of female-to-male transmission is
estimated as 0.38% per act, and of male-to-female transmission as 0.30%
per act; the equivalent estimates for high-income countries are 0.04%
per act for female-to-male transmission, and 0.08% per act for
male-to-female transmission.
[49]
The risk of transmission from anal intercourse is especially high,
estimated as 1.4–1.7% per act in both heterosexual and homosexual
contacts.
[49][50] While the risk of transmission from
oral sex is relatively low, it is still present.
[51] The risk from receiving oral sex has been described as "nearly nil";
[52] however, a few cases have been reported.
[53] The per-act risk is estimated at 0–0.04% for receptive oral intercourse.
[54] In settings involving
prostitution
in low income countries, risk of female-to-male transmission has been
estimated as 2.4% per act and male-to-female transmission as 0.05% per
act.
[49]
Risk of transmission increases in the presence of many
sexually transmitted infections[55] and
genital ulcers.
[49] Genital ulcers appear to increase the risk approximately fivefold.
[49] Other sexually transmitted infections, such as
gonorrhea,
chlamydia,
trichomoniasis, and
bacterial vaginosis, are associated with somewhat smaller increases in risk of transmission.
[54]
The
viral load of an infected person is an important risk factor in both sexual and mother-to-child transmission.
[56] During the first 2.5 months of an HIV infection a person's infectiousness is twelve times higher due to this high viral load.
[54] If the person is in the late stages of infection, rates of transmission are approximately eightfold greater.
[49]
Commercial sex workers (including
those in pornography) have an increased rate of HIV.
[57][58] Rough sex can be a factor associated with an increased risk of transmission.
[59] Sexual assault
is also believed to carry an increased risk of HIV transmission as
condoms are rarely worn, physical trauma to the vagina or rectum is
likely, and there may be a greater risk of concurrent sexually
transmitted infections.
[60]
Body fluids
CDC poster from 1989 highlighting the threat of AIDS associated with drug use
The second most frequent mode of HIV transmission is via blood and blood products.
[10]
Blood-borne transmission can be through needle-sharing during
intravenous drug use, needle stick injury, transfusion of contaminated
blood or blood product, or medical injections with unsterilised
equipment. The risk from sharing a needle during
drug injection is between 0.63 and 2.4% per act, with an average of 0.8%.
[61]
The risk of acquiring HIV from a needle stick from an HIV-infected
person is estimated as 0.3% (about 1 in 333) per act and the risk
following
mucous membrane exposure to infected blood as 0.09% (about 1 in 1000) per act.
[46] In the United States intravenous drug users made up 12% of all new cases of HIV in 2009,
[62] and in some areas more than 80% of people who inject drugs are HIV positive.
[10]
HIV is transmitted in about 93% of
blood transfusions using infected blood.
[61]
In developed countries the risk of acquiring HIV from a blood
transfusion is extremely low (less than one in half a million) where
improved donor selection and
HIV screening is performed;
[10] for example, in the UK the risk is reported at one in five million
[63] and in the United States it was one in 1.5 million in 2008.
[64] In low income countries, only half of transfusions may be appropriately screened (as of 2008),
[65]
and it is estimated that up to 15% of HIV infections in these areas
come from transfusion of infected blood and blood products, representing
between 5% and 10% of global infections.
[10][66] Although rare because of
screening, it is possible to acquire HIV from organ and tissue
transplantation.
[67]
Unsafe medical injections play a significant role in
HIV spread in sub-Saharan Africa. In 2007, between 12 and 17% of infections in this region were attributed to medical syringe use.
[68] The World Health Organization estimates the risk of transmission as a result of a medical injection in Africa at 1.2%.
[68] Significant risks are also associated with invasive procedures, assisted delivery, and dental care in this area of the world.
[68]
People giving or receiving
tattoos,
piercings, and
scarification are theoretically at risk of infection but no confirmed cases have been documented.
[69] It is not possible for
mosquitoes or other insects to transmit HIV.
[70]
Mother-to-child
HIV can be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy, during
delivery, or through breast milk resulting in infection in the baby.
[71][72] This is the third most common way in which HIV is transmitted globally.
[10]
In the absence of treatment, the risk of transmission before or during
birth is around 20% and in those who also breastfeed 35%.
[71] As of 2008, vertical transmission accounted for about 90% of cases of HIV in children.
[71] With appropriate treatment the risk of mother-to-child infection can be reduced to about 1%.
[71] Preventive treatment involves the mother taking antiretrovirals during pregnancy and delivery, an elective
caesarean section, avoiding breastfeeding, and administering antiretroviral drugs to the newborn.
[73] Antiretrovirals when taken by either the mother or the infant decrease the risk of transmission in those who do breastfeed.
[74] Many of these measures are however not available in the developing world.
[73] If blood contaminates food during
pre-chewing it may pose a risk of transmission.
[69]
Virology
Diagram of a HIV virion structure
HIV is the cause of the spectrum of disease known as HIV/AIDS. HIV is a
retrovirus that primarily infects components of the human
immune system such as CD4
+ T cells,
macrophages and
dendritic cells. It directly and indirectly destroys CD4
+ T cells.
[75]
HIV is a member of the
genus Lentivirus,
[76] part of the family
Retroviridae.
[77] Lentiviruses share many
morphological and
biological
characteristics. Many species of mammals are infected by lentiviruses,
which are characteristically responsible for long-duration illnesses
with a long
incubation period.
[78] Lentiviruses are transmitted as single-stranded, positive-
sense, enveloped
RNA viruses. Upon entry into the target cell, the viral
RNA genome is converted (reverse transcribed) into double-stranded
DNA by a virally encoded
reverse transcriptase
that is transported along with the viral genome in the virus particle.
The resulting viral DNA is then imported into the cell nucleus and
integrated into the cellular DNA by a virally encoded
integrase and host co-factors.
[79] Once integrated, the virus may become
latent, allowing the virus and its host cell to avoid detection by the immune system.
[80] Alternatively, the virus may be
transcribed,
producing new RNA genomes and viral proteins that are packaged and
released from the cell as new virus particles that begin the replication
cycle anew.
[81]
HIV is now known to spread between CD4
+ T cells by two parallel routes: cell-free spread and cell-to-cell spread, i.e. it employs hybrid spreading mechanisms.
[82]
In the cell-free spread, virus particles bud from an infected T cell,
enter the blood/extracellular fluid and then infect another T cell
following a chance encounter.
[82] HIV can also disseminate by direct transmission from one cell to another by a process of cell-to-cell spread.
[83][84] The hybrid spreading mechanisms of HIV contribute to the virus's ongoing replication against antiretroviral therapies.
[82][85]
Two
types of HIV
have been characterized: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-1 is the virus that was
originally discovered (and initially referred to also as LAV or
HTLV-III). It is more
virulent, more
infective,
[86]
and is the cause of the majority of HIV infections globally. The lower
infectivity of HIV-2 as compared with HIV-1 implies that fewer people
exposed to HIV-2 will be infected per exposure. Because of its
relatively poor capacity for transmission, HIV-2 is largely confined to
West Africa.
[87]
Pathophysiology
HIV/AIDS explained in a simple way
After the virus enters the body there is a period of rapid
viral replication,
leading to an abundance of virus in the peripheral blood. During
primary infection, the level of HIV may reach several million virus
particles per milliliter of blood.
[88] This response is accompanied by a marked drop in the number of circulating CD4
+ T cells. The acute
viremia is almost invariably associated with activation of
CD8+ T cells, which kill HIV-infected cells, and subsequently with antibody production, or
seroconversion. The CD8
+ T cell response is thought to be important in controlling virus levels, which peak and then decline, as the CD4
+ T cell counts recover. A good CD8
+ T cell response has been linked to slower disease progression and a better prognosis, though it does not eliminate the virus.
[89]
Ultimately, HIV causes AIDS by depleting
CD4+ T cells. This weakens the immune system and allows
opportunistic infections.
T cells are essential to the immune response and without them, the body
cannot fight infections or kill cancerous cells. The mechanism of CD4
+ T cell depletion differs in the acute and chronic phases.
[90] During the acute phase, HIV-induced cell lysis and killing of infected cells by
cytotoxic T cells accounts for CD4
+ T cell depletion, although
apoptosis
may also be a factor. During the chronic phase, the consequences of
generalized immune activation coupled with the gradual loss of the
ability of the immune system to generate new T cells appear to account
for the slow decline in CD4
+ T cell numbers.
[91]
Although the symptoms of immune deficiency characteristic of AIDS do
not appear for years after a person is infected, the bulk of CD4
+
T cell loss occurs during the first weeks of infection, especially in
the intestinal mucosa, which harbors the majority of the lymphocytes
found in the body.
[92] The reason for the preferential loss of mucosal CD4
+ T cells is that the majority of mucosal CD4
+ T cells express the
CCR5 protein which HIV uses as a
co-receptor to gain access to the cells, whereas only a small fraction of CD4
+ T cells in the bloodstream do so.
[93] A specific genetic change that alters the
CCR5 protein when present in both
chromosomes very effectively prevents HIV-1 infection.
[94]
HIV seeks out and destroys CCR5 expressing CD4
+ T cells during acute infection.
[95] A vigorous immune response eventually controls the infection and initiates the clinically latent phase. CD4
+ T cells in mucosal tissues remain particularly affected.
[95] Continuous HIV replication causes a state of generalized immune activation persisting throughout the chronic phase.
[96] Immune activation, which is reflected by the increased activation state of immune cells and release of pro-inflammatory
cytokines, results from the activity of several HIV
gene products
and the immune response to ongoing HIV replication. It is also linked
to the breakdown of the immune surveillance system of the
gastrointestinal mucosal barrier caused by the depletion of mucosal CD4
+ T cells during the acute phase of disease.
[97]
Diagnosis
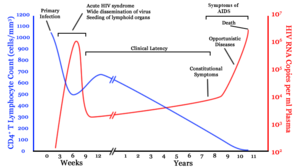
A generalized graph of the relationship between HIV copies (viral load) and CD4
+ T cell counts over the average course of untreated HIV infection.
CD4+ T Lymphocyte count (cells/mm³)
HIV RNA copies per mL of plasma
HIV/AIDS is diagnosed via laboratory testing and then staged based on the presence of
certain signs or symptoms.
[23] HIV screening is recommended by the
United States Preventive Services Task Force for all people 15 years to 65 years of age including all pregnant women.
[98]
Additionally, testing is recommended for those at high risk, which
includes anyone diagnosed with a sexually transmitted illness.
[26]
In many areas of the world, a third of HIV carriers only discover they
are infected at an advanced stage of the disease, when AIDS or severe
immunodeficiency has become apparent.
[26]
HIV testing
Most people infected with HIV develop specific
antibodies (i.e.
seroconvert) within three to twelve weeks of the initial infection.
[25] Diagnosis of primary HIV before seroconversion is done by measuring HIV-
RNA or
p24 antigen.
[25] Positive results obtained by antibody or
PCR testing are confirmed either by a different antibody or by PCR.
[23]
Antibody tests in children younger than 18 months are typically inaccurate due to the continued presence of
maternal antibodies.
[99] Thus HIV infection can only be diagnosed by PCR testing for HIV RNA or DNA, or via testing for the p24 antigen.
[23]
Much of the world lacks access to reliable PCR testing and many places
simply wait until either symptoms develop or the child is old enough for
accurate antibody testing.
[99] In sub-Saharan Africa as of 2007–2009 between 30 and 70% of the population were aware of their HIV status.
[100] In 2009, between 3.6 and 42% of men and women in Sub-Saharan countries were tested
[100] which represented a significant increase compared to previous years.
[100]
Classifications
Two main clinical staging systems are used to classify HIV and HIV-related disease for
surveillance purposes: the
WHO disease staging system for HIV infection and disease,
[23] and the
CDC classification system for HIV infection.
[101] The
CDC's classification system is more frequently adopted in developed countries. Since the
WHO's
staging system does not require laboratory tests, it is suited to the
resource-restricted conditions encountered in developing countries,
where it can also be used to help guide clinical management. Despite
their differences, the two systems allow comparison for statistical
purposes.
[3][23][101]
The World Health Organization first proposed a definition for AIDS in 1986.
[23]
Since then, the WHO classification has been updated and expanded
several times, with the most recent version being published in 2007.
[23] The WHO system uses the following categories:
- Primary HIV infection: May be either asymptomatic or associated with acute retroviral syndrome.[23]
- Stage I: HIV infection is asymptomatic with a CD4+ T cell count (also known as CD4 count) greater than 500 per microlitre (µl or cubic mm) of blood.[23] May include generalized lymph node enlargement.[23]
- Stage II: Mild symptoms which may include minor mucocutaneous manifestations and recurrent upper respiratory tract infections. A CD4 count of less than 500/µl.[23]
- Stage III: Advanced symptoms which may include unexplained chronic diarrhea for longer than a month, severe bacterial infections including tuberculosis of the lung, and a CD4 count of less than 350/µl.[23]
- Stage IV or AIDS: severe symptoms which include toxoplasmosis of the brain, candidiasis of the esophagus, trachea, bronchi or lungs and Kaposi's sarcoma. A CD4 count of less than 200/µl.[23]
The United States
Center for Disease Control and Prevention also created a classification system for HIV, and updated it in 2008 and 2014.
[101][102] This system classifies HIV infections based on CD4 count and clinical symptoms, and describes the infection in five groups.
[102] In those greater than six years of age it is:
[102]
- Stage 0: the time between a negative or indeterminate HIV test followed less than 180 days by a positive test
- Stage 1: CD4 count ≥ 500 cells/µl and no AIDS defining conditions
- Stage 2: CD4 count 200 to 500 cells/µl and no AIDS defining conditions
- Stage 3: CD4 count ≤ 200 cells/µl or AIDS defining conditions
- Unknown: if insufficient information is available to make any of the above classifications
For surveillance purposes, the AIDS diagnosis still stands even if, after treatment, the CD4
+ T cell count rises to above 200 per µL of blood or other AIDS-defining illnesses are cured.
[3]
Prevention
AIDS Clinic,
McLeod Ganj, Himachal Pradesh, India, 2010
Sexual contact
Consistent
condom use reduces the risk of HIV transmission by approximately 80% over the long term.
[103]
When condoms are used consistently by a couple in which one person is
infected, the rate of HIV infection is less than 1% per year.
[104] There is some evidence to suggest that
female condoms may provide an equivalent level of protection.
[105] Application of a vaginal gel containing
tenofovir (a
reverse transcriptase inhibitor) immediately before sex seems to reduce infection rates by approximately 40% among African women.
[106] By contrast, use of the
spermicide nonoxynol-9 may increase the risk of transmission due to its tendency to cause vaginal and rectal irritation.
[107]
Circumcision in
Sub-Saharan Africa "reduces the acquisition of HIV by heterosexual men by between 38% and 66% over 24 months".
[108]
Based on these studies, the World Health Organization and UNAIDS both
recommended male circumcision as a method of preventing female-to-male
HIV transmission in 2007.
[109] Whether it protects against male-to-female transmission is disputed
[110][111] and whether it is of benefit in
developed countries and among
men who have sex with men is undetermined.
[112][113][114]
The International Antiviral Society, however, does recommend for all
sexually active heterosexual males and that it be discussed as an option
with men who have sex with men.
[115]
Some experts fear that a lower perception of vulnerability among
circumcised men may cause more sexual risk-taking behavior, thus
negating its preventive effects.
[116]
Programs encouraging
sexual abstinence do not appear to affect subsequent HIV risk.
[117] Evidence of any benefit from
peer education is equally poor.
[118] Comprehensive sexual education provided at school may decrease high risk behavior.
[119]
A substantial minority of young people continues to engage in high-risk
practices despite knowing about HIV/AIDS, underestimating their own
risk of becoming infected with HIV.
[120]
Voluntary counseling and testing people for HIV does not affect risky
behavior in those who test negative but does increase condom use in
those who test positive.
[121] It is not known whether treating other sexually transmitted infections is effective in preventing HIV.
[55]
Pre-exposure
Antiretroviral treatment among people with HIV whose CD4 count ≤ 550
cells/µL is a very effective way to prevent HIV infection of their
partner (a strategy known as treatment as prevention, or TASP).
[122] TASP is associated with a 10 to 20 fold reduction in transmission risk.
[122][123] Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with a daily dose of the medications
tenofovir, with or without
emtricitabine,
is effective in a number of groups including men who have sex with men,
couples where one is HIV positive, and young heterosexuals in Africa.
[106] It may also be effective in intravenous drug users with a study finding a decrease in risk of 0.7 to 0.4 per 100 person years.
[124]
Universal precautions within the health care environment are believed to be effective in decreasing the risk of HIV.
[125] Intravenous drug use is an important risk factor and
harm reduction strategies such as
needle-exchange programmes and
opioid substitution therapy appear effective in decreasing this risk.
[126][127]
Post-exposure
A course of antiretrovirals administered within 48 to 72 hours after
exposure to HIV-positive blood or genital secretions is referred to as
post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP).
[128] The use of the single agent
zidovudine reduces the risk of a HIV infection five-fold following a needle-stick injury.
[128] As of 2013, the prevention regimen recommended in the United States consists of three medications—
tenofovir,
emtricitabine and
raltegravir—as this may reduce the risk further.
[129]
PEP treatment is recommended after a
sexual assault when the perpetrator is known to be HIV positive, but is controversial when their HIV status is unknown.
[130] The duration of treatment is usually four weeks
[131]
and is frequently associated with adverse effects—where zidovudine is
used, about 70% of cases result in adverse effects such as nausea (24%),
fatigue (22%), emotional distress (13%) and headaches (9%).
[46]
Mother-to-child
Programs to prevent the
vertical transmission of HIV (from mothers to children) can reduce rates of transmission by 92–99%.
[71][126]
This primarily involves the use of a combination of antiviral
medications during pregnancy and after birth in the infant and
potentially includes
bottle feeding rather than
breastfeeding.
[71][132]
If replacement feeding is acceptable, feasible, affordable,
sustainable, and safe, mothers should avoid breastfeeding their infants;
however exclusive breastfeeding is recommended during the first months
of life if this is not the case.
[133]
If exclusive breastfeeding is carried out, the provision of extended
antiretroviral prophylaxis to the infant decreases the risk of
transmission.
[134] In 2015,
Cuba became the first country in the world to eradicate mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
[135]
Vaccination
Main article:
HIV vaccine
Currently, there is no licensed
vaccine for HIV or AIDS.
[12] The most effective vaccine trial to date,
RV 144,
was published in 2009 and found a partial reduction in the risk of
transmission of roughly 30%, stimulating some hope in the research
community of developing a truly effective vaccine.
[136] Further trials of the RV 144 vaccine are ongoing.
[137][138]
Treatment
There is currently no cure or effective
HIV vaccine. Treatment consists of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) which slows progression of the disease.
[139] As of 2010 more than 6.6 million people were taking them in low and middle income countries.
[140] Treatment also includes preventive and active treatment of opportunistic infections.
Antiviral therapy
Current HAART options are combinations (or "cocktails") consisting of
at least three medications belonging to at least two types, or
"classes," of
antiretroviral agents.
[141] Initially treatment is typically a
non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) plus two
nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs).
[142] Typical NRTIs include:
zidovudine (AZT) or
tenofovir (TDF) and
lamivudine (3TC) or
emtricitabine (FTC).
[142] Combinations of agents which include
protease inhibitors (PI) are used if the above regimen loses effectiveness.
[141]
The World Health Organization and United States recommends
antiretrovirals in people of all ages including pregnant women as soon
as the diagnosis is made regardless of CD4 count.
[13][115][143] Once treatment is begun it is recommended that it is continued without breaks or "holidays".
[26] Many people are diagnosed only after treatment ideally should have begun.
[26] The desired outcome of treatment is a long term plasma HIV-RNA count below 50 copies/mL.
[26]
Levels to determine if treatment is effective are initially recommended
after four weeks and once levels fall below 50 copies/mL checks every
three to six months are typically adequate.
[26] Inadequate control is deemed to be greater than 400 copies/mL.
[26] Based on these criteria treatment is effective in more than 95% of people during the first year.
[26]
Benefits of treatment include a decreased risk of progression to AIDS and a decreased risk of death.
[144] In the developing world treatment also improves physical and mental health.
[145] With treatment there is a 70% reduced risk of acquiring tuberculosis.
[141]
Additional benefits include a decreased risk of transmission of the
disease to sexual partners and a decrease in mother-to-child
transmission.
[141] The effectiveness of treatment depends to a large part on compliance.
[26] Reasons for non-adherence include poor access to medical care,
[146] inadequate social supports,
mental illness and
drug abuse.
[147] The complexity of treatment regimens (due to pill numbers and dosing frequency) and
adverse effects may reduce adherence.
[148] Even though cost is an important issue with some medications,
[149] 47% of those who needed them were taking them in low and middle income countries as of 2010
[140] and the rate of adherence is similar in low-income and high-income countries.
[150]
Specific adverse events are related to the antiretroviral agent taken.
[151] Some relatively common adverse events include:
lipodystrophy syndrome,
dyslipidemia, and
diabetes mellitus, especially with protease inhibitors.
[3] Other common symptoms include
diarrhea,
[151][152] and an increased risk of
cardiovascular disease.
[153] Newer recommended treatments are associated with fewer adverse effects.
[26] Certain medications may be associated with
birth defects and therefore may be unsuitable for women hoping to have children.
[26]
Treatment recommendations for children are somewhat different from
those for adults. The World Health Organisation recommends treating all
children less than 5 years of age; children above 5 are treated like
adults.
[154]
The United States guidelines recommend treating all children less than
12 months of age and all those with HIV RNA counts greater than
100,000 copies/mL between one year and five years of age.
[155]
Opportunistic infections
Measures to prevent opportunistic infections are effective in many
people with HIV/AIDS. In addition to improving current disease,
treatment with antiretrovirals reduces the risk of developing additional
opportunistic infections.
[151]
Adults and adolescents who are living with HIV (even on anti-retroviral
therapy) with no evidence of active tuberculosis in settings with high
tuberculosis burden should receive
isoniazid preventive therapy (IPT), the
tuberculin skin test can be used to help decide if IPT is needed.
[156] Vaccination against
hepatitis A and B is advised for all people at risk of HIV before they become infected; however it may also be given after infection.
[157] Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
prophylaxis between four and six weeks of age and ceasing breastfeeding
in infants born to HIV positive mothers is recommended in resource
limited settings.
[158]
It is also recommended to prevent PCP when a person's CD4 count is
below 200 cells/uL and in those who have or have previously had PCP.
[159] People with substantial immunosuppression are also advised to receive prophylactic therapy for
toxoplasmosis and
Cryptococcus meningitis.
[160] Appropriate preventive measures have reduced the rate of these infections by 50% between 1992 and 1997.
[161]
Diet
The
World Health Organization (WHO) has issued recommendations regarding nutrient requirements in HIV/AIDS.
[162] A generally healthy diet is promoted. Some evidence has shown a benefit from
micronutrient supplements.
[163] Evidence for supplementation with
selenium is mixed with some tentative evidence of benefit.
[164] There is some evidence that
vitamin A supplementation in children reduces mortality and improves growth.
[163] In Africa in nutritionally compromised pregnant and lactating women a
multivitamin supplementation has improved outcomes for both mothers and children.
[163] Dietary intake of micronutrients at
RDA levels by HIV-infected adults is recommended by the WHO; higher intake of vitamin A,
zinc, and iron can produce adverse effects in HIV positive adults, and is not recommended unless there is documented deficiency.
[162][165][166][167]
Alternative medicine
In the US, approximately 60% of people with HIV use various forms of
complementary or alternative medicine,
[168] even though the effectiveness of most of these therapies has not been established.
[169] There is not enough evidence to support the use of
herbal medicines.
[170] There is insufficient evidence to recommend or support the use of
medical cannabis to try to increase appetite or weight gain.
[171]
Prognosis
Disability-adjusted life year for HIV and AIDS per 100,000 inhabitants as of 2004.
no data
≤ 10
10–25
25–50
50–100
100–500
500–1000
|
1000–2500
2500–5000
5000–7500
7500-10000
10000-50000
≥ 50000
|
HIV/AIDS has become a
chronic rather than an acutely fatal disease in many areas of the world.
[172] Prognosis varies between people, and both the CD4 count and viral load are useful for predicted outcomes.
[25]
Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is
estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype.
[14] After the diagnosis of AIDS, if treatment is not available, survival ranges between 6 and 19 months.
[173][174] HAART
and appropriate prevention of opportunistic infections reduces the
death rate by 80%, and raises the life expectancy for a newly diagnosed
young adult to 20–50 years.
[172][175][176] This is between two thirds
[175] and nearly that of the general population.
[26][177] If treatment is started late in the infection, prognosis is not as good:
[26] for example, if treatment is begun following the diagnosis of AIDS, life expectancy is ~10–40 years.
[26][172] Half of infants born with HIV die before two years of age without treatment.
[158]
The primary causes of death from HIV/AIDS are
opportunistic infections and
cancer, both of which are frequently the result of the progressive failure of the immune system.
[161][178] Risk of cancer appears to increase once the CD4 count is below 500/μL.
[26]
The rate of clinical disease progression varies widely between
individuals and has been shown to be affected by a number of factors
such as a person's susceptibility and immune function;
[179] their access to health care, the presence of co-infections;
[173][180] and the particular strain (or strains) of the virus involved.
[181][182]
Tuberculosis
co-infection is one of the leading causes of sickness and death in
those with HIV/AIDS being present in a third of all HIV infected people
and causing 25% of HIV related deaths.
[183] HIV is also one of the most important risk factors for tuberculosis.
[184] Hepatitis C is another very common co-infection where each disease increases the progression of the other.
[185] The two most common cancers associated with HIV/AIDS are
Kaposi's sarcoma and AIDS-related
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
[178]
Even with anti-retroviral treatment, over the long term HIV-infected people may experience
neurocognitive disorders,
[186] osteoporosis,
[187] neuropathy,
[188] cancers,
[189][190] nephropathy,
[191] and
cardiovascular disease.
[152] Some conditions like
lipodystrophy may be caused both by HIV and its treatment.
[152]
Epidemiology
Estimated
prevalence in % of HIV among young adults (15–49) per country as of 2011.
[192]
No data
<0 .10="" small="">
0.10–0.5
0.5–1
|
|
HIV/AIDS is a global
pandemic.
[193]
As of 2014, approximately 37 million people have HIV worldwide with the
number of new infections that year being about 2 million.
[194] This is down from 3.1 million new infections in 2001.
[195] Of these 37 million more than half are women and 2.6 million are less than 15 years old.
[194][196] It resulted in about 1.2 million deaths in 2014,
[194] down from a peak of 2.2 million in 2005.
[140][195]
Sub-Saharan Africa
is the region most affected. In 2010, an estimated 68% (22.9 million)
of all HIV cases and 66% of all deaths (1.2 million) occurred in this
region.
[197] This means that about 5% of the adult population is infected
[198] and it is believed to be the cause of 10% of all deaths in children.
[199] Here in contrast to other regions women compose nearly 60% of cases.
[197] South Africa has the largest population of people with HIV of any country in the world at 5.9 million.
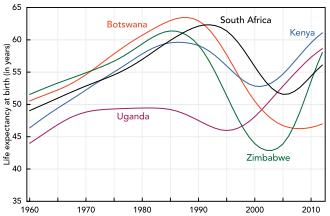
[197] Life expectancy
has fallen in the worst-affected countries due to HIV/AIDS; for
example, in 2006 it was estimated that it had dropped from 65 to 35
years in
Botswana.
[16]
Mother-to-child transmission, as of 2013, in Botswana and South Africa
has decreased to less than 5% with improvement in many other African
nations due to improved access to antiretroviral therapy.
[200]
South & South East Asia
is the second most affected; in 2010 this region contained an estimated
4 million cases or 12% of all people living with HIV resulting in
approximately 250,000 deaths.
[198] Approximately 2.4 million of these cases are in India.
[197]
In 2008 in the United States approximately 1.2 million people were
living with HIV, resulting in about 17,500 deaths. The US Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention estimated that in 2008 20% of infected
Americans were unaware of their infection.
[201] In the United Kingdom as of 2009 there were approximately 86,500 cases which resulted in 516 deaths.
[202] In Canada as of 2008 there were about 65,000 cases causing 53 deaths.
[203] Between the first recognition of AIDS in 1981 and 2009 it has led to nearly 30 million deaths.
[204] Prevalence is lowest in Middle East and North Africa at 0.1% or less,
East Asia at 0.1% and Western and Central Europe at 0.2%.
[198] The worst affected European countries, in 2009 and 2012 estimates, are
Russia,
Ukraine,
Latvia,
Moldova,
Portugal and
Belarus, in decreasing order of prevalence.
[205]
History
Discovery
AIDS was first clinically observed in 1981 in the United States.
[34]
The initial cases were a cluster of injecting drug users and homosexual
men with no known cause of impaired immunity who showed symptoms of
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), a rare opportunistic infection that was known to occur in people with very compromised immune systems.
[206] Soon thereafter, an unexpected number of homosexual men developed a previously rare skin cancer called
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS).
[207][208]
Many more cases of PCP and KS emerged, alerting U.S. Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and a CDC task force was formed to
monitor the outbreak.
[209]
In the early days, the CDC did not have an official name for the
disease, often referring to it by way of the diseases that were
associated with it, for example,
lymphadenopathy, the disease after which the discoverers of HIV originally named the virus.
[210][211] They also used
Kaposi's sarcoma and opportunistic infections, the name by which a task force had been set up in 1981.
[212] At one point, the CDC coined the phrase "the 4H disease", since the syndrome seemed to affect heroin users, homosexuals,
hemophiliacs, and
Haitians.
[213][214] In the general press, the term "GRID", which stood for
gay-related immune deficiency, had been coined.
[215] However, after determining that AIDS was not isolated to the
gay community,
[212] it was realized that the term GRID was misleading and the term AIDS was introduced at a meeting in July 1982.
[216] By September 1982 the CDC started referring to the disease as AIDS.
[217]
In 1983, two separate research groups led by
Robert Gallo and
Luc Montagnier
declared that a novel retrovirus may have been infecting people with
AIDS, and published their findings in the same issue of the journal
Science.
[218][219] Gallo claimed that a virus his group had isolated from a person with AIDS was strikingly similar in
shape to other
human T-lymphotropic viruses
(HTLVs) his group had been the first to isolate. Gallo's group called
their newly isolated virus HTLV-III. At the same time, Montagnier's
group isolated a virus from a person presenting with swelling of the
lymph nodes of the neck and
physical weakness,
two characteristic symptoms of AIDS. Contradicting the report from
Gallo's group, Montagnier and his colleagues showed that core proteins
of this virus were immunologically different from those of HTLV-I.
Montagnier's group named their isolated virus lymphadenopathy-associated
virus (LAV).
[209] As these two viruses turned out to be the same, in 1986, LAV and HTLV-III were renamed HIV.
[220]
Origins
Both HIV-1 and HIV-2 are believed to have originated in non-human
primates in West-central Africa and were
transferred to humans in the early 20th century.
[17] HIV-1 appears to have originated in southern
Cameroon through the evolution of SIV(cpz), a
simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) that infects wild
chimpanzees (HIV-1 descends from the SIVcpz endemic in the chimpanzee subspecies
Pan troglodytes troglodytes).
[221][222] The closest relative of HIV-2 is SIV(smm), a virus of the
sooty mangabey (
Cercocebus atys atys), an Old World monkey living in coastal West Africa (from southern
Senegal to western
Côte d'Ivoire).
[87] New World monkeys such as the
owl monkey are resistant to
HIV-1 infection, possibly because of a genomic
fusion of two viral resistance genes.
[223]
HIV-1 is thought to have jumped the species barrier on at least three
separate occasions, giving rise to the three groups of the virus, M, N,
and O.
[224]
There is evidence that humans who participate in
bushmeat activities, either as hunters or as bushmeat vendors, commonly acquire SIV.
[225]
However, SIV is a weak virus which is typically suppressed by the human
immune system within weeks of infection. It is thought that several
transmissions of the virus from individual to individual in quick
succession are necessary to allow it enough time to mutate into HIV.
[226]
Furthermore, due to its relatively low person-to-person transmission
rate, SIV can only spread throughout the population in the presence of
one or more high-risk transmission channels, which are thought to have
been absent in Africa before the 20th century.
Specific proposed high-risk transmission channels, allowing the virus
to adapt to humans and spread throughout the society, depend on the
proposed timing of the animal-to-human crossing. Genetic studies of the
virus suggest that the most recent common ancestor of the HIV-1 M group
dates back to circa 1910.
[227] Proponents of this dating link the HIV epidemic with the emergence of
colonialism
and growth of large colonial African cities, leading to social changes,
including a higher degree of sexual promiscuity, the spread of
prostitution, and the accompanying high frequency of
genital ulcer diseases (such as
syphilis) in nascent colonial cities.
[228]
While transmission rates of HIV during vaginal intercourse are low
under regular circumstances, they are increased many fold if one of the
partners suffers from a
sexually transmitted infection
causing genital ulcers. Early 1900s colonial cities were notable due to
their high prevalence of prostitution and genital ulcers, to the degree
that, as of 1928, as many as 45% of female residents of eastern
Kinshasa were thought to have been prostitutes, and, as of 1933, around 15% of all residents of the same city had
syphilis.
[228]
An alternative view holds that unsafe medical practices in Africa
after World War II, such as unsterile reuse of single use syringes
during mass vaccination, antibiotic and anti-malaria treatment
campaigns, were the initial vector that allowed the virus to adapt to
humans and spread.
[226][229][230]
The earliest well-documented case of HIV in a human dates back to 1959 in the
Congo.
[231] In July 1960, in the wake its independence, the
United Nations recruited
Francophone experts and technicians from all over the world to assist in filling administrative gaps left by
Belgium,
who did not leave behind an African elite to run the country. By 1962,
Haitians made up the second largest group of well-educated experts (out
of the 48 national groups recruited), that totaled around 4500 in the
country.
[232][233] Dr. Jacques Pépin, a
Quebecer author of
The Origins of AIDS,
stipulates that Haiti was one of HIV's entry points to the United
States and that one of them may have carried HIV back across the
Atlantic in the 1960s.
[233] Although, the virus may have been present in the United States as early as 1966,
[234]
the vast majority of infections occurring outside sub-Saharan Africa
(including the U.S.) can be traced back to a single unknown individual
who became infected with HIV in
Haiti and then brought the infection to the United States some time around 1969.
[235]
The epidemic then rapidly spread among high-risk groups (initially,
sexually promiscuous men who have sex with men). By 1978, the prevalence
of HIV-1 among homosexual male residents of
New York and
San Francisco was estimated at 5%, suggesting that several thousand individuals in the country had been infected.
[235]
Society and culture
Stigma
AIDS stigma exists around the world in a variety of ways, including
ostracism,
rejection, discrimination and avoidance of HIV infected people; compulsory HIV testing without prior
consent or protection of
confidentiality; violence against HIV infected individuals or people who are perceived to be infected with HIV; and the
quarantine of HIV infected individuals.
[19]
Stigma-related violence or the fear of violence prevents many people
from seeking HIV testing, returning for their results, or securing
treatment, possibly turning what could be a manageable chronic illness
into a death sentence and perpetuating the spread of HIV.
[237]
AIDS stigma has been further divided into the following three categories:
- Instrumental AIDS stigma—a reflection of the fear and apprehension that are likely to be associated with any deadly and transmissible illness.[238]
- Symbolic AIDS stigma—the use of HIV/AIDS to express attitudes toward the social groups or lifestyles perceived to be associated with the disease.[238]
- Courtesy AIDS stigma—stigmatization of people connected to the issue of HIV/AIDS or HIV-positive people.[239]
Often, AIDS stigma is expressed in conjunction with one or more other
stigmas, particularly those associated with homosexuality,
bisexuality,
promiscuity, prostitution, and
intravenous drug use.
[240]
In many
developed countries, there is
an association between AIDS and homosexuality or bisexuality, and this association is correlated with higher levels of sexual prejudice, such as
anti-homosexual/
bisexual attitudes.
[241] There is also a perceived association between AIDS and all male-male sexual behavior, including sex between uninfected men.
[238] However, the dominant mode of spread worldwide for HIV remains heterosexual transmission.
[242]
In 2003, as part of an overall reform of marriage and population
legislation, it became legal for people with AIDS to marry in China.
[243]
Economic impact
Changes in life expectancy in some African countries, 1960-2012
HIV/AIDS affects the economics of both individuals and countries.
[199] The
gross domestic product of the most affected countries has decreased due to the lack of
human capital.
[199][244]
Without proper nutrition, health care and medicine, large numbers of
people die from AIDS-related complications. They will not only be unable
to work, but will also require significant medical care. It is
estimated that as of 2007 there were 12 million
AIDS orphans.
[199] Many are cared for by elderly grandparents.
[245]
Returning to work after beginning treatment for HIV/AIDS is
difficult, and affected people often work less than the average worker.
Unemployment in people with HIV/AIDS also is associated with
suicidal ideation, memory problems, and social isolation; employment increases
self-esteem, sense of dignity, confidence, and
quality of life.
A 2015 Cochrane review found low-quality evidence that antiretroviral
treatment helps people with HIV/AIDS work more, and increases the chance
that a person with HIV/AIDS will be employed.
[246]
By affecting mainly young adults, AIDS reduces the taxable population, in turn reducing the resources available for
public expenditures
such as education and health services not related to AIDS resulting in
increasing pressure for the state's finances and slower growth of the
economy. This causes a slower growth of the tax base, an effect that is
reinforced if there are growing expenditures on treating the sick,
training (to replace sick workers), sick pay and caring for AIDS
orphans. This is especially true if the sharp increase in adult
mortality shifts the responsibility and blame from the family to the
government in caring for these orphans.
[245]
At the household level, AIDS causes both loss of income and increased spending on healthcare. A study in
Côte d'Ivoire
showed that households having a person with HIV/AIDS spent twice as
much on medical expenses as other households. This additional
expenditure also leaves less income to spend on education and other
personal or family investment.
[247]
Religion and AIDS
The topic of religion and AIDS has become highly controversial in the
past twenty years, primarily because some religious authorities have
publicly declared their opposition to the use of condoms.
[248][249] The religious approach to prevent the spread of AIDS according to a report by American health expert Matthew Hanley titled
The Catholic Church and the Global AIDS Crisis
argues that cultural changes are needed including a re-emphasis on
fidelity within marriage and sexual abstinence outside of it.
[249]
Some religious organisations have claimed that prayer can cure
HIV/AIDS. In 2011, the BBC reported that some churches in London were
claiming that prayer would cure AIDS, and the
Hackney-based
Centre for the Study of Sexual Health and HIV reported that several
people stopped taking their medication, sometimes on the direct advice
of their pastor, leading to a number of deaths.
[250] The
Synagogue Church Of All Nations advertise an "anointing water" to promote God's healing, although the group deny advising people to stop taking medication.
[250]
Media portrayal
One of the first high-profile cases of AIDS was the American
Rock Hudson,
a gay actor who had been married and divorced earlier in life, who died
on October 2, 1985 having announced that he was suffering from the
virus on July 25 that year. He had been diagnosed during 1984.
[251] A notable British casualty of AIDS that year was
Nicholas Eden, a gay politician and son of the late prime minister
Anthony Eden.
[252] On November 24, 1991, the virus claimed the life of British rock star
Freddie Mercury, lead singer of the band
Queen, who died from an AIDS-related illness having only revealed the diagnosis on the previous day.
[253] However, he had been diagnosed as HIV positive in 1987.
[254] One of the first high-profile heterosexual cases of the virus was
Arthur Ashe,
the American tennis player. He was diagnosed as HIV positive on August
31, 1988, having contracted the virus from blood transfusions during
heart surgery earlier in the 1980s. Further tests within 24 hours of the
initial diagnosis revealed that Ashe had AIDS, but he did not tell the
public about his diagnosis until April 1992.
[255] He died as a result on February 6, 1993 at age 49.
[256]
Therese Frare's photograph of gay activist
David Kirby, as he lay dying from AIDS while surrounded by family, was taken in April 1990.
LIFE magazine said the photo became the one image "most powerfully identified with the HIV/AIDS epidemic." The photo was displayed in
LIFE magazine, was the winner of the
World Press Photo, and acquired worldwide notoriety after being used in a
United Colors of Benetton advertising campaign in 1992.
[257] In 1996,
Johnson Aziga,
a Ugandan-born Canadian was diagnosed with HIV, but subsequently had
unprotected sex with 11 women without disclosing his diagnosis. By 2003
seven had contracted HIV, and two died from complications related to
AIDS.
[258][259] Aziga was convicted of
first-degree murder and is liable to a life sentence.
[260]
Criminal transmission
Criminal transmission of HIV is the
intentional or
reckless infection of a person with the
human immunodeficiency virus
(HIV). Some countries or jurisdictions, including some areas of the
United States, have laws that criminalize HIV transmission or exposure.
[261] Others may charge the accused under laws enacted before the HIV pandemic.
Misconceptions
There are many
misconceptions about HIV and AIDS. Three of the most common are that AIDS can spread through casual contact, that
sexual intercourse with a virgin will cure AIDS,
[262][263][264]
and that HIV can infect only gay men and drug users. In 2014, some
among the British public wrongly thought you could get HIV from kissing
(16%), sharing a glass (5%), spitting (16%), a public toilet seat (4%),
and coughing or sneezing (5%).
[265]
Other misconceptions are that any act of anal intercourse between two
uninfected gay men can lead to HIV infection, and that open discussion
of HIV and homosexuality in schools will lead to increased rates of
AIDS.
[266][267]
A small group of individuals continue to dispute the connection between HIV and AIDS,
[268] the existence of HIV itself, or the validity of HIV testing and treatment methods.
[269][270] These claims, known as AIDS denialism, have been examined and rejected by the scientific community.
[271] However, they have had a significant political impact, particularly
in South Africa,
where the government's official embrace of AIDS denialism (1999–2005)
was responsible for its ineffective response to that country's AIDS
epidemic, and has been blamed for hundreds of thousands of avoidable
deaths and HIV infections.
[272][273][274]
Several discredited
conspiracy theories have held that HIV was created by scientists, either inadvertently or deliberately.
Operation INFEKTION was a worldwide Soviet
active measures
operation to spread the claim that the United States had created
HIV/AIDS. Surveys show that a significant number of people believed –
and continue to believe – in such claims.
[275]
Research
HIV/AIDS research includes all
medical research which attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS along with fundamental research about the nature of
HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV.
Many governments and research institutions participate in HIV/AIDS research. This research includes behavioral
health interventions such as
sex education, and
drug development, such as research into
microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases,
HIV vaccines, and
antiretroviral drugs. Other medical research areas include the topics of
pre-exposure prophylaxis,
post-exposure prophylaxis, and
circumcision and HIV.
References













No comments:
Post a Comment