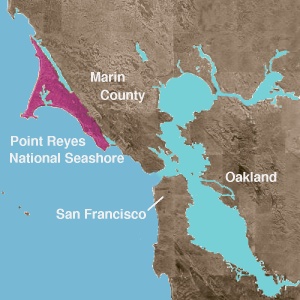
Point Reyes National Seashore
Point Reyes National Seashore is a 71,028-acre (287.44 km
2) park preserve located on the
Point Reyes Peninsula in
Marin County, California. As a
national seashore, it is maintained by the US
National Park Service as an important nature preserve. Some existing agricultural uses are allowed to continue within the park.
Clem Miller, a US
Congressman from
Marin County wrote and introduced the bill for the establishment of Point Reyes National Seashore in 1962 to protect the peninsula from development which was proposed at the time for the slopes above Drake's Bay. All of the park's beaches were listed as the cleanest in the state in 2010.
[4]
Description[edit]
The Point Reyes peninsula is a well defined area, geologically separated from the rest of Marin County and almost all of the continental United States by a
rift zone of the
San Andreas Fault,
[5] about half of which is sunk below sea level and forms
Tomales Bay. The fact that the peninsula is on a different tectonic plate than the east shore of Tomales Bay produces a difference in soils and therefore to some extent a noticeable difference in vegetation.
The small town of
Point Reyes Station, although not actually located on the peninsula, nevertheless provides most services to it, though some services are also available at
Inverness on the west shore of Tomales Bay. The even smaller town of
Olema, about 3 miles (4.8 km) south of Point Reyes Station, serves as the gateway to the Seashore and its visitor center, located on Bear Valley Road.
The peninsula includes wild coastal beaches and headlands, estuaries, and uplands. Although parts of the Seashore are commercially farmed, and parts are under the jurisdiction of other conservation authorities, the National Park Service provides signage and seeks to manage visitor impact on the entire peninsula and virtually all of Tomales Bay. The Seashore also administers the parts of the Golden Gate National Recreation area, such as the Olema Valley, that are adjacent to the Seashore.
The northernmost part of the peninsula is maintained as a reserve for
tule elk, which are readily seen there.
[6] The preserve is also very rich in
raptors and
shorebirds.
[5]
Point Reyes National Seashore Association, formed in 1964, collaborates with the Seashore on maintenance, restoration and educational projects.
[9]
Marine Protected Areas[edit]
Drakes Estero oyster farm closure[edit]
A large shellfish farm raising Japanese (kumamoto) oysters,
Crassostrea gigas, was located in
Drakes Estero until, under court order, it closed down at end of 2014. Court appeals to keep the operation in place were dropped in December, 2014.
[10]
The farm was purchased by the National Park Service in 1972, and the agency issued a permit to allow the previous owner to continue operations for 40 years. The business was sold to a new owner in 2004, the
Drakes Bay Oyster Company, who was informed by the NPS at the time of purchase that their permit to operate would not be renewed beyond the November 30, 2012 expiration date.
[11] A federal law enacted in 2009 authorized, but did not require,
Interior Secretary Ken Salazar to renew the permit.
[12] The NPS and conservation groups viewed the farm as an inappropriate and environmentally-insensitive use of the estero, which was designated a "potential wilderness area" by Congress. The farm's supporters argued that it was not ecologically harmful and was important to the local economy.
[12][13]

Point Reyes National Shoreline 2018
On November 29, 2012, Salazar announced that he would not renew the permit, citing the original intent of the Point Reyes Wilderness Act to designate the area as wilderness upon the removal of the oyster farm.
[11] Salazar visited the farm the previous week and later personally phoned the farm's owner to give him the news.
[14]
The oyster farm closure was challenged in
U.S. District Court on January 25, 2013.
[15] The challenge was rejected by a federal court judge, who ruled that the law gave Salazar unfettered discretion to approve or deny a renewal of the permit.
[16] The California Coastal Commission voted on February 7, 2013 to unanimously approve cease and desist and restoration orders for violations of the California Coastal Act.
[17] The
United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit rejected an appeal of the district court's decision, ruling on Sept. 3, 2013 that the oyster farm's owner had not shown a likelihood of success on the merits because Salazar had acted within his discretion in denying the permit.
[18] An attempt to have the appeals court rehear the case was rejected on January 14, 2014 and a petition to the
United States Supreme Court[19] was denied on June 30, 2014.
[20] The oyster farm closed its on site retail operation on July 31, 2014.
[21][22] However, controversy continued over the condition of the estero sea floor and the ongoing off shore operations.
[23] Another lawsuit challenging the closure itself was rejected in September 2014.
[24][25]
The work to remove the offshore racks and onshore buildings was completed in May 2017; 1700 tons of debris had been hauled away. The estero is part of the
Phillip Burton Wilderness.
[26][27]

A group of people gathered to watch the sunset at Point Reyes National Seashore.
Point Reyes has a system of
hiking trails for dayhiking and backpacking. Bear Valley Trail is the most popular hike in the park. It travels mostly streamside through a shaded, fern-laden canyon, breaking out at Divide Meadow before heading downward to the coast, where it emerges at Arch Rock. A portion of Arch Rock collapsed on 21 March 2015, killing one person.
[28]
Three trails connecting from the west with the Bear Valley trail head upward toward Mt. Wittenberg, at 1,407 feet (429 m), the highest point in the park.
[5] The Earthquake Trail, a 0.6-mile (0.97 km) loop that runs over the
San Andreas Fault. The trail provides descriptions of the fault and the surrounding geology, and features a fence that was pulled 18 feet (5.5 m) apart during the
1906 San Francisco earthquake.
[29]
At the western end of the Point Reyes Peninsula is the historic Point Reyes Lighthouse, reached by descending 308 steps. Unlike many lighthouses, that were built high so the light could be seen by ships far out to sea, the Point Reyes lighthouse was built low to get the light below the fog that is so prevalent in the area. Nearby is the short Chimney Rock hike, which is noted for its spring wildflower displays.
[5]
Point Reyes offers several beach walks. Limantour Spit winds up on a narrow sandy beach, from which Drakes Beach can be glimpsed across
Drakes Bay. North Beach and South Beach are often windswept and wave-pounded. Ocean vistas from higher ground can be seen from the Tomales Point Trail and, to the south, from the Palomarin trailhead at the park's southern entrance outside the town of
Bolinas.
A colony of
elephant seals usually congregate on Chimney Beach, which is protected by 100-foot (30 m) cliffs. In January 2019, during the
federal government shutdown, park rangers were not working and the seals colonized and had pups on Drakes Beach, and its parking lot.
[30][31] Small-group tours to view the seals from the edge of the parking lot began the following month after the shutdown ended.
[32]
For
backpackers, Point Reyes has four hike-in campgrounds available by reservation.

Fog rolling in from the Pacific at Point Reyes National Seashore.
In his book
The Natural History of the Point Reyes Peninsula, Jules Evens identifies several plant communities. One of the most prominent is the
Coastal Douglas-fir (
Pseudotsuga menziesii) forest, which includes
Coast live oak,
Tanoak, and
California bay and reaches across the southern half of Inverness Ridge toward
Bolinas Lagoon. Unlogged parts of this Douglas-fir forest contain trees over 300 years old and up to 6 feet (1.8 m) in diameter. But despite these large, old trees, the forest may nevertheless be a result of European settlement. The
Coast Miwok people who once lived in the area set frequent fires to clear brush and increase game animal populations, and early explorers' accounts describe the hills as bare and grassy. But as the Native American settlements were replaced by European ones from the seventeenth century onward, the forests expanded as fire frequency decreased, resulting in the forests we see today.
[34]
The
Bishop pine (
Pinus muricata) forest is found on slopes in the northern half of the park. Many of these trees growing in thick swaths came from seeds released after the 1995 Mt. Vision fire.
Point Reyes is home to the only known population of the endangered Sonoma spineflower,
Chorizanthe valida.
[36]
Gallery[edit]
Point Reyes Beach from the Lighthouse Visitor Center
-
-
-
Tomales Bay on the Eastern side
Coastline as seen from Chimney Rock
Point Reyes Marsh at dusk
Drakes Beach during the 2015 Annual Sand Sculpture Contest.
-
See also[edit]

















No comments:
Post a Comment