This article is about the war that started in 2003 and ended in 2011. For other conflicts in Iraq, see Iraq War (disambiguation).
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||
| Part of a series on |
| Ba'athism |
|---|
 |
| Politics portal |
The invasion began on 20 March 2003. The U.S., joined by the United Kingdom and several coalition allies, launched a "shock and awe" surprise attack without declaring war. Iraqi forces were quickly overwhelmed as U.S. forces swept through the country. The invasion led to the collapse of the Ba'athist government; Saddam was captured in December 2003 and executed by a military court three years later. However, the power vacuum following Saddam's demise and the mismanagement of the occupation led to widespread sectarian violence between Shias and Sunnis as well as a lengthy insurgency against U.S. and coalition forces. The United States responded with a troop surge in 2007, identified as the COIN strategy; the heavy American security presence and deals made between the occupying forces and Sunni militias reduced the level of violence. The U.S. began withdrawing its troops in the winter of 2007–2008. The winding down of U.S. involvement in Iraq accelerated under President Barack Obama. The U.S. formally withdrew all combat troops from Iraq by December 2011.[45]
The Bush Administration based its rationale for war principally on the assertion that Iraq possessed weapons of mass destruction (WMDs) and that Saddam's government posed an immediate threat to the United States and its coalition allies.[46][47] Select U.S. officials accused Saddam of harboring and supporting al-Qaeda,[48] while others cited the desire to end a repressive dictatorship and bring democracy to the people of Iraq.[49][50] After the invasion, no substantial evidence was found to verify the initial claims about WMDs. The rationale and misrepresentation of pre-war intelligence faced heavy criticism within the U.S. and internationally.
As a result of the war, Iraq held multi-party elections in 2005. Nouri al-Maliki became Prime Minister in 2006 and remained in office until 2014. The Maliki government enacted policies that were widely seen as having the effect of alienating the country's Sunni minority, worsening sectarian tensions. In the summer of 2014, the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) launched a military offensive in Northern Iraq and declared a worldwide Islamic caliphate, eliciting another military response from the United States and its allies. The Iraq War caused hundreds of thousands of civilian and military casualties (see estimates below). The majority of casualties occurred as a result of the insurgency and civil conflicts between 2004 and 2007.
Contents
- 1 Background
- 2 The invasion
- 3 Post-invasion phase
- 3.1 2003: Beginnings of insurgency
- 3.2 2004: Insurgency expands
- 3.3 2005: Elections and transitional government
- 3.4 2006: Civil war and permanent Iraqi government
- 3.5 2007: U.S. troops surge
- 3.6 2008: Civil war continues
- 3.7 2009: Coalition redeployment
- 3.8 2010: U.S. drawdown and Operation New Dawn
- 3.9 2011: U.S. withdrawal
- 4 Aftermath – post U.S.-withdrawal
- 5 Casualty estimates
- 6 Criticism and cost
- 7 Humanitarian crises
- 8 Human rights abuses
- 9 Public opinion on the war
- 10 Relation to the Global War on Terrorism
- 11 Foreign involvement
- 12 See also
- 13 Footnotes
- 14 References
- 15 Further reading
- 16 External links
Background
Iraq disarmament and pre-war intelligence
See also: Lead up to the Iraq War, Rationale for the Iraq War, Public relations preparations for 2003 invasion of Iraq, Governments' pre-war positions on invasion of Iraq, Saddam Hussein and al-Qaeda, Iraq and weapons of mass destruction and Stovepiping
Main articles: Iraq disarmament timeline 1990–2003 and 2002 in Iraq
Prior to September 2002, the CIA was the Bush administration's main provider of intelligence on Iraq. In September, a Pentagon unit called Office of Special Plans (OSP), was created by Paul Wolfowitz and Douglas Feith, and headed by Feith, as charged by then-United States Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld, to supply senior George W. Bush administration officials with raw intelligence pertaining to Iraq.[51] Seymour Hersh writes that, according to a Pentagon adviser, "[OSP] was created in order to find evidence of what Wolfowitz and his boss, Defense Secretary Donald Rumsfeld, wanted to be true—that Saddam Hussein had close ties to Al Qaeda, and that Iraq had an enormous arsenal of chemical, biological, and possibly even nuclear weapons (WMD) that threatened the region and, potentially, the United States. [...] 'The agency [CIA] was out to disprove linkage between Iraq and terrorism,' the Pentagon adviser told me."[52]U.N. weapons inspections resume
The issue of Iraq's disarmament reached a turning point in 2002–2003, when President Bush demanded a complete end to alleged Iraqi production of weapons of mass destruction and full compliance with U.N. Security Council Resolutions requiring U.N. weapons inspectors unfettered access to suspected weapons production facilities. The U.N. had prohibited Iraq from developing or possessing such weapons after the Persian Gulf War and required Iraq to permit inspections confirming compliance. During inspections in 1999, U.S. intelligence agents supplied the United States with a direct feed of conversations between Iraqi security agencies as well as other information. This was confirmed by the New York Times and the Wall Street Journal.[53]During 2002, U.S. President George Bush repeatedly warned of military action against Iraq unless inspections were allowed to progress unfettered. In accordance with U.N. Security Council Resolution 1441 Iraq agreed to new inspections in late 2002. With the cooperation of the Iraqis, a third weapons inspection team in 2003 led by David Kelly viewed and photographed two alleged mobile weapons laboratories, which were actually facilities for the production of hydrogen gas to fill balloons.[54]
As part of its weapons inspection obligations, Iraq was required to supply a full declaration of its current weapons capabilities and manufacturing. On 3 November 2002, Iraq supplied an 11,800-page report to the UN Security Council and the IAEA, stating that it had no WMDs. Copies of the report were also unofficially supplied to several European journalists. Columbia, chair of the Security Council, allowed US officials to secretly remove 8,000 pages from the report before it was viewed by the full security council, and on the basis of this the report was declared incomplete and Iraq in breach of its obligations. The removed pages contained details of US and European companies and government agencies who had historically assisted Iraq in developing its chemical and biological weapons capabilities.[55]
Shortly before the invasion, Hans Blix, the lead weapons inspector, advised the U.N. Security Council that Iraq was cooperating with inspections and the confirmation of disarmament through inspections could be achieved quickly if Iraq remained cooperative.[56]
Weapons of mass destruction
Yellowcake uranium
A UN weapons inspector examines an Iraqi factory in 2002.
In response, Wilson wrote a critical New York Times op-ed piece in June 2003 stating that he had personally investigated claims of yellowcake purchases and believed them to be fraudulent.[59] After Wilson's op-ed, Wilson's wife Valerie Plame was publicly identified as an undercover CIA analyst by a columnist. This led to a Justice Department investigation into the source of the leak. The federal investigation led to the conviction of I. Lewis (Scooter) Libby, Vice President Dick Cheney's chief of staff, on charges of perjury and obstruction of justice.[57]
On 1 May 2005, the "Downing Street memo" was published in The Sunday Times. It contained an overview of a secret 23 July 2002, meeting among British government, Ministry of Defence, and British intelligence figures who discussed the build-up to the Iraq war—including direct references to classified US policy of the time. The memo stated that "Bush wanted to remove Saddam, through military action, justified by the conjunction of terrorism and WMD. But the intelligence and facts were being fixed around the policy".[60]
In September 2002, the Bush administration, the CIA and the DIA said attempts by Iraq to acquire high-strength aluminum tubes that were prohibited under the UN monitoring program and which they said pointed to a clandestine effort to make centrifuges to enrich uranium for nuclear bombs.[61] This analysis was opposed by the United States Department of Energy (DOE) and INR, which was significant because of DOE's expertise in such gas centrifuges and nuclear weapons programs. The DOE and INR argued that the Iraqi tubes were poorly suited for centrifuges and that while it was technically possible with additional modification, conventional military uses were more plausible.[62] A report released by the Institute for Science and International Security in 2002 reported that it was highly unlikely that the tubes could be used to enrich uranium.[63]
An effort by the DOE to correct this detail in comments prepared for United States Secretary of State Colin Powell's UN appearance was rebuffed by the administration[63][64] and Powell, in his address to the UN Security Council just before the war, referenced the aluminum tubes, stating that while experts disagreed on whether or not the tubes were destined for a centrifuge program, the specifications of the tubes were unusually tight.[65] Powell later admitted he had presented what turned out to be an inaccurate case to the UN on Iraqi weapons, and the intelligence he was relying on was, in some cases, "deliberately misleading."[66][67][68] After the 2008 US presidential election, and the election of Democratic party nominee Barack Obama, President Bush stated that "[my] biggest regret of all the presidency has to have been the intelligence failure in Iraq".[69]
Poison gas
The CIA had contacted Iraq's foreign minister, Naji Sabri, who was being paid by the French as an agent. Sabri informed them that Saddam had hidden poison gas among Sunni tribesmen, had ambitions for a nuclear program but that it was not active, and that no biological weapons were being produced or stockpiled, although research was underway.[70] According to Sidney Blumenthal, George Tenet briefed Bush on 18 September 2002, that Sabri had informed them that Iraq did not have WMD.On 21 June 2006 the US House of Representatives Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence released key points from a classified report from the National Ground Intelligence Center on the recovery of a small number of degraded chemical munitions in Iraq. The report stated that "Coalition forces have recovered approximately 500 weapons munitions which contain degraded mustard or sarin nerve agent." However, all are thought to be pre-Gulf War munitions.[71]
Biological weapons
Based on reports obtained by the German intelligence service from an Iraqi defector codenamed "Curveball", Colin Powell presented evidence to the United Nations security council that Iraq had an active biological weapons programs. On 15 February 2011, the defector—a scientist identified as Rafid Ahmed Alwan al-Janafi—admitted to journalists working for The Guardian newspaper that he lied to the Bundesnachrichtendienst in order to strengthen the case against Saddam Hussein, whom he wished to see removed from power.[72]Post-invasion views on WMD
In December 2009, the former British prime minister, Tony Blair, stated that he "would still have thought it right to remove [Saddam Hussein]" regardless of whether Iraq possessed weapons of mass destruction or not.[73]Preparations for Iraq war
President George Bush, surrounded by leaders of the House and Senate, announces the Joint Resolution to Authorize the Use of United States Armed Forces Against Iraq, 2 October 2002

Excerpt from Donald Rumsfeld memo dated 27 November 2001[74]
During 2002 the amount of ordnance used by British and American aircraft patrolling the no-fly zones of Iraq increased compared to the previous years[76] and by August had "become a full air offensive". Tommy Franks, the allied commander, later stated that the bombing was designed to "degrade" the Iraqi air defense system before an invasion.[77]
In October 2002, a few days before the US Senate voted on the Joint Resolution to Authorize the Use of United States Armed Forces Against Iraq, about 75 senators were told in closed session that Iraq had the means of attacking the Eastern Seaboard of the US with biological or chemical weapons delivered by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs.)[47] On 5 February 2003, Colin Powell presented further evidence in his Iraqi WMD program presentation to the UN Security Council that UAVs were ready to be launched against the United States. At the time, there was a vigorous dispute within the US military and intelligence communities as to whether CIA conclusions about Iraqi UAVs were accurate[78] and other intelligence agencies suggested that Iraq did not possess any offensive UAV capability, saying the few they had were designed for surveillance and intended for reconnaissance.[79] The Senate voted to approve the Joint Resolution with the support of large bipartisan majorities on 11 October 2002, providing the Bush administration with a legal basis for the US invasion under US law.
The resolution granted the authorization by the Constitution of the United States and the United States Congress for the President to command the military to fight anti-United States violence. Citing the Iraq Liberation Act of 1998, the resolution reiterated that it should be the policy of the United States to remove the Saddam regime and promote a democratic replacement. The authorization was signed by President George W. Bush on 16 October 2002.
Chief UN weapons inspector Hans Blix remarked in January 2003 that "Iraq appears not to have come to a genuine acceptance—not even today—of the disarmament, which was demanded of it and which it needs to carry out to win the confidence of the world and to live in peace."[80] Among other things he noted that 1,000 short tons (910 t) of chemical agent were unaccounted for, information on Iraq's VX nerve agent program was missing, and that "no convincing evidence" was presented for the destruction of 8,500 litres (1,900 imp gal; 2,200 US gal) of anthrax that had been declared.[80]
United States Secretary of State Colin Powell holding a model vial of anthrax while giving a presentation to the United Nations Security Council
From the left: French President Jacques Chirac, US President George W. Bush, UK Prime Minister Tony Blair and Italian Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi. Chirac was against the invasion, the other three leaders were in favor.
A meeting between George W. Bush and Tony Blair took place on 31 January 2003, in the White House. A secret memo of this meeting purportedly showed that the Bush administration had already decided on the invasion of Iraq at that point. Bush was allegedly floating the idea of painting a U‑2 spyplane in UN colors and letting it fly low over Iraq to provoke Iraqi forces into shooting it down, thereby providing a pretext for the United States and Britain to invade. Bush and Blair made a secret deal to carry out the invasion regardless of whether WMD were discovered by UN weapons inspectors, in direct contradiction with statements Blair made to the British House of Commons afterwards that the Iraqi regime would be given a final chance to disarm. In the memo, Bush is paraphrased as saying, "The start date for the military campaign was now pencilled in for 10 March. This was when the bombing would begin."[87] Bush said to Blair that he "thought it unlikely that there would be internecine warfare between the different religious and ethnic groups" in Iraq after the war.
Opposition to invasion
Further information: criticism of the Iraq War, legitimacy of the 2003 invasion of Iraq, legality of the Iraq War and Protests against the Iraq War
In October 2002, former US President Bill Clinton warned about possible dangers of pre-emptive military action against Iraq. Speaking in the UK on a Labour Party
conference he said: "As a preemptive action today, however
well-justified, may come back with unwelcome consequences in the
future....I don't care how precise your bombs and your weapons are, when
you set them off, innocent people will die."[88][89]
Anti-War protest in London, 2002.
In February 2003, the US Army's top general, Eric Shinseki, told the Senate Armed Services Committee that it would take "several hundred thousand soldiers" to secure Iraq.[93] Two days later, US Defense Secretary Donald Rumsfeld said the post-war troop commitment would be less than the number of troops required to win the war, and that "the idea that it would take several hundred thousand US forces is far from the mark." Deputy Defense Secretary Paul Wolfowitz said Shinseki's estimate was "way off the mark," because other countries would take part in an occupying force.[94]
In March 2003, Hans Blix reported that "No evidence of proscribed activities have so far been found" in Iraq, saying that progress was made in inspections which would continue. He estimated the time remaining for disarmament being verified through inspections to be "months".[83] But the US government announced that "diplomacy has failed", and that it would proceed with a coalition of allied countries—named the "coalition of the willing"—to rid Iraq of its alleged WMD. The US government abruptly advised UN weapons inspectors to leave Baghdad immediately.
There were serious legal questions surrounding the launching of the war against Iraq and the Bush Doctrine of preemptive war in general. On 16 September 2004, Kofi Annan, the Secretary General of the United Nations, said of the invasion, "I have indicated it was not in conformity with the UN Charter. From our point of view, from the Charter point of view, it was illegal."
In November 2008 Lord Bingham, the former British Law Lord, described the war a serious violation of international law, and accused Britain and the United States of acting like a "world vigilante". He also criticized the post-invasion record of Britain as "an occupying power in Iraq". Regarding the treatment of Iraqi detainees in Abu Ghraib, Bingham said: "Particularly disturbing to proponents of the rule of law is the cynical lack of concern for international legality among some top officials in the Bush administration."[95] In July 2010, Deputy Prime Minister of the UK Nick Clegg, in an official PMQs session in Parliament, condemned the invasion of Iraq as illegal.[96] Theorist Francis Fukuyama has argued that "the Iraq war and the close association it created between military invasion and democracy promotion tarnished the latter".[97]
The invasion
Main articles: 2003 invasion of Iraq, 2003 in Iraq, 2003 Iraq war timeline and List of people associated with the 2003 invasion of Iraq
Destroyed remains of Iraqi tanks near Al Qadisiyah.
US Marines escort captured enemy prisoners to a holding area in the desert of Iraq on 21 March 2003.
US soldiers at the Hands of Victory monument in Baghdad
Most importantly, their efforts organized the Kurdish Peshmerga to become the northern front of the invasion. Together this force defeated Ansar al-Islam in Iraqi Kurdistan before the invasion and then defeated the Iraqi army in the north.[99][100] The battle against Ansar al-Islam led to the death of a substantial number of militants and the uncovering of a chemical weapons facility at Sargat.[98][101]
At 5:34 a.m. Baghdad time on 20 March 2003 (9:34 p.m., 19 March EST) the surprise[102] military invasion of Iraq began.[103] There was no declaration of war.[104] The 2003 invasion of Iraq, led by US Army General Tommy Franks, under the codename "Operation Iraqi Freedom",[105] the UK codename Operation Telic, and the Australian codename Operation Falconer. Coalition forces also cooperated with Kurdish Peshmerga forces in the north. Approximately forty other governments, the "Coalition of the Willing," participated by providing troops, equipment, services, security, and special forces, with 248,000 soldiers from the United States, 45,000 British soldiers, 2,000 Australian soldiers and 194 Polish soldiers from Special Forces unit GROM sent to Kuwait for the invasion.[106] The invasion force was also supported by Iraqi Kurdish militia troops, estimated to number upwards of 70,000.[107]
Iraqi tank on Highway 27 destroyed in April 2003
Map of the invasion routes and major operations/battles of the Iraq War as of 2007.
Coalition troops launched air and amphibious assault on the Al-Faw peninsula to secure the oil fields there and the important ports, supported by warships of the Royal Navy, Polish Navy, and Royal Australian Navy. The United States Marine Corps' 15th Marine Expeditionary Unit, attached to 3 Commando Brigade and the Polish Special Forces unit GROM attacked the port of Umm Qasr, while the British Army's 16 Air Assault Brigade secured the oil fields in southern Iraq.
US Marines from 1st Battalion 7th Marines enter a palace during the Fall of Baghdad.
With the Nasiriyah and Talil Airfields secured in its rear, the 3rd Infantry Division supported by 101st Airborne Division continued its attack north toward Najaf and Karbala, but a severe sand storm slowed the coalition advance and there was a halt to consolidate and make sure the supply lines were secure. When they started again they secured the Karbala Gap, a key approach to Baghdad, then secured the bridges over the Euphrates River, and US forces poured through the gap on to Baghdad. In the middle of Iraq, the 1st Marine Division fought its way to the eastern side of Baghdad, and prepared for the attack into Baghdad to seize it.[110]
In the north, OIF‑1 used the largest special operations force since the successful attack on the Taliban government of Afghanistan just over a year earlier.
On 9 April, Baghdad fell, ending Saddam's 24‑year rule. US forces seized the deserted Ba'ath Party ministries and stage-managed[111] the tearing down of a huge iron statue of Saddam, photos and video of which became symbolic of the event, although later controversial. Not seen in the photos or heard on the videos, shot with a zoom lens, was the chant of the inflamed crowd for Muqtada al-Sadr, the radical Shiite cleric.[112] In November 2008, Iraqi protesters staged a similar stomping on and burning of an effigy of George W. Bush.[113] The abrupt fall of Baghdad was accompanied by a widespread outpouring of gratitude toward the invaders, but also massive civil disorder, including the looting of public and government buildings and drastically increased crime.[114][115]
According to the Pentagon, 250,000 short tons (230,000 t) (of 650,000 short tons (590,000 t) total) of ordnance was looted, providing a significant source of ammunition for the Iraqi insurgency. The invasion phase concluded when Tikrit, Saddam's home town, fell with little resistance to the US Marines of Task Force Tripoli.
In the invasion phase of the war (19 March–30 April), an estimated 9,200 Iraqi combatants were killed by coalition forces along with an estimated 3,750 non-combatants, i.e. civilians who did not take up arms.[116] Coalition forces reported the death in combat of 139 US military personnel[117] and 33 UK military personnel.[118]
Post-invasion phase
Main article: Post-invasion Iraq, 2003–present
Further information: Iraqi insurgency (Iraq War) and Iraq War insurgent attacks
2003: Beginnings of insurgency
A Marine Corps M1 Abrams tank patrols a Baghdad street after its fall in 2003 during Operation Iraqi Freedom.
18 May 2004: Staff Sgt. Kevin Jessen checks the underside of two anti-tank mines found in a village outside Ad Dujayl in the Sunni Triangle.
Polish GROM forces in sea operations during Operation Iraqi Freedom
Marines from D Company, 3rd Light Armored Reconnaissance Battalion guard detainees prior to loading them into their vehicle
Nevertheless, Saddam remained at large and significant pockets of resistance remained. After President Bush's speech, coalition forces noticed a gradually increasing flurry of attacks on its troops in various regions, especially in the "Sunni Triangle".[119] The initial Iraqi insurgents were supplied by hundreds of weapons caches created before the invasion by the Iraqi army and Republican Guard.
Initially, Iraqi resistance (described by the coalition as "Anti-Iraqi Forces") largely stemmed from fedayeen and Saddam/Ba'ath Party loyalists, but soon religious radicals and Iraqis angered by the occupation contributed to the insurgency. The three provinces with the highest number of attacks were Baghdad, Al Anbar, and Salah Ad Din. Those three provinces account for 35% of the population, but as of 5 December 2006, were responsible for 73% of U.S. military deaths and an even higher percentage of recent U.S. military deaths (about 80%.)[120]
Insurgents used guerrilla tactics including: mortars, missiles, suicide attacks, snipers, improvised explosive devices (IEDs), car bombs, small arms fire (usually with assault rifles), and RPGs (rocket propelled grenades), as well as sabotage against the petroleum, water, and electrical infrastructure.
Post-invasion Iraq coalition efforts commenced after the fall of Saddam's regime. The coalition nations, together with the United Nations, began to work to establish a stable, compliant democratic state capable of defending itself from non-coalition forces, as well as overcoming internal divisions.[121][122]
Meanwhile, coalition military forces launched several operations around the Tigris River peninsula and in the Sunni Triangle. A series of similar operations were launched throughout the summer in the Sunni Triangle. Toward the end of 2003, the intensity and pace of insurgent attacks began to increase. A sharp surge in guerrilla attacks ushered in an insurgent effort that was termed the "Ramadan Offensive", as it coincided with the beginning of the Muslim holy month of Ramadan.
To counter this offensive, coalition forces begin to use air power and artillery again for the first time since the end of the invasion by striking suspected ambush sites and mortar launching positions. Surveillance of major routes, patrols, and raids on suspected insurgents were stepped up. In addition, two villages, including Saddam's birthplace of al-Auja and the small town of Abu Hishma were surrounded by barbed wire and carefully monitored.
Coalition Provisional Authority and the Iraq Survey Group
See also: Iraqi Governing Council, International Advisory and Monitoring Board, CPA Program Review Board, Development Fund for Iraq and Reconstruction of Iraq
Occupation zones in Iraq as of September 2003.
The CPA was originally headed by Jay Garner, a former US military officer, but his appointment lasted only until 11 May 2003, when President Bush appointed L. Paul Bremer. On 16 May 2003 on his first day on the job Paul Bremer issued CPA executive order No1 to exclude from the new Iraqi government and administration members of the Baathist party. This eventually led to the removal of 85,000 to 100,000 Iraqi people from their job. [123] including 40,000 school teachers who had joined the Baath Party simply to keep their jobs. US army general Sanchez called the decision a "catastrophic failure" [124] Bremer served until the CPA's dissolution in July 2004.
Another group created by the multinational force in Iraq post-invasion was the 1,400-member international Iraq Survey Group who conducted a fact-finding mission to find Iraqi weapons of mass destruction (WMD) programmes. In 2004 the ISG's Duelfer Report[125] stated that Iraq did not have a viable WMD program.
Capturing former government leaders
See also: Supreme Iraqi Criminal Tribunal and Trial of Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein being pulled from his hideaway in Operation Red Dawn, 13 December 2003.
Two insurgents in Iraq with SA-7b and SA-14 MANPADS
Most significantly, Saddam Hussein himself was captured on 13 December 2003, on a farm near Tikrit in Operation Red Dawn.[126] The operation was conducted by the United States Army's 4th Infantry Division and members of Task Force 121. Intelligence on Saddam's whereabouts came from his family members and former bodyguards.[127]
With the capture of Saddam and a drop in the number of insurgent attacks, some concluded the multinational forces were prevailing in the fight against the insurgency. The provisional government began training the new Iraqi security forces intended to police the country, and the United States promised over $20 billion in reconstruction money in the form of credit against Iraq's future oil revenues. Oil revenue was also used for rebuilding schools and for work on the electrical and refining infrastructure.
Shortly after the capture of Saddam, elements left out of the Coalition Provisional Authority began to agitate for elections and the formation of an Iraqi Interim Government. Most prominent among these was the Shia cleric Grand Ayatollah Ali al-Sistani. The Coalition Provisional Authority opposed allowing democratic elections at this time.[128] The insurgents stepped up their activities. The two most turbulent centers were the area around Fallujah and the poor Shia sections of cities from Baghdad (Sadr City) to Basra in the south.
2004: Insurgency expands
Main article: 2004 in Iraq
- See also: Military operations of the Iraq War for a list of all Coalition operations for this period, 2004 in Iraq, Iraqi coalition counter-insurgency operations, Iraqi insurgency (2003–11), United States occupation of Fallujah, Iraq Spring Fighting of 2004
Footage from the gun camera of a U.S. Apache helicopter killing suspected Iraqi insurgents.[129]
Coalition Provisional Authority director L. Paul Bremer signs over sovereignty to the appointed Iraqi Interim Government, 28 June 2004.
US troops fire mortars
The most serious fighting of the war so far began on 31 March 2004, when Iraqi insurgents in Fallujah ambushed a Blackwater USA convoy led by four U.S. private military contractors who were providing security for food caterers Eurest Support Services.[130] The four armed contractors, Scott Helvenston, Jerko Zovko, Wesley Batalona, and Michael Teague, were killed with grenades and small arms fire. Subsequently, their bodies were dragged from their vehicles by local people, beaten, set ablaze, and their burned corpses hung over a bridge crossing the Euphrates.[131] Photos of the event were released to news agencies worldwide, causing a great deal of indignation and moral outrage in the United States, and prompting an unsuccessful "pacification" of the city: the First Battle of Fallujah in April 2004.
The offensive was resumed in November 2004 in the bloodiest battle of the war so far: the Second Battle of Fallujah, described by the U.S. military as "the heaviest urban combat (that they had been involved in) since the battle of Hue City in Vietnam."[132] During the assault, U.S. forces used white phosphorus as an incendiary weapon against insurgent personnel, attracting controversy. The 46‑day battle resulted in a victory for the coalition, with 95 U.S. soldiers killed along with approximately 1,350 insurgents. Fallujah was totally devastated during the fighting, though civilian casualties were low, as they had mostly fled before the battle.[133]
Another major event of that year was the revelation of widespread prisoner abuse at Abu Ghraib which received international media attention in April 2004. First reports of the Abu Ghraib prisoner abuse, as well as graphic pictures showing U.S. military personnel taunting and abusing Iraqi prisoners, came to public attention from a 60 Minutes II news report (28 April) and a Seymour M. Hersh article in The New Yorker (posted online on 30 April.)[134] Military correspondent Thomas Ricks claimed that these revelations dealt a blow to the moral justifications for the occupation in the eyes of many people, especially Iraqis, and was a turning point in the war.[135]
2004 also marked the beginning of Military Transition Teams in Iraq, which were teams of U.S. military advisors assigned directly to New Iraqi Army units.
2005: Elections and transitional government
Further information: 2005 in Iraq and Military transition team
Convention center for Council of Representatives of Iraq
The Battle of Abu Ghraib on 2 April 2005 was an attack on United States forces at Abu Ghraib prison, which consisted of heavy mortar and rocket fire, under which armed insurgents attacked with grenades, small arms, and two vehicle-borne improvised explosive devices (VBIED). The U.S. force's munitions ran so low that orders to fix bayonets were given in preparation for hand-to-hand fighting. An estimated 80–120 armed insurgents launched a massive coordinated assault on the U.S. military facility and internment camp at Abu Ghraib, Iraq. It was considered to be the largest coordinated assault on a U.S. base since the Vietnam War.[137]
Hopes for a quick end to the insurgency and a withdrawal of US troops were dashed in May, Iraq's bloodiest month since the invasion. Suicide bombers, believed to be mainly disheartened Iraqi Sunni Arabs, Syrians and Saudis, tore through Iraq. Their targets were often Shia gatherings or civilian concentrations of Shias. As a result, over 700 Iraqi civilians died in that month, as well as 79 U.S. soldiers.
The summer of 2005 saw fighting around Baghdad and at Tall Afar in northwestern Iraq as U.S. forces tried to seal off the Syrian border. This led to fighting in the autumn in the small towns of the Euphrates valley between the capital and that border.[138]
A referendum was held on 15 October in which the new Iraqi constitution was ratified. An Iraqi national assembly was elected in December, with participation from the Sunnis as well as the Kurds and Shia.[138]
Insurgent attacks increased in 2005 with 34,131 recorded incidents, compared to a total 26,496 for the previous year.[139]
2006: Civil war and permanent Iraqi government
Further information: 2006 in Iraq, Civil war in Iraq (2006–07), Operation Together Forward and Provincial Reconstruction Team
Although no injuries occurred in the blast, the mosque was severely damaged and the bombing resulted in violence over the following days. Over 100 dead bodies with bullet holes were found on 23 February, and at least 165 people are thought to have been killed. In the aftermath of this attack the U.S. military calculated that the average homicide rate in Baghdad tripled from 11 to 33 deaths per day. In 2006 the UN described the environment in Iraq as a "civil war-like situation".[140]
On March 12, five United States Army soldiers of the 502nd Infantry Regiment, raped the 14-year-old Iraqi girl Abeer Qassim Hamza al‑Janabi, and then murdered her, her father, her mother Fakhriya Taha Muhasen and her six-year-old sister Hadeel Qassim Hamza al-Janabi. The soldiers then set fire to the girl's body to conceal evidence of the crime.[141] Four of the soldiers were convicted of rape and murder and the fifth was convicted of lesser crimes for the involvement in the war crime, that became known as the Mahmudiyah killings.[142][143]
Nouri al-Maliki meets with George W. Bush, June 2006
The current government of Iraq took office on 20 May 2006, following approval by the members of the Iraqi National Assembly. This followed the general election in December 2005. The government succeeded the Iraqi Transitional Government which had continued in office in a caretaker capacity until the formation of the permanent government.
Iraq Study Group report and Saddam's execution
Main articles: Iraq Study Group and Execution of Saddam Hussein
The Iraq Study Group Report was released on 6 December 2006. Iraq Study Group, made up of people from both of the major U.S. parties, was led by co-chairs James Baker, a former Secretary of State (Republican), and Lee H. Hamilton,
a former U.S. Representative (Democrat). It concluded that "the
situation in Iraq is grave and deteriorating" and "U.S. forces seem to
be caught in a mission that has no foreseeable end." The report's
79 recommendations include increasing diplomatic measures with Iran and Syria
and intensifying efforts to train Iraqi troops. On 18 December, a
Pentagon report found that insurgent attacks were averaging about 960
attacks per week, the highest since the reports had begun in 2005.[144]Coalition forces formally transferred control of a province to the Iraqi government, the first since the war. Military prosecutors charged eight U.S. Marines with the murders of 24 Iraqi civilians in Haditha in November 2005, 10 of them women and children. Four officers were also charged with dereliction of duty in relation to the event.[145]
Saddam Hussein was hanged on 30 December 2006, after being found guilty of crimes against humanity by an Iraqi court after a year-long trial.[146]
2007: U.S. troops surge
President George W. Bush announces the new strategy on Iraq from the White House Library, 10 January 2007.
Further information: 2007 in Iraq, Iraq War troop surge of 2007, Timeline of the Iraq War troop surge of 2007 and Strategic reset
In a 10 January 2007, televised address to the US public, Bush
proposed 21,500 more troops for Iraq, a job program for Iraqis, more
reconstruction proposals, and $1.2 billion for these programs.[147] On 23 January 2007, in the 2007 State of the Union Address, Bush announced "deploying reinforcements of more than 20,000 additional soldiers and Marines to Iraq".On 10 February 2007, David Petraeus was made commander of Multi-National Force – Iraq (MNF-I), the four-star post that oversees all coalition forces in country, replacing General George Casey. In his new position, Petraeus oversaw all coalition forces in Iraq and employed them in the new "Surge" strategy outlined by the Bush administration.[148][149] 2007 also saw a sharp increase in insurgent chlorine bombings.
On 10 May 2007, 144 Iraqi Parliamentary lawmakers signed onto a legislative petition calling on the United States to set a timetable for withdrawal.[150] On 3 June 2007, the Iraqi Parliament voted 85 to 59 to require the Iraqi government to consult with Parliament before requesting additional extensions of the UN Security Council Mandate for Coalition operations in Iraq.[151] Despite this, the mandate was renewed on 18 December 2007, without the approval of the Iraqi parliament.[152]
Pressures on US troops were compounded by the continuing withdrawal of coalition forces.[citation needed] In early 2007, British Prime Minister Blair announced that following Operation Sinbad British troops would begin to withdraw from Basra Governorate, handing security over to the Iraqis.[153] In July Danish Prime Minister Anders Fogh Rasmussen also announced the withdrawal of 441 Danish troops from Iraq, leaving only a unit of nine soldiers manning four observational helicopters.[154]
Planned troop reduction
See also: Provincial Iraqi Control
In a speech made to Congress on 10 September 2007, Petraeus
"envisioned the withdrawal of roughly 30,000 U.S. troops by next summer,
beginning with a Marine contingent [in September]."[155] On 13 September, Bush backed a limited withdrawal of troops from Iraq.[156]
Bush said 5,700 personnel would be home by Christmas 2007, and expected
thousands more to return by July 2008. The plan would take troop
numbers back to their level before the surge at the beginning of 2007.Effects of the surge on security
Historically, the daily counts tallied by the New York Times have underestimated the total death toll by 50% or more when compared to studies by the United Nations, which rely upon figures from the Iraqi Health Ministry and morgue figures.[160]
The rate of U.S. combat deaths in Baghdad nearly doubled to 3.14 per day in the first seven weeks of the "surge" in security activity, compared to previous period. Across the rest of Iraq it decreased slightly.[161][162]
On 14 August 2007, the deadliest single attack of the whole war occurred. Nearly 800 civilians were killed by a series of coordinated suicide bomb attacks on the northern Iraqi settlement of Kahtaniya. More than 100 homes and shops were destroyed in the blasts. U.S. officials blamed al‑Qaeda. The targeted villagers belonged to the non-Muslim Yazidi ethnic minority. The attack may have represented the latest in a feud that erupted earlier that year when members of the Yazidi community stoned to death a teenage girl called Du'a Khalil Aswad accused of dating a Sunni Arab man and converting to Islam. The killing of the girl was recorded on camera-mobiles and the video was uploaded onto the internet.[163][164][165][166]
On 13 September 2007, Abdul Sattar Abu Risha was killed in a bomb attack in the city of Ramadi.[167] He was an important U.S. ally because he led the "Anbar Awakening", an alliance of Sunni Arab tribes that opposed al-Qaeda. The latter organisation claimed responsibility for the attack.[168] A statement posted on the Internet by the shadowy Islamic State of Iraq called Abu Risha "one of the dogs of Bush" and described Thursday's killing as a "heroic operation that took over a month to prepare".[169]
A graph of U.S. troop fatalities in Iraq March 2003 – July 2010, the orange and blue months are the period of the troop surge and its aftermath.
Data from the Pentagon and other U.S. agencies such as the Government Accountability Office (GAO) found that daily attacks against civilians in Iraq remained "about the same" since February. The GAO also stated that there was no discernible trend in sectarian violence.[173] However, this report ran counter to reports to Congress, which showed a general downward trend in civilian deaths and ethno-sectarian violence since December 2006.[174] By late 2007, as the U.S. troop surge began to wind down, violence in Iraq had begun to decrease from its 2006 highs.[175]
Entire neighborhoods in Baghdad were ethnically cleansed by Shia and Sunni militias and sectarian violence has broken out in every Iraqi city where there is a mixed population.[176][177][178] Investigative reporter Bob Woodward cites U.S. government sources according to which the U.S. "surge" was not the primary reason for the drop in violence in 2007–2008. Instead, according to that view, the reduction of violence was due to newer covert techniques by U.S. military and intelligence officials to find, target and kill insurgents, including working closely with former insurgents.[179]
In the Shia region near Basra, British forces turned over security for the region to Iraqi Security Forces. Basra is the ninth province of Iraq's 18 provinces to be returned to local security forces' control since the beginning of the occupation.[180]
Political developments
Official Iraq-benchmark of the Congress, 2007.
In mid-2007, the Coalition began a controversial program to recruit Iraqi Sunnis (often former insurgents) for the formation of "Guardian" militias. These Guardian militias are intended to support and secure various Sunni neighborhoods against the Islamists.[184]
Tensions with Iran
Further information: United States-Iran relations and Karbala provincial headquarters raid
In 2007, tensions increased greatly between Iran and Iraqi Kurdistan due to the latter's giving sanctuary to the militant Kurdish secessionist group Party for a Free Life in Kurdistan
(PEJAK.) According to reports, Iran had been shelling PEJAK positions
in Iraqi Kurdistan since 16 August. These tensions further increased
with an alleged border incursion on 23 August by Iranian troops who
attacked several Kurdish villages killing an unknown number of civilians
and militants.[185]Coalition forces also began to target alleged Iranian Quds force operatives in Iraq, either arresting or killing suspected members. The Bush administration and coalition leaders began to publicly state that Iran was supplying weapons, particularly EFP devices, to Iraqi insurgents and militias although to date have failed to provide any proof for these allegations. Further sanctions on Iranian organizations were also announced by the Bush administration in the autumn of 2007. On 21 November 2007, Lieutenant General James Dubik, who is in charge of training Iraqi security forces, praised Iran for its "contribution to the reduction of violence" in Iraq by upholding its pledge to stop the flow of weapons, explosives and training of extremists in Iraq.[186]
Tensions with Turkey
Further information: 2008 Turkish incursion into northern Iraq
Border incursions by PKK
militants based in Northern Iraq have continued to harass Turkish
forces, with casualties on both sides. In the fall of 2007, the Turkish
military stated their right to cross the Iraqi Kurdistan border in "hot
pursuit" of PKK militants and began shelling Kurdish areas in Iraq and
attacking PKK bases in the Mount Cudi region with aircraft.[187][188] The Turkish parliament approved a resolution permitting the military to pursue the PKK in Iraqi Kurdistan.[189]
In November, Turkish gunships attacked parts of northern Iraq in the
first such attack by Turkish aircraft since the border tensions
escalated.[190]
Another series of attacks in mid-December hit PKK targets in the
Qandil, Zap, Avashin and Hakurk regions. The latest series of attacks
involved at least 50 aircraft and artillery and Kurdish officials
reported one civilian killed and two wounded.[191]Additionally, weapons that were given to Iraqi security forces by the U.S. military were being recovered by authorities in Turkey after being used by PKK in that state.[192]
Blackwater private security controversy
Main article: Blackwater Baghdad shootings
On 17 September 2007, the Iraqi government announced that it was revoking the license of the U.S. security firm Blackwater USA over the firm's involvement in the killing of eight civilians, including a woman and an infant,[193] in a firefight that followed a car bomb explosion near a State Department motorcade.2008: Civil war continues
Further information: 2008 in Iraq
Soldiers of the 3rd Brigade, 14th Iraqi Army division graduate from basic training.
According to the Brookings Institution, Iraqi civilian fatalities numbered 490 in November 2008 as against 3,500 in January 2007, whereas attacks against the coalition numbered somewhere between 200 and 300 per week in the latter half of 2008, as opposed to a peak of nearly 1,600 in summer 2007. The number of Iraqi security forces killed was under 100 per month in the second half of 2008, from a high of 200 to 300 in summer 2007.[195]
Meanwhile, the proficiency of the Iraqi military increased as it launched a spring offensive against Shia militias which Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki had previously been criticized for allowing to operate. This began with a March operation against the Mehdi Army in Basra, which led to fighting in Shia areas up and down the country, especially in the Sadr City district of Baghdad. By October, the British officer in charge of Basra said that since the operation the town had become "secure" and had a murder rate comparable to Manchester in England.[196] The U.S. military also said there had been a decrease of about a quarter in the quantity of Iranian-made explosives found in Iraq in 2008, possibly indicating a change in Iranian policy.[197]
Progress in Sunni areas continued after members of the Awakening movement were transferred from U.S. military to Iraqi control.[198] In May, the Iraqi army – backed by coalition support – launched an offensive in Mosul, the last major Iraqi stronghold of al-Qaeda. Despite detaining thousands of individuals, the offensive failed to lead to major long-term security improvements in Mosul. At the end of the year, the city remained a major flashpoint.[199][200]
3D Map of southern Turkey and northern Iraq.
Shortly after the incursion began, both the Iraqi cabinet and the Kurdistan regional government condemned Turkey's actions and called for the immediate withdrawal of Turkish troops from the region.[206] Turkish troops withdrew on 29 February.[207] The fate of the Kurds and the future of the ethnically diverse city of Kirkuk remained a contentious issue in Iraqi politics.
U.S. military officials met these trends with cautious optimism as they approached what they described as the "transition" embodied in the U.S.-Iraq Status of Forces Agreement which was negotiated throughout 2008.[194] The commander of the coalition, U.S. General Raymond T. Odierno, noted that "in military terms, transitions are the most dangerous time" in December 2008.[194]
Spring offensives on Shia militias
An Iraqi soldier and vehicles from the 42nd Brigade, 11th Iraqi Army
Division during a firefight with armed militiamen in the Sadr City
district of Baghdad 17 April 2008.
Following talks with Brig. Gen. Qassem Suleimani, commander of the Qods brigades of Iran's Revolutionary Guard Corps, and the intercession of the Iranian government, on 31 March 2008, al‑Sadr ordered his followers to ceasefire.[210] The militiamen kept their weapons.
By 12 May 2008, Basra "residents overwhelmingly reported a substantial improvement in their everyday lives" according to the New York Times. "Government forces have now taken over Islamic militants' headquarters and halted the death squads and 'vice enforcers' who attacked women, Christians, musicians, alcohol sellers and anyone suspected of collaborating with Westerners", according to the report; however, when asked how long it would take for lawlessness to resume if the Iraqi army left, one resident replied, "one day".[209]
In late April roadside bombings continued to rise from a low in January—from 114 bombings to more than 250, surpassing the May 2007 high.
Congressional testimony
General David Petraeus in testimony before Congress on 8 April 2008.
Upon questioning by then Senate committee chair Joe Biden, Ambassador Crocker admitted that Al‑Qaeda in Iraq was less important than the Al Qaeda organization led by Osama bin Laden along the Afghan-Pakistani border.[213] Lawmakers from both parties complained that U.S. taxpayers are carrying Iraq's burden as it earns billions of dollars in oil revenues.
Iraqi security forces rearm
An Iraqi Army unit prepares to board a Task Force Baghdad UH-60 Blackhawk helicopter for a counterinsurgency mission in Baghdad in 2007.
Iraq sought 36 F‑16s, the most sophisticated weapons system Iraq has attempted to purchase. The Pentagon notified Congress that it had approved the sale of 24 American attack helicopters to Iraq, valued at as much as $2.4 billion. Including the helicopters, Iraq announced plans to purchase at least $10 billion in U.S. tanks and armored vehicles, transport planes and other battlefield equipment and services. Over the summer, the Defense Department announced that the Iraqi government wanted to order more than 400 armored vehicles and other equipment worth up to $3 billion, and six C-130J transport planes, worth up to $1.5 billion.[216][217] From 2005 to 2008, the United States had completed approximately $20 billion in arms sales agreements with Iraq.[218]
Status of forces agreement
Main article: U.S.-Iraq Status of Forces Agreement
The U.S.-Iraq Status of Forces Agreement was approved by the Iraqi government on 4 December 2008.[219]
It establishes that U.S. combat forces will withdraw from Iraqi cities
by 30 June 2009, and that all U.S. forces will be completely out of Iraq
by 31 December 2011. The pact is subject to possible negotiations which
could delay withdrawal and a referendum scheduled for mid-2009 in Iraq
which may require all U.S. forces to completely leave by the middle of
2010.[220][221]
The pact requires criminal charges for holding prisoners over 24 hours,
and requires a warrant for searches of homes and buildings that are not
related to combat.[222]U.S. contractors working for U.S. forces will be subject to Iraqi criminal law, while contractors working for the State Department and other U.S. agencies may retain their immunity. If U.S. forces commit still undecided "major premeditated felonies" while off-duty and off-base, they will be subject to the still undecided procedures laid out by a joint U.S.‑Iraq committee if the United States certifies the forces were off-duty.[223][224][225][226]
Some Americans have discussed "loopholes"[227] and some Iraqis have said they believe parts of the pact remain a "mystery".[228] U.S. Secretary of Defense Robert Gates has predicted that after 2011 he would expect to see "perhaps several tens of thousands of American troops" as part of a residual force in Iraq.[229]
Several groups of Iraqis protested the passing of the SOFA accord[230][231][232] as prolonging and legitimizing the occupation. Tens of thousands of Iraqis burned an effigy of George W. Bush in a central Baghdad square where U.S. troops five years previously organized a tearing down of a statue of Saddam Hussein.[111][228][233] Some Iraqis expressed skeptical optimism that the U.S. would completely end its presence by 2011.[234] On 4 December 2008, Iraq's presidential council approved the security pact.[219]
A representative of Grand Ayatollah Ali Husseini al‑Sistani's expressed concern with the ratified version of the pact and noted that the government of Iraq has no authority to control the transfer of occupier forces into and out of Iraq, no control of shipments, and that the pact grants the occupiers immunity from prosecution in Iraqi courts. He said that Iraqi rule in the country is not complete while the occupiers are present, but that ultimately the Iraqi people would judge the pact in a referendum.[233] Thousands of Iraqi have gathered weekly after Friday prayers and shouted anti‑U.S. and anti-Israeli slogans protesting the security pact between Baghdad and Washington. A protester said that despite the approval of the Interim Security pact, the Iraqi people would break it in a referendum next year.[235]
2009: Coalition redeployment
Further information: 2009 in Iraq
Transfer of Green Zone
Aerial view of the Green Zone, Baghdad International Airport, and the contiguous Victory Base Complex in Baghdad.
The U.S. military attributed a decline in reported civilians deaths to several factors including the U.S.‑led "troop surge", the growth of U.S.-funded Awakening Councils, and Shiite cleric Muqtada al-Sadr's call for his militia to abide by a cease fire.[236]
Provincial elections
Main article: Iraqi governorate elections, 2009
Election map. Shows what was the largest list in every governorate.
Iraqi voter turnout failed to meet the original expectations which were set and was the lowest on record in Iraq,[242] but U.S. Ambassador Ryan Crocker characterized the turnout as "large".[243] Of those who turned out to vote, some groups complained of disenfranchisement and fraud.[242][244][245] After the post-election curfew was lifted, some groups made threats about what would happen if they were unhappy with the results.[246]
US President Barack Obama delivering a speech at Camp Lejeune on 27 February 2009.
Exit strategy announcement
On 27 February, United States President Barack Obama gave a speech at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune in the US state of North Carolina announcing that the US combat mission in Iraq would end by 31 August 2010. A "transitional force" of up to 50,000 troops tasked with training the Iraqi Security Forces, conducting counterterrorism operations, and providing general support may remain until the end of 2011, the president added.[247]The day before Obama's speech, Prime Minister of Iraq Nuri al‑Maliki said at a press conference that the government of Iraq had "no worries" over the impending departure of U.S. forces and expressed confidence in the ability of the Iraqi Security Forces and police to maintain order without US military support.[248]
Sixth anniversary protests
On 9 April, the 6th anniversary of Baghdad's fall to coalition forces, tens of thousands of Iraqis thronged Baghdad to mark the anniversary and demand the immediate departure of coalition forces. The crowds of Iraqis stretched from the Sadr City slum in northeast Baghdad to the square around 5 km (3.1 mi) away, where protesters burned an effigy featuring the face of U.S. President George W. Bush.[249] There were also Sunni Muslims in the crowd. Police said many Sunnis, including prominent leaders such as a founding sheikh from the Sons of Iraq, took part.[250]Coalition forces withdraw
On 30 April, the United Kingdom formally ended combat operations. Prime Minister Gordon Brown characterized the operation in Iraq as a "success story" because of UK troops' efforts. Britain handed control of Basra to the United States Armed Forces.[251]On 28 July, Australia withdrew its combat forces as the Australian military presence in Iraq ended, per an agreement with the Iraqi government.
The withdrawal of U.S. forces began at the end of June, with 38 bases to be handed over to Iraqi forces. On 29 June 2009, U.S. forces withdrew from Baghdad. On 30 November 2009, Iraqi Interior Ministry officials reported that the civilian death toll in Iraq fell to its lowest level in November since the 2003 invasion.[252]
Iraq awards oil contracts
U.S. Navy and Coast Guard personnel stand guard aboard the Al Basrah Oil Terminal in July 2009.
2010: U.S. drawdown and Operation New Dawn
Further information: 2010 in Iraq and Withdrawal of U.S. troops from Iraq
On 17 February 2010, U.S. Secretary of Defense Robert Gates announced that as of 1 September, the name "Operation Iraqi Freedom" would be replaced by "Operation New Dawn".[256]On 18 April, US and Iraqi forces killed Abu Ayyub al-Masri the leader of al-Qaeda in Iraq in a joint American and Iraqi operation near Tikrit, Iraq.[257] The coalition forces believed al-Masri to be wearing a suicide vest and proceeded cautiously. After the lengthy exchange of fire and bombing of the house, the Iraqi troops stormed inside and found two women still alive, one of whom was al-Masri's wife, and four dead men, identified as al-Masri, Abu Abdullah al-Rashid al-Baghdadi, an assistant to al-Masri, and al-Baghdadi's son. A suicide vest was indeed found on al-Masri's corpse, as the Iraqi Army subsequently stated.[258] Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki announced the killings of Abu Omar al-Baghdadi and Abu Ayyub al-Masri at a news conference in Baghdad and showed reporters photographs of their bloody corpses. "The attack was carried out by ground forces which surrounded the house, and also through the use of missiles," Mr Maliki said. "During the operation computers were seized with e-mails and messages to the two biggest terrorists, Osama bin Laden and [his deputy] Ayman al-Zawahiri", Maliki added. U.S. forces commander Gen. Raymond Odierno praised the operation. "The death of these terrorists is potentially the most significant blow to al‑Qaeda in Iraq since the beginning of the insurgency", he said. "There is still work to do but this is a significant step forward in ridding Iraq of terrorists."
U.S. Vice President Joe Biden stated that the deaths of the top two al‑Qaeda figures in Iraq are "potentially devastating" blows to the terror network there and proof that Iraqi security forces are gaining ground.[259]
On 20 June, Iraq's Central Bank was bombed in an attack that left 15 people dead and brought much of downtown Baghdad to a standstill. The attack was claimed to have been carried out by the Islamic State of Iraq. This attack was followed by another attack on Iraq's Bank of Trade building that killed 26 and wounded 52 people.[260]
Iraqi commandos training under the supervision of soldiers from the US 82nd Airborne in December 2010.
From the end of August 2010, the United States attempted to dramatically cut its combat role in Iraq, with the withdrawal of all US ground forces designated for active combat operations. The last US combat brigades departed Iraq in the early morning of 19 August. Convoys of US troops had been moving out of Iraq to Kuwait for several days, and NBC News broadcast live from Iraq as the last convoy crossed the border. While all combat brigades left the country, an additional 50,000 personnel (including Advise and Assist Brigades) remained in the country to provide support for the Iraqi military.[262][263] These troops are required to leave Iraq by 31 December 2011 under an agreement between the US and Iraqi governments.[264]
The desire to step back from an active counter-insurgency role did not however mean that the Advise and Assist Brigades and other remaining US forces would not be caught up in combat. A standards memo from the Associated Press reiterated "combat in Iraq is not over, and we should not uncritically repeat suggestions that it is, even if they come from senior officials".[265]
State Department spokesman P. J. Crowley stated "...we are not ending our work in Iraq, We have a long-term commitment to Iraq."[266] On 31 August, Obama announced the end of Operation Iraqi Freedom from the Oval Office. In his address, he covered the role of the United States' soft power, the effect the war had on the United States economy, and the legacy of the Afghanistan and Iraq wars.[267]
On the same day in Iraq, at a ceremony at one of Saddam Hussein's former residences at Al Faw Palace in Baghdad, a number of US dignitaries spoke in a ceremony for television cameras, avoiding overtones of the triumphalism present in US announcements made earlier in the war. Vice President Joe Biden expressed concerns regarding the ongoing lack of progress in forming a new Iraqi government, saying of the Iraqi people that "they expect a government that reflects the results of the votes they cast". Gen. Ray Odierno stated that the new era "in no way signals the end of our commitment to the people of Iraq". Speaking in Ramadi earlier in the day, Gates said that U.S. forces "have accomplished something really quite extraordinary here, [but] how it all weighs in the balance over time I think remains to be seen". When asked by reporters if the seven-year war was worth doing, Gates commented that "It really requires a historian's perspective in terms of what happens here in the long run". He noted the Iraq War "will always be clouded by how it began" in regards Saddam Hussein's supposed weapons of mass destruction, which were never confirmed to have existed. Gates continued, "This is one of the reasons that this war remains so controversial at home".[268] On the same day Gen. Ray Odierno was replaced by Lloyd Austin as Commander of US forces in Iraq.
Alabama Army National Guard MP, MSG Schur, during a joint community policing patrol in Basra, 3 April 2010.
On 8 September, the U.S. Army announced the arrival in Iraq of the first specifically-designated Advise and Assist Brigade, the 3d Armored Cavalry Regiment. It was announced that the unit would assume responsibilities in five southern provinces.[270] From 10–13 September, Second Advise and Assist Brigade, 25th Infantry Division fought Iraqi insurgents near Diyala.
According to reports from Iraq, hundreds of members of the Sunni Awakening Councils may have switched allegiance back to the Iraqi insurgency or al Qaeda.[271]
Wikileaks disclosed 391,832 classified U.S. military documents on the Iraq War.[272][273][274] Approximately, 58 people were killed with another 40 wounded in an attack on the Sayidat al‑Nejat church, a Chaldean Catholic church in Baghdad. Responsibility for the attack was claimed by the Islamic State in Iraq organization.[275]
Coordinated attacks in primarily Shia areas struck throughout Baghdad on 2 November, killing approximately 113 and wounding 250 with around 17 bombs.[276]
Iraqi security forces transition towards self-reliance
Preparing to buy $13 billion worth of American arms, the Iraq Defense Ministry intends to transform the country's degraded conventional forces into a state-of-the-art military and become among the world's biggest customers for American military arms and equipment. Part of the planned purchase includes 140 M1 Abrams main battle tanks. Iraqi crews have already begun training on them. In addition to the $13 billion purchase, the Iraqis have requested 18 F-16 Fighting Falcons as part of a $4.2 billion program that also includes aircraft training and maintenance, AIM‑9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles, laser-guided bombs and reconnaissance equipment.[277] If approved by Congress, the first aircraft could arrive in spring 2013. Under the plan, the first 10 pilots would be trained in the United States.[278]The Iraqi navy also inaugurated U.S.‑built Swift Class patrol boat at Umm Qasr, Iraq's main port at the northern end of the gulf. Iraq is to take delivery of 14 more of these $20 million, 50‑foot craft before U.S. forces depart. The high-speed vessels' main mission will be to protect the oil terminals at al‑Basra and Khor al-Amiya through which some 1.7 million barrels a day are loaded into tankers for export. Two U.S.‑built offshore support vessels, each costing $70 million, were expected to be delivered in 2011.[277]
M1 Abrams tanks in Iraqi service, January 2011
UN lifts restrictions on Iraq
In a move to legitimize the existing Iraqi government, the United Nations lifted the Saddam Hussein-era UN restrictions on Iraq. These included allowing Iraq to have a civilian nuclear program, permitting the participation of Iraq in international nuclear and chemical weapons treaties, as well as returning control of Iraq's oil and gas revenue to the government and ending the Oil-for-Food Programme.[280]2011: U.S. withdrawal
Main article: Withdrawal of U.S. troops from Iraq
Further information: 2011 in Iraq
U.S. troops in Iraq and US casualties by month, 2003–2011.
On 15 January 2011, three U.S. troops were killed in Iraq. One of the troops was killed on a military operation in central Iraq, while the other two troops were deliberately shot by one or two Iraqi soldiers during a training exercise.[282]
On 6 June, five U.S. troops were killed in an apparent rocket attack on Camp Victory, located near Baghdad International Airport.[283] A sixth soldier, who was wounded in the attack, died 10 days later of his wounds.[284]
On 29 June, three U.S. troops were killed in a rocket attack on a U.S. base located near the border with Iran. It was speculated that the militant group responsible for the attack was the same one which attacked Camp Victory just over three weeks before.[285] With the three deaths, June 2011, became the bloodiest month in Iraq for the U.S. military since June 2009, with 15 U.S. soldiers killed, only one of them outside combat.[286]
In September, Iraq signed a contract to buy 18 Lockheed Martin F-16 warplanes, becoming the 26th nation to operate the F-16. Because of windfall profits from oil, the Iraqi government is planning to double this originally planned 18, to 36 F-16s. Iraq is relying on the U.S. military for air support as it rebuilds its forces and battles a stubborn Islamist insurgency.[287]
With the collapse of the discussions about extending the stay of any U.S. troops beyond 2011, where they would not be granted any immunity from the Iraqi government, on 21 October 2011, President Obama announced at a White House press conference that all remaining U.S. troops and trainers would leave Iraq by the end of the year as previously scheduled, bringing the U.S. mission in Iraq to an end.[288] The last American soldier to die in Iraq before the withdrawal was killed by a roadside bomb in Baghdad on 14 November.[289]
In November 2011, the U.S. Senate voted down a resolution to formally end the war by bringing its authorization by Congress to an end.[290]
U.S. and Kuwaiti troops closing the gate between Kuwait and Iraq on 18 December 2011.
Aftermath – post U.S.-withdrawal
Main article: Iraqi insurgency (post-U.S. withdrawal)
5 June 2015 military situation:
Controlled by Iraqi government
Controlled by the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIS)
Controlled by Iraqi Kurds
Controlled by Syrian government
Controlled by Syrian rebels
Controlled by Syrian Kurds
Iraqi insurgency surged in the aftermath of the U.S. withdrawal. The terror campaigns have since been engaged by Iraqi, primarily radical Sunni, insurgent groups against the central government and the warfare between various factions within Iraq. The events of post U.S. withdrawal violence succeeded the previous insurgency in Iraq (prior to 18 December 2011), but have showed different patterns, raising concerns that the surging violence might slide into another civil war. Some 1,000 people were killed across Iraq within the first two months after U.S. withdrawal.
Sectarian violence continued in the first half of 2013— at least 56 people died in April when a Sunni protest in Hawija was interrupted by a government-supported helicopter raid and a series of violent incidents occurred in May. On 20 May 2013, at least 95 people died in a wave of car bomb attacks that was preceded by a car bombing on 15 May that led to 33 deaths; also, on 18 May, 76 people were killed in the Sunni areas of Baghdad. Some experts have stated that Iraq could return to the brutal sectarian conflict of 2006.[295][296]
On 22 July 2013, at least five hundred convicts, most of whom were senior members of al-Qaida who had received death sentences, broke out of Iraq's Abu Ghraib jail when comrades launched a military-style assault to free them. The attack began when a suicide bomber drove a car packed with explosives into prison gates.[297] James F. Jeffrey, the United States ambassador in Baghdad when the last American troops exited, said the assault and resulting escape "will provide seasoned leadership and a morale boost to Al Qaeda and its allies in both Iraq and Syria ... it is likely to have an electrifying impact on the Sunni population in Iraq, which has been sitting on the fence."[298]
By mid-2014 the country was in chaos with a new government yet to be formed following national elections, and the insurgency reaching new heights. In early June 2014 the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIS) took over the cities of Mosul and Tikrit and said it was ready to march on Baghdad, while Iraqi Kurdish forces took control of key military installations in the major oil city of Kirkuk. Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki asked his parliament to declare a state of emergency that would give him increased powers, but the lawmakers refused.[299]
In the summer of 2014 President Obama announced the return of U.S. Forces to Iraq, but only in the form of aerial support, in an effort to halt the advance of ISIS forces, render humanitarian aid to stranded refugees and stabilize the political situation.[300] On 14 August 2014, Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki succumbed to pressure at home and abroad to step down. This paved the way for Haidar al-Abadi to take over On 19 August 2014. In what was claimed to be revenge for the aerial bombing ordered by President Obama, ISIS, which by this time had changed their name to the Islamic State, beheaded an American journalist, James Foley, who had been kidnapped two years previously. Despite U.S. bombings and breakthroughs on the political front, Iraq remained in chaos with the Islamic State consolidating its gains, and sectarian violence continuing unabated. On 22 August 2014, suspected Shia militants opened fire on a Sunni mosque during Friday prayers, killing 70 worshippers. Separately, Iraqi forces in helicopters killed 30 Sunni fighters in the town of Dhuluiya.[301] A day later, apparently in retaliation for the attack on the mosque, three bombings across Iraq killed 35 people.[302]
Casualty estimates
Main article: Casualties of the Iraq War
See also: Foreign hostages in Iraq and Suicide bombings in Iraq since 2003
Wounded U.S. personnel flown from Iraq to Ramstein, Germany, for medical treatment (February 2007).
Marines unload a wounded comrade from an Army UH-60 Blackhawk helicopter for medical treatment at Al Qaim.
There have been several attempts by the media, coalition governments and others to estimate the Iraqi casualties. The table below summarizes some of these estimates and methods.
| Source | Iraqi casualties | March 2003 to ... |
|---|---|---|
| Iraq Family Health Survey | 151,000 violent deaths. | June 2006 |
| Lancet survey | 601,027 violent deaths out of 654,965 excess deaths. | June 2006 |
| Opinion Research Business survey | 1,033,000 violent deaths from the conflict. | August 2007 |
| Iraqi Health Ministry | 87,215 violent deaths per death certificates issued. Deaths prior to January 2005 unrecorded. Ministry estimates up to 20% more deaths are undocumented. |
January 2005 to February 2009 |
| Associated Press | 110,600 violent deaths. Health Ministry death certificates plus AP estimate of casualties for 2003–2004. |
April 2009 |
| Iraq Body Count | 105,052–114,731 violent civilian deaths. compiled from commercial news media, NGO and official reports. Over 162,000 civilian and combatant deaths |
January 2012 |
| WikiLeaks. Classified Iraq war logs | 109,032 violent deaths including 66,081 civilian deaths. | January 2004 to December 2009 |
Criticism and cost
Further information: Criticism of the Iraq War, Opposition to the Iraq War, Legitimacy of the 2003 invasion of Iraq, Legality of the Iraq War, Views on the 2003 invasion of Iraq, Protests against the Iraq War, American popular opinion on invasion of Iraq, Governmental positions on the Iraq War prior to the 2003 invasion of Iraq, Media coverage of the Iraq War and Public relations preparations for 2003 invasion of Iraq
A local memorial in North Carolina in December 2007; U.S. casualty count can be seen in the background.[303]
Both proponents and opponents of the invasion have also criticized the prosecution of the war effort along a number of other lines. Most significantly, critics have assailed the United States and its allies for not devoting enough troops to the mission, not adequately planning for post-invasion Iraq, and for permitting and perpetrating human rights abuses. As the war has progressed, critics have also railed against the high human and financial costs.
States participating in the invasion of Iraq
States in support of an invasion
States in opposition to an invasion
States with an uncertain or no official standpoint
- Legality of the invasion[307][308]
- Human casualties
- Insufficient post-invasion plans, in particular inadequate troop levels (a RAND Corporation study stated that 500,000 troops would be required for success)[309]
- Financial costs with approximately $612 billion spent as of 4/09 the CBO has estimated the total cost of the war in Iraq to the United States will be around $1.9 trillion.[310]
- Adverse effect on US-led global "war on terror"[311][312]
- Damage to U.S.' traditional alliances and influence in the region, especially Israel[313] and Saudi Arabia.[314]
- Endangerment and ethnic cleansing of religious and ethnic minorities by insurgents[177][315][316][317][318]
- Disruption of Iraqi oil production and related energy security concerns (the price of oil has quadrupled since 2002)[319][320]
Financial cost
The financial cost of the war has been more than £4.55 billion ($9 billion) to the UK,[322] and over $845 billion to the US government. According to Nobel Prize-winning economist Joseph E. Stiglitz and Harvard public finance professor Linda Bilmes it costs the United States $720 million a day to wage the Iraq war. This number takes into account the long-term health care for veterans, interest on debt and replacement of military hardware.[323]In March 2013, the total cost of the Iraq War was estimated to have been $1.7 trillion by the Watson Institute of International Studies at Brown University.[324] Critics have argued that the total cost of the war to the US economy is estimated to be from $3 trillion[325] to $6 trillion,[326] including interest rates, by 2053. The upper ranges of these estimates include long-term veterans costs and economic impacts. For example Harvard's public finance expert Linda J. Bilmes has estimated that the long-term cost of providing disability compensation and medical care to US troops injured in the Iraq conflict will reach nearly $1 trillion over the next 40 years. [327]
A CNN report noted that the United States-led interim government, the Coalition Provisional Authority lasting until 2004 in Iraq had lost $8.8 billion in the Development Fund for Iraq. In June 2011, it was reported by CBS News that $6 billion in neatly packaged blocks of $100 bills was air-lifted into Iraq by the George W. Bush administration, which flew it into Baghdad aboard C‑130 military cargo planes. In total, the Times says $12 billion in cash was flown into Iraq in 21 separate flights by May 2004, all of which has disappeared. An inspector general's report mentioned that "'Severe inefficiencies and poor management' by the Coalition Provisional Authority would leave no guarantee that the money was properly used", said Stuart W. Bowen, Jr., director of the Office of the Special Inspector General for Iraq Reconstruction. "The CPA did not establish or implement sufficient managerial, financial and contractual controls to ensure that funds were used in a transparent manner."[328] Bowen told the Times the missing money may represent "the largest theft of funds in national history."[329]
Humanitarian crises
Main articles: Humanitarian crises of the Iraq War and Refugees of Iraq
Child killed by a car bomb in Kirkuk, July 2011
As of 2011, nearly 3 million Iraqis have been displaced, with 1.3 million within the Iraq and 1.6 million in neighboring countries, mainly Jordan and Syria.[338] More than half of Iraqi Christians have fled to neighboring countries since the start of the war.[339][340]
The Foreign Policy Association reported that "Perhaps the most perplexing component of the Iraq refugee crisis...has been the inability for the United States to absorb more Iraqis following the 2003 invasion of the country. To date, the United States has granted around 84,000 Iraqis refugee status, of the more than two million global Iraqi refugees. By contrast, the United States granted asylum to more than 100,000 Vietnamese refugees during the Vietnam War."[341][342][343]
Human rights abuses
Main articles: Human rights in post-invasion Iraq and Suicide bombings in Iraq since 2003
|
|
This article is in a list format that may be better presented using prose. (July 2013) |
Iraqi government
- The use of torture by Iraqi security forces.[344]
- Iraqi police from the Interior Ministry accused of forming Death Squads and committing numerous massacres and tortures of Sunni Arabs[345] and the police collusion with militias in Iraq have compounded the problems.
Coalition forces and private contractors
This photograph from Abu Ghraib released in 2006 shows several naked Iraqis in hoods, of whom one has the words "I'm a rapeist" [sic] written on his hip.
- Abu Ghraib torture and prisoner abuse by U.S. Army personnel.[346]
- Haditha killings of 24 civilians (ongoing with some charges dropped)
- White phosphorus use in Iraq
- Murder of an Iraqi girl and her family.[347]
- The torture and killing of prisoner of war, Iraqi Air Force commander, Abed Hamed Mowhoush
- The killing of Baha Mousa
- Mukaradeeb wedding party massacre[348] where 42 civilians were allegedly killed by coalition forces.
- Planting weapons on noncombatant, unarmed Iraqis by three U.S. Marines after killing them.[349][350] According to a report by The Nation, other similar acts have been witnessed by U.S. soldiers.[351] Members of Iraq Veterans Against the War tell similar stories.[dubious ][352]
- Blackwater Baghdad shootings
- Allegations of beatings, electrocution, mock executions, and sexual assault by British troops were presented to the International Criminal Court (ICC) by Public Interest Lawyers (PIL) and the European Center for Constitutional and Human Rights (ECCHR) on 12 January 2014.[353]
Insurgent groups
Main article: Iraq War insurgent attacks
Further information: List of massacres of the Iraq War, List of suicide bombings in Iraq since 2003, and Tactics of the Iraqi insurgency
Car bombings are a frequently used tactic by insurgents in Iraq.
- Killing over 12,000 Iraqis from January 2005 to June 2006, according to Iraqi Interior Minister Bayan Jabr, giving the first official count for the victims of bombings, ambushes and other deadly attacks.[354] The insurgents have also conducted numerous suicide attacks on the Iraqi civilian population, mostly targeting the majority Shia community.[355][356] An October 2005 report from Human Rights Watch examines the range of civilian attacks and their purported justification.[357]
- Attacks against civilians including children through bombing of market places and other locations reachable by suicide bombers.
- Attacks against civilians by sectarian death squads primarily during the Iraqi Civil war.
- Attacks on diplomats and diplomatic facilities including; the bombing of the UN headquarters in Baghdad in August 2003 killing the top UN representative in Iraq and 21 other UN staff members;[358] beheading several diplomats: two Algerian diplomatic envoys Ali Belaroussi and Azzedine Belkadi,[359] Egyptian diplomatic envoy al-Sherif,[360] and four Russian diplomats.[361]
- The February 2006 bombing of the al-Askari Mosque, destroying one of the holiest Shiite shrines, killing over 165 worshipers and igniting sectarian strife and reprisal killings.[362]
- The publicised killing of several contractors; Eugene Armstrong, Jack Hensley, Kenneth Bigley, Ivaylo Kepov and Georgi Lazov (Bulgarian truck drivers.)[363] Other non-military personnel murdered include: translator Kim Sun-il, Shosei Koda, Fabrizio Quattrocchi (Italian), charity worker Margaret Hassan, reconstruction engineer Nick Berg, photographer Salvatore Santoro (Italian)[364] and supply worker Seif Adnan Kanaan (Iraqi.) Four private armed contractors, Scott Helvenston, Jerko Zovko, Wesley Batalona and Michael Teague, were killed with grenades and small arms fire, their bodies dragged from their vehicles, beaten and set ablaze. Their burned corpses were then dragged through the streets before being hung over a bridge crossing the Euphrates.[365]
- Torture or killing of members of the New Iraqi Army,[366] and assassination of civilians associated with the Coalition Provisional Authority, such as Fern Holland, or the Iraqi Governing Council, such as Aqila al-Hashimi and Ezzedine Salim, or other foreign civilians, such as those from Kenya.[367]
Public opinion on the war
Main article: Public opinion on the Iraq War
International opinion
According to a January 2007 BBC World Service poll of more than 26,000 people in 25 countries, 73% of the global population disapproved of U.S. handling of the Iraq War.[368] A September 2007 poll conducted by the BBC found that two-thirds of the world's population believed the U.S. should withdraw its forces from Iraq.[369]In 2006 it was found that majorities in the UK and Canada believed that the war in Iraq was "unjustified" and – in the UK – were critical of their government's support of U.S. policies in Iraq.[370]
According to polls conducted by the Arab American Institute, four years after the invasion of Iraq, 83% of Egyptians had a negative view of the U.S. role in Iraq; 68% of Saudi Arabians had a negative view; 96% of the Jordanian population had a negative view; 70% of the population of the United Arab Emirates and 76% of the Lebanese population also described their view as negative.[371] The Pew Global Attitudes Project reports that in 2006 majorities in the Netherlands, Germany, Jordan, France, Lebanon, Russia, China, Canada, Poland, Pakistan, Spain, Indonesia, Turkey, and Morocco believed the world was safer before the Iraq War and the toppling of Saddam, while pluralities in the United States and India believe the world is safer without Saddam Hussein.[372]
Iraqi opinion
A woman pleads with an Iraqi army soldier from 2nd Company, 5th Brigade, 2nd Iraqi Army Division to let a suspected insurgent free during a raid near Tafaria, Iraq
Relation to the Global War on Terrorism
Main article: Iraq War and U.S. Global War on Terror
Further information: Criticism of the War on Terrorism, Saddam Hussein and al-Qaeda and Saddam Hussein and al-Qaeda timeline
Former President George W. Bush consistently referred to the Iraq war as "the central front in the War on Terror", and argued that if the United States pulled out of Iraq, "terrorists will follow us here".[379][380][381]
While other proponents of the war have regularly echoed this assertion,
as the conflict has dragged on, members of the US Congress, the
US public, and even US troops have questioned the connection between
Iraq and the fight against anti-US terrorism. In particular, a consensus
has developed among intelligence experts that the Iraq war has
increased terrorism. Counterterrorism expert Rohan Gunaratna frequently refers to the invasion of Iraq as a "fatal mistake".[382]London's conservative International Institute for Strategic Studies concluded in 2004 that the occupation of Iraq had become "a potent global recruitment pretext" for Mujahideen and that the invasion "galvanised" al-Qaeda and "perversely inspired insurgent violence" there.[383] The US National Intelligence Council concluded in a January 2005 report that the war in Iraq had become a breeding ground for a new generation of terrorists; David Low, the national intelligence officer for transnational threats, indicated that the report concluded that the war in Iraq provided terrorists with "a training ground, a recruitment ground, the opportunity for enhancing technical skills ... There is even, under the best scenario, over time, the likelihood that some of the jihadists who are not killed there will, in a sense, go home, wherever home is, and will therefore disperse to various other countries." The Council's chairman Robert Hutchings said, "At the moment, Iraq is a magnet for international terrorist activity."[384] And the 2006 National Intelligence Estimate, which outlined the considered judgment of all 16 US intelligence agencies, held that "The Iraq conflict has become the 'cause celebre' for jihadists, breeding a deep resentment of U.S. involvement in the Muslim world and cultivating supporters for the global jihadist movement."[385]
Foreign involvement
Role of Saudi Arabia and non-Iraqis
See also: Saudi Arabia and terrorism
According to studies, most of the suicide bombers in Iraq are foreigners, especially Saudis.[386][387][388]Iranian involvement
Although some military intelligence analysts have concluded there is no concrete evidence, U.S. Major General Rick Lynch has claimed that Iran has provided training, weapons, money, and intelligence to Shiite insurgents in Iraq and that up to 150 Iranian intelligence agents, plus members of the Iranian Revolutionary Guard are believed to be active in Iraq at any given time.[389][390] Lynch thinks that members of the Iranian Quds Force and the Iranian Revolutionary Guard have trained members of the Qazali terror network in explosives technology and also provided the network with arms, munitions, and military advisors. Many explosive devices, including improvised explosives (IEDs) and explosively-formed projectiles (EFPs), used by insurgents are claimed by Lynch to be Iranian-made or designed.According to two unnamed US officials, the Pentagon is examining the possibility that the Karbala provincial headquarters raid, in which insurgents managed to infiltrate an American base, kill five US soldiers, wound three, and destroy three humvees before fleeing, was supported by Iranians. In a speech on 31 January 2007, Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki stated that Iran was supporting attacks against Coalition forces in Iraq[391] and some Iraqis suspect that the raid may have been perpetrated by the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps's Qods Force in retaliation for the detention of five Iranian officials by U.S. forces in the northern Iraqi city of Irbil on 11 January.[392][393]
Michael Weiss and Dexter Filkins have described the extensive involvement of Iranian Quds Force commander Qasem Suleimani in arming and training both Sunni and Shi'ite militias in Iraq. According to Weiss, Iranian strategy was designed to prevent the Iraqi government from functioning so that Iran could exert greater control over the country under the guise of providing stability. Weiss also traced the origins of al Qaeda in Iraq, which entered Iraqi Kurdistan through Iran, to covert Iranian operations to destabilize the Iraqi government of Saddam Hussein.[394] According to a Western diplomat quoted by Filkins: "Suleimani wanted to bleed the Americans, so he invited in the jihadis, and things got out of control."[395] In 2011, US ambassador James Jeffrey stated that Iranian proxies were responsible for roughly one-fourth of US casualties in Iraq.[396]
See also
Footnotes
- The conflict is also known as the War in Iraq, the Occupation of Iraq, the Second Gulf War, Gulf War II, and Gulf War 2. The period of the war lasting from 2003 to 2010 was referred to as Operation Iraqi Freedom by the United States military.
References
- Chulov, Martin (2011-07-28). "Qassem Suleimani: the Iranian general 'secretly running' Iraq". The Guardian. Retrieved 2014-08-20.
Further reading
- Bellavia, David (2007). House to House: An Epic Memoir of War. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-1416574712.
- Dexter Filkins, "General Principles", New Yorker, 17 December 2012, pp. 76–81.
- Gates, Robert M. (2014). Duty: Memoirs of a Secretary at War. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 9780307959478. 318 pages
- Gordon, Michael R. (2006). Cobra II: The Inside Story of the Invasion and Occupation of Iraq. Pantheon. ISBN 978-1557782328.
- Larson, Luke S. (2008). Senator's Son: An Iraq War Novel. Phoenix, Arizona: Key Edition Incorporated. ISBN 978-1449969868.
- North, Richard (2009). Ministry of Defeat: The British War in Iraq 2003–2009. Continuum Publishing Corporation. ISBN 978-1441169976.
- Bruce R. Pirnie; Edward O'Connell (2008). Counterinsurgency in Iraq (2003–2006). Santa Monico, CA: Rand Corporation. ISBN 978-0-8330-4297-2.
- Thomas E. Ricks (2006). Fiasco: The American Military Adventure in Iraq. Penguin. ISBN 9781594201035.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Iraq War. |
| Wikinews has news related to: |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Iraq War |
- Electronic Iraq Daily news and analysis from Iraq with a special focus on the Iraqi experience of war
- News from Iraq: Aggregated news on the war, including politics and economics.
- Dollar cost of war: total U.S. cost of the Iraq War
- "Bleak Pentagon study admits 'civil war' in Iraq", by Rupert Cornwell, The Independent, March 2007
- High resolution maps of Iraq, GulfWarrior.org
- Presidential address by George W. Bush on the evening of 19 March 2003, announcing war against Iraq.
- Bibliography: The Second U.S. – Iraq War (2003– )
- "1st Major Survey of Iraq". Zogby International, 10 September 2003.
- Iraq at Polling Report.com. Chronological polls of Americans 18 and older
- Just War in Iraq 2003 pdf Legal dissertation by Thomas Dyhr from University of Copenhagen.
- Iraq war stories, a Guardian and Observer archive in words and pictures documenting the human and political cost, The Guardian, April 2009.
- Iraq: The War Card. Center for Public Integrity.
- Jargin SV. Health care in Iraq: 2013 vs. 2003. CMAJ September 17, 2013 http://www.cmaj.ca/content/181/9/576.figures-only/reply#cmaj_el_716427
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
|||
Categories:
- Iraq War
- 2003 in Iraq
- 2004 in Iraq
- 2005 in Iraq
- 2006 in Iraq
- 2007 in Iraq
- 2008 in Iraq
- 2009 in Iraq
- 2010 in Iraq
- 2011 in Iraq
- Conflicts in 2003
- Conflicts in 2004
- Conflicts in 2005
- Conflicts in 2006
- Conflicts in 2007
- Conflicts in 2008
- Conflicts in 2009
- Conflicts in 2010
- Conflicts in 2011
- George W. Bush administration controversies
- Iraq–United States relations
- Imperialism
- Iraq War legal issues
- Modern history of Iraq
- Occupation of Iraq
- Politics of Iraq
- Wars involving the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
- Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
- War on Terror
- Wars involving Iraq
- Wars involving the United Kingdom
- Wars involving the United States
- Wars involving Poland
- Wars involving Australia
- Wars involving Romania
- Wars involving El Salvador
- Wars involving Estonia
- Wars involving Albania
- Wars involving Moldova
- Wars involving Ukraine
- Wars involving Bulgaria
- Wars involving Denmark
- Wars involving Armenia
- Wars involving Azerbaijan
- Wars involving Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Wars involving the Czech Republic
- Wars involving Latvia
- Wars involving Singapore
- Wars involving South Korea
- Wars involving the Republic of Macedonia
- Wars involving Kazakhstan
- Wars involving Tonga
- Wars involving Georgia (country)
- Wars involving Mongolia
- Wars involving Slovakia
- Wars involving Norway
- Wars involving Lithuania
- Wars involving Italy
- Wars involving the Netherlands
- Wars involving Portugal
- Wars involving Japan
- Wars involving New Zealand
- Wars involving Iceland
- Wars involving Nicaragua
- Wars involving the Dominican Republic
- Wars involving Spain
- Wars involving the Philippines
- Wars involving Honduras
- Wars involving Thailand
|chapter= ignored (help)|chapter= ignored (help) "Iraq was prohibited from possessing tubes composed of 7075 T6 aluminum alloy with outer diameters exceeding 75 mm under Annex III to United Nations Security Council Resolution 687 because of their potential use in gas centrifuges."From three Iraqi defectors we know that Iraq, in the late 1990s, had several mobile biological weapons labs. These are designed to produce germ warfare agents, and can be moved from place to a place to evade inspectors. Saddam Hussein has not disclosed these facilities. He's given no evidence that he has destroyed them.
NBC News later quoted U.S. military officials as saying that the unreleased photographs showed American soldiers “severely beating an Iraqi prisoner nearly to death, having sex with a female Iraqi prisoner, and ‘acting inappropriately with a dead body.’ The officials said there also was a videotape, apparently shot by U.S. personnel, showing Iraqi guards raping young boys.”
Iraq War - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iraq_WarCachedThe Iraq War was a protracted armed conflict that began with the 2003 invasion of Iraq led by the United States. The invasion toppled the government of Saddam Hussein.














































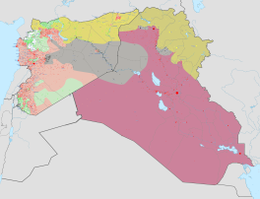



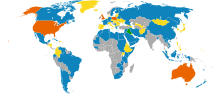
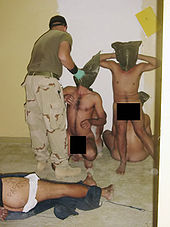


No comments:
Post a Comment