The
Syrian Civil War also, also known as the
Syrian Uprising (Arabic: الثورة السورية ), is an ongoing armed conflict taking place in
Syria. The unrest ...
Syrian Civil War
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Syrian civil war)
| Syrian Civil War |
Part of the Arab Spring and Arab Winter
Spillover of the Iraqi insurgency |
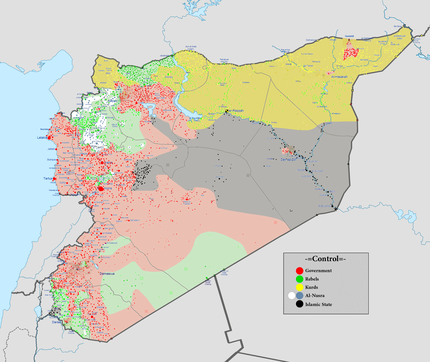
Current military situation: Red: government, Green: rebels, Yellow: Kurds (Rojava), Grey: Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, White: al-Nusra Front
(for a more detailed map, see Cities and towns during the Syrian Civil War). |
| Date |
15 March 2011 – present
(4 years, 3 months and 1 day) |
| Location |
Syria (with spillovers in neighboring countries) |
| Status |
Ongoing |
|
| Main belligerents |
Allied militias
 Iran Iran
Supported by:
 Russia[2][3] Russia[2][3]
 North Korea[4] North Korea[4] |
 Opposition
Supported by: Opposition
Supported by:
 Qatar Qatar
 Saudi Arabia Saudi Arabia
 Turkey[5][6] Turkey[5][6]
 United States[7] United States[7]
 France[8] France[8]
 Libya[Ω][9] Libya[Ω][9]
 al-Nusra Front al-Nusra Front
Muhajirin wa-Ansar
Jabhat Ansar al-Din |
|
 Peshmerga Allied militias Peshmerga Allied militias
See: Rojava conflict
 CJTF–OIR CJTF–OIR
|
| Commanders and leaders |
|
|
|
|
|
| Strength |
Syrian Armed Forces: 178,000[30]
General Security Directorate: 8,000[32]
National Defense Force: 80,000[33]
Iran: 15,000[34]
Ba'ath Brigades: 7,000[35][36]
al-Abbas brigade: 10,000[37] (8,000 Iraqis)[38]
Hezbollah: 3,000–5,000[39]
Syrian Resistance: 2,000[40] |
FSA: 40,000–50,000[41]
Islamic Front: 40,000–70,000[42]
Ajnad al-Sham Union: up to 15,000
AD Front: 13,000[43]
Army of Mujahedeen: 5,000[44]–12,000[45]
Sham Legion:2,000+[46]
al-Nusra Front: 13,000[47][48]
Muhajirin wa-Ansar: 7,000
Jabhat Ansar al-Din 1,500+ |
31,500[49]–100,000[50] |
People's Protection Units (YPG): 65,000[51]
Jabhat al-Akrad: 7,000[52] |
| Casualties and losses |
Syrian Government: 49,106–84,106 soldiers killed[53][54]
32,533–46,533 militiamen killed[53][54]
1,000 government officials killed[55]
7,000 soldiers and militiamen and 2,000 supporters captured[53]
Hezbollah:
838 killed[53]
Other non-Syrian fighters:
2,844 killed[53] |
72,363–113,363 fighters killed[‡]
979 protesters killed[56]
25,500 fighters and supporters captured or missing[53] |
7,377–9,078 killed (per SOHR; certain events January 2014–May 2015)[57]
4,800+ killed (per SAA; conflict with the Syrian gov. September–December 2014)[58] |
1,236–1,405 fighters killed[59] |
69,494[53]–84,268[60] (2,996 foreign) civilian deaths documented by opposition
75 other foreign soldiers killed
Total killed:
230,620–320,620 (June 2015 SOHR estimate)[53]
220,000 (January 2015 UN estimate)[61]
130,000 captured or missing overall[62]
4.5 million (UN, Sep 2013) – 5.1 million (iDMC, Sep 2013) internally displaced[63][64][65]
Over 3,420,000 refugees (by February 2015)[66][67][68]
* Also aligned with Syrian opposition forces[69][70][71]
Ω Due to the ongoing Second Libyan Civil War, there are two governments in charge of the country. The Council of Deputies (Tobruk) is the government aiding the Syrian opposition.
‡ Number includes Kurdish and ISIL fighters, whose deaths are also listed in their separate columns[72][53][54] |
The
Syrian Civil War (
Arabic:
الحرب الأهلية السورية), also known as the
Syrian Revolution (
Arabic:
الثورة السورية), is an ongoing armed conflict taking place in
Syria. The
unrest began in the early spring of 2011 within the context of
Arab Spring protests, with nationwide protests against President
Bashar al-Assad's
government, whose forces responded with violent crackdowns. The
conflict gradually morphed from prominent protests to an armed rebellion
after months of military sieges.
[73]
The armed opposition consists of various groups that were formed during the course of the conflict, primarily the
Free Syrian Army, which was the first to take up arms in 2011, and the
Islamic Front formed in 2013. In 2013,
Hezbollah entered the war in support of the Syrian army.
[74][75] In the east, the
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), a jihadist militant group originating from
Iraq, made rapid military gains in both Syria
and Iraq, eventually
conflicting
with the other rebels. By July 2014, ISIL controlled a third of Syria's
territory and most of its oil and gas production, thus establishing
itself as the major opposition force.
[76]
By July 2013, the Syrian government was in control of approximately
30–40% of the country's territory and 60% of the Syrian population.
[77] A United Nations report in late 2012 described the conflict as being "overtly
sectarian in nature", between mostly
Alawite government forces, militias and other
Shia groups
[78] fighting largely against
Sunni-dominated rebel groups,
[79][80] although both opposition and government forces have denied it.
[81][82] Due to
foreign involvement this conflict has been called a
proxy war.
[83]
As of January 2015 the death toll had risen above 220,000,
[84] with estimates in April 2015 as high as 310,000.
[85]
International organizations have accused the Syrian government, ISIS
and other opposition forces of severe human rights violations, with
many massacres occurring.
[86][87][88][89][90] Chemical weapons have been
used many times during the conflict as well.
[91][92] [93]
The Syrian government is reportedly responsible for the majority of
civilian casualties, at least those before September 2014, often through
bombings.
[86][88][94] In addition, tens of thousands of protesters and activists have been imprisoned and there are reports of
torture in state prisons.
[95][96][97][98]
The severity of the humanitarian disaster in Syria has been outlined
by the UN and many international organizations. More than 6.5 million
Syrians have been displaced, almost 4 million Syrians have fled the
country to countries such as
Turkey,
Lebanon,
Jordan,
Iraq, and
Egypt and become
refugees, and millions more have been left in poor living conditions with shortages of food and drinking water.
Background
Assad government
Syria became an independent republic in 1946, although democratic
rule was ended by a coup in March 1949, followed by two more coups that
same year.
[99][100] A popular
uprising against military rule in 1954 saw the army transfer power to civilians; from 1958 to 1961 a
brief union with Egypt replaced Syria's parliamentary system with a highly centralized presidential regime.
[101] The
Ba'ath Syrian Regional Branch government came to power in 1963 after
a successful coup d'état. In 1966,
another coup overthrew the traditional leaders of the party,
Michel Aflaq and
Salah al-Din al-Bitar.
[102] General
Hafez al-Assad, the
Minister of Defense, seized power in a "
corrective revolution" in November 1970, becoming
Prime Minister. In March 1971, Assad declared himself
President,
a position that he held until his death in 2000. Since then, the
secular Syrian Regional Branch has remained the dominant political
authority in what is virtually a
single-party state in Syria; Syrian citizens may only approve the President by
referendum and – until the government-controlled multi-party
2012 parliamentary election – could not vote in multi-party elections for the legislature.
[103]
Bashar al-Assad, the President of Syria and
Asma al-Assad, his wife – who is a British-born and British-educated Sunni Muslim,
[104] initially inspired hopes for democratic and state reforms and a "
Damascus Spring" of intense social and political debate took place between July 2000 and August 2001.
[105] The period was characterized by the emergence of numerous political forums or
salons, where groups of like-minded people met in private houses to debate political and social issues. Political activists such as
Riad Seif,
Haitham al-Maleh,
Kamal al-Labwani,
Riyad al-Turk and
Aref Dalila were important in mobilizing the movement.
[106] The most famous of the forums were the
Riad Seif Forum and the
Jamal al-Atassi
Forum. The Damascus Spring largely ended in August 2001 with the arrest
and imprisonment of ten leading activists who had called for democratic
elections and a campaign of civil disobedience.
[107]
From 2001 even reformists in Parliament had begun to criticize the
legacy of stagnation since the rule of former President Hafez al-Assad;
Bashar al-Assad has talked about reform but carried out very little, and
he has failed to deliver on promised reforms since 2000, analysts say.
[108]
Demographics
Ethno-religious composition of people of Syria (% of 22,538,256)
[109][110]
The
Assad family comes from the minority
Alawite religious group, an offshoot of
Shi'ite Islam that comprises an estimated 12 percent of the total
Syrian population.
[111] It has maintained tight control on Syria's security services,
[112] generating resentment among some
Sunni Muslims,
[113] a religious group that makes up about three-quarters of Syria's population. Ethnic minority
Syrian Kurds have also protested and complained over ethnic discrimination and denial of their cultural and language rights.
[114][115] Assad's younger brother
Maher al-Assad commands the
army's elite
Fourth Armoured Division, and his brother-in-law,
Assef Shawkat, was the deputy minister of defense until the latter's assassination in the
18 July 2012 Damascus bombing.
Socio-economics
Discontent against the government was strongest in Syria's poorer areas, predominantly among conservative Sunnis.
[116] These included cities with high poverty rates, such as
Daraa and
Homs,
rural areas hit hard by a drought in early 2011, and the poorer
districts of large cities. Socio-economic inequality increased
significantly after free market policies were initiated by Hafez
al-Assad in his later years, and accelerated after Bashar al-Assad came
to power. With an emphasis on the
service sector,
these policies benefited a minority of the nation's population, mostly
people who had connections with the government, and members of the Sunni
merchant class of Damascus and Aleppo.
[116] By 2011, Syria was facing a deterioration in the national standard of living and steep rises in the prices of commodities.
[117] The country also faced particularly high youth unemployment rates.
[118]
Human rights
The state of human rights in Syria has long been the subject of harsh criticism from global organizations.
[119] The country was under
emergency rule from 1963 until 2011, banning public gatherings of more than five people,
[120] and effectively granting security forces sweeping powers of arrest and detention.
[121] Bashar al-Assad is widely regarded as having been unsuccessful in implementing democratic change, with a 2010 report from
Human Rights Watch
stating that he had failed to substantially improve the state of human
rights since taking power, although some minor aspects had seen
improvement.
[122]
In December 2010, mass anti-government protests began in Tunisia and later spread across other parts of the
Arab world, including
Syria. By February 2011, revolutions occurred in Tunisia and Egypt, while Libya began to experience
its own civil war.
Numerous other Arab countries also faced protests, with some attempting
to calm the masses by making concessions and governmental changes. The
uprisings in Tunisia and Egypt are supposed to have inspired the
mid-March 2011 protests in Syria.
[123]
Rights of
free expression,
association and
assembly were strictly controlled in Syria even before the uprising.
[124] The authorities harass and imprison
human rights activists and other critics of the government, who are often indefinitely detained and
tortured in poor prison conditions.
[124] Women and
ethnic minorities have faced discrimination in the public sector.
[124] Thousands of
Syrian Kurds were denied citizenship in 1962 and their descendants continued to be labeled as "foreigners".
[125] A number of riots in 2004 prompted increased tension in Syria's Kurdish areas,
[126][127] and there have been occasional clashes between Kurdish protesters and security forces ever since.
Course of events
Anti-Assad protests in Baniyas, April 2011
Protests, civil uprising, and defections (January – July 2011)
Small protests began in Syria on 28 January 2011. Mass protests
erupted on 15 March in Damascus and Aleppo, and spread in the following
days to more cities, while growing in size. The week of 15–21 March is
considered by news media as the beginning of the Syrian uprising. On 18
March, the protests turned bloody when the Syrian government reacted
with deadly violence. On 20 March in Daraa, after security forces opened
fire on the protesting crowd, protesters burned the local Ba'ath Party
headquarters, the town’s courthouse and a telephone company building.
That day 15 demonstrators and 7 policemen were killed in Daraa. By 25
March, 90 civilians and 7 policemen had been killed in Syria. In his 30
March 2011 speech addressing the protests, Assad claimed that
conspirators and foreign powers sought to topple his government.
The protesters' demands until 7 April were predominantly democratic
reforms, release of political prisoners, more freedom, abolition of
emergency law and an end to corruption. After 8 April, the emphasis in
demonstration slogans gradually shifted towards the call for
overthrowing the Assad government. Protests spread: on Friday 8 April,
they occurred simultaneously in ten cities. By Friday 22 April protests
occurred in twenty cities. On 25 April, the
Syrian Army
started a series of large-scale deadly military attacks on towns, using
tanks, infantry carriers, and artillery, leading to hundreds of
civilian deaths. By the end of May 2011, 1,000 civilians
[128] and 150 soldiers and policemen
[129] had been killed and thousands detained;
[130] among the arrested were many students, liberal activists and human rights advocates.
[131]
Significant armed rebellion against the state began on 4 June in
Jisr al-Shugur, a city in
Idlib Governorate
near the Turkish border, after security forces on a post office roof
had fired at a funeral demonstration. Protesting mourners set fire to
the building, killing eight security officers, and then overran a police
station, seizing weapons from it. Violence continued and escalated over
the following days. Unverified reports claim that a portion of the
security forces in Jisr defected after secret police and intelligence
officers executed soldiers who had refused to fire on civilians.
[132] Later, more protesters in Syria took up arms, and more soldiers defected to protect protesters.
Both sides in the conflict used propaganda to promote their own righteousness and their opponents' wickedness (see
Reporting, censoring and propaganda in the Syrian Civil War). By the end of July 2011, around 1,600 civilians and 500 security forces had been killed and 13,000 arrested.
Protests and armed insurgency (July – October 2011)
An
FSA fighter engaged in a firefight in Aleppo
On 29 July 2011, seven defecting Syrian officers formed the
Free Syrian Army (FSA), composed of defected
Syrian Armed Forces officers and soldiers, aiming "to bring this regime [= the Assad government] down" with united opposition forces.
[133][134]
On 31 July, a nationwide crackdown nicknamed the "Ramadan Massacre"
resulted in the death of at least 142 people and hundreds of injuries.
[135]
An FSA fighter walking among rubble in Aleppo, October 2012
On 23 August, a coalition of anti-government groups was formed, the
Syrian National Council.
The group, based in Turkey, attempted to organize the opposition.
However, the opposition, including the FSA, remained a fractious
collection of political groups, longtime exiles, grass-roots organizers
and armed militants, divided along ideological, ethnic or sectarian
lines.
[136]
Throughout August, Syrian forces stormed major urban centres and
outlying regions, and continued to attack protests. On 14 August, the
Siege of Latakia continued as the
Syrian Navy became involved in the military crackdown for the first time.
Gunboats fired
heavy machine guns at waterfront districts in Latakia, as ground troops and security agents backed by armour stormed several neighbourhoods.
[137] The
Eid ul-Fitr
celebrations, started in near the end of August, were muted after
security forces fired on protesters gathered in Homs, Daraa, and the
suburbs of Damascus.
[138]
By September 2011, organized units of Syrian rebels were engaged in
an active insurgency campaign in multiple areas of Syria. A major
confrontation between the FSA and the Syrian armed forces
occurred in Rastan.
From 27 September to 1 October, Syrian government forces, backed by
tanks and helicopters, led a major offensive on the town of
Al-Rastan in
Homs Governorate, in order to drive out army defectors.
[139]
The 2011 battle of Rastan between the government forces and the FSA was
the longest and most intense action up until that time. After a week of
fighting, the FSA was forced to retreat from Rastan.
[140] To avoid government forces, the leader of the FSA, Col. Riad Asaad, retreated to the Turkish side of Syrian-Turkish border.
[141] Many of the rebels fled to the nearby city of Homs.
[110]
By October, the FSA started to receive support from Turkey, who allowed the rebel army to operate its
command and headquarters from the country's southern
Hatay Province close to the Syrian border, and its
field command from inside Syria.
[142]
The FSA would often launch attacks into Syria's northern towns and
cities, while using the Turkish side of the border as a safe zone and
supply route. A year after its formation, the FSA gained control over
many towns close to the Turkish border.
In October 2011, clashes between government and defected army units
were being reported fairly regularly. During the first week of the
month, sustained
clashes were reported in Jabal al-Zawiya in the mountainous regions of Idlib Governorate. Syrian rebels captured most of Idlib city as well.
[143] In mid-October, other clashes in Idlib Governorate include the city of
Binnish and the town of
Hass in the governorate near the mountain range of
Jabal al-Zawiya.
[144][145] In late October, other clashes occurred in the northwestern town of
Maarrat al-Nu'man
in the governorate between government forces and defected soldiers at a
roadblock on the edge of the town, and near the Turkish border, where
10 security agents and a deserter were killed in a bus ambush.
[146] It was not clear if the defectors linked to these incidents were connected to the FSA.
[147]
According to defectors, in 2011 the Syrian government intentionally
released imprisoned Islamic radicals and provided them with arms "in
order to make itself the least bad choice for the international
community."
[148][149]
Escalation (November 2011 – March 2012)
Syrian army checkpoint in Douma, January 2012
In early November, clashes between the FSA and security forces in Homs escalated as the
siege
continued. After six days of bombardment, the Syrian Army stormed the
city on 8 November, leading to heavy street fighting in several
neighborhoods. Resistance in Homs was significantly greater than that
seen in other towns and cities, and some in opposition have referred to
the city as the "Capital of the Revolution". Unlike events in Deraa and
Hama, operations in Homs have thus far failed to quell the unrest.
[110]
November and December 2011 saw increasing rebel attacks, as
opposition forces grew in number. In the two months, the FSA launched
deadly attacks on an
air force intelligence complex in the Damascus suburb of
Harasta, the Ba'ath Syrian Regional Branch youth headquarters in
Idlib Governorate, Syrian Regional Branch offices in Damascus,
an airbase in Homs Governorate, and an intelligence building in Idlib.
[150]
On 15 December, opposition fighters ambushed checkpoints and military
bases around Daraa, killing 27 soldiers, in one of the largest attacks
yet on security forces.
[151]
The opposition suffered a major setback on 19 December, when a failed
defection in Idlib governorate lead to 72 defectors killed.
[152]
In January 2012, Assad began using large-scale artillery operations
against the insurgency, which led to the destruction of many civilian
homes due to indiscriminate shelling.
[153][154] By this time, daily protests had dwindled, eclipsed by the spread of armed conflict.
[155] January saw intensified
clashes around the suburbs of Damascus, with the Syrian Army use of tanks and artillery becoming common.
Fighting in Zabadani
began on 7 January when the Syrian Army stormed the town in an attempt
to rout out FSA presence. After the first phase of the battle ended with
a ceasefire on 18 January, leaving the FSA in control of the town,
[156] the FSA launched an offensive into nearby Douma.
Fighting in the town
lasted from 21 to 30 January, before the rebels were forced to retreat
as result of a government counteroffensive. Although, the Syrian Army
managed to retake most of the suburbs, sporadic fighting continued.
[157] Fighting erupted in Rastan
again on 29 January, when dozens of soldiers manning the town's
checkpoints defected and began opening fire on troops loyal to the
government. Opposition forces gained complete control of the town and
surrounding suburbs on 5 February.
[158]
On 3 February, the Syrian army launched
a major offensive
to retake rebel-held neighborhoods. In early March, after weeks of
artillery bombardments and heavy street fighting, the Syrian army
eventually captured the district of Baba Amr, a major rebel stronghold.
The Syrian Army also captured the district of Karm al-Zeitoun by 9
March, where activists said that government forces killed 47 women and
children. By the end of March, the Syrian army retook control of half a
dozen districts, leaving them in control of 70 percent of the city.
[159] By 14 March, Syrian troops successfully
ousted insurgents from the city of Idlib after days of fighting.
[160] By early April, the estimated death toll of the conflict, according to activists, reached 10,000.
[161]
Ceasefire attempt (April – May 2012)
A Syrian soldier manning a checkpoint near Damascus
Kofi Annan was acting as UN–
Arab League Joint Special Representative for
Syria. His peace plan provided for a ceasefire, but even as the
negotiations for it were being conducted, Syrian armed forces attacked a
number of towns and villages, and summarily executed scores of people.
[162]:11 Incommunicado detention, including of children, also continued.
[163] In April, Assad began employing
attack helicopters against rebel forces.
[153]
On 12 April, both sides, the Syrian Government and rebels of the FSA
entered a UN mediated ceasefire period. It was a failure, with
infractions of the ceasefire by both sides resulting in several dozen
casualties. Acknowledging its failure, Annan called for Iran to be "part
of the solution", though the country has been excluded from the Friends
of Syria initiative.
[164]
The peace plan practically collapsed by early June and the UN mission
was withdrawn from Syria. Annan officially resigned in frustration on 2
August 2012.
[165]
Renewed fighting (June – July 2012)
Following the
Houla massacre
of 25 May 2012, in which 108 people were summarily executed and the
consequent FSA ultimatum to the Syrian government, the ceasefire
practically collapsed, as the FSA began nationwide offensives against
government troops. On 1 June, President Assad vowed to crush the
anti-government uprising.
[166]
On 5 June,
fighting broke out in Haffa and nearby villages in the coastal governorate of
Latakia Governorate. Government forces were backed by
helicopter gunships
in the heaviest clashes in the governorate since the revolt began.
Syrian forces seized the territory following days of fighting and
shelling.
[167] On 6 June 78 civilians were killed in the
Al-Qubeir massacre. According to activist sources, government forces started by shelling the village before the
Shabiha militia moved in.
[168]
The UN observers headed to Al-Qubeir in the hope of investigating the
alleged massacre, but they were met with a roadblock and small arms fire
and were forced to retreat.
[169]
After aerial bombardment by the Syrian government of rebel-held areas of
Azaz in Aleppo governorate
On 12 June 2012, the UN for the first time officially proclaimed Syria to be in a state of civil war.
[170]
The conflict began moving into the two largest cities, Damascus and
Aleppo. In both cities, peaceful protests – including a general strike
by Damascus shopkeepers and a small strike in Aleppo were interpreted as
indicating that the historical alliance between the government and the
business establishment in the large cities had become weak.
[171]
On 22 June, a Turkish
F-4 fighter jet was
shot down by Syrian government forces, killing both pilots. Syria and Turkey disputed whether the jet had been flying in Syrian or international
airspace when it was shot down. Despite Turkish Prime Minister
Recep Tayyip Erdoğan's
vows to retaliate harshly against Assad's government, no such
intervention materialised. Bashar al-Assad publicly apologised for the
incident. By 10 July, rebel forces had captured most of the city of
Al-Qusayr, in
Homs Governorate, after weeks of fighting.
[172] By mid-July, rebels had captured the town of
Saraqeb, in Idlib Governorate.
[173]
Battles of Damascus and Aleppo (July – October 2012)
Wounded civilians arrive at a hospital in Aleppo, October 2012.
By mid-July 2012, with fighting spread across the country and 16,000 people killed, the
International Committee of the Red Cross declared the conflict a
civil war.
[174] Fighting in Damascus intensified, with a
major rebel push to take the city.
[175] On 18 July,
Syrian Defense Minister Dawoud Rajiha, former defense minister
Hasan Turkmani, and the president's brother-in-law General
Assef Shawkat were killed by a
suicide bomb attack in Damascus.
[176] The Syrian intelligence chief
Hisham Ikhtiyar, who was injured in the same explosion, later succumbed to his wounds.
[177] Both the FSA and Liwa al-Islam claimed responsibility for the assassination.
[178]
In late July, government forces managed to break the rebel offensive on Damascus, although
fighting still continued in the outskirts. After this, the focus shifted to the
battle for control of Aleppo.
[179]
On 25 July, multiple sources reported that the Assad government was
using fighter jets to attack rebel positions in Aleppo and Damascus,
[180] and on 1 August, UN observers in Syria witnessed government fighter jets firing on rebels in Aleppo.
[181]
In early August, the Syrian Army recaptured Salaheddin district, an
important rebel stronghold in Aleppo. In August, the government began
using fixed-wing warplanes against the rebels.
[153][154]
On 19 July, Iraqi officials reported that the FSA had gained control
of all four border checkpoints between Syria and Iraq, increasing
concerns for the safety of Iraqis trying to escape the violence in
Syria.
[182] On 19 September, rebel forces seized a border crossing between Syria and Turkey in
Ar-Raqqah Governorate. It was speculated that this crossing could provide opposition forces with strategic and logistical advantages.
[183]
In late September, the FSA moved its command headquarters from southern Turkey into northern Syria.
[184] On 9 October, rebel forces
seized control of Maarat al-Numan, a town in Idlib governorate on the highway linking Damascus with Aleppo.
[185] By 18 October, the FSA had captured
Douma, the biggest suburb of Damascus.
[186] Lakhdar Brahimi arranged for a ceasefire during Eid al-Adha in late October, but it quickly collapsed.
[187]
Rebel offensives (November 2012 – April 2013)
After Brahimi's ceasefire agreement ended on 30 October, the Syrian
military expanded its aerial bombing campaign in Damascus. A bombing of
the Damascus district of Jobar was the first instance of a
fighter jet
being used to bomb Damascus. The following day, Gen. Abdullah Mahmud
al-Khalidi, a Syrian Air Force commander, was assassinated by opposition
gunmen in the Damascus district of Rukn al-Din.
[188] In early November 2012, rebels made significant gains in northern Syria. The rebel capture of
Saraqib in Idlib governorate, which lies on the M5 highway, further isolated Aleppo.
[189]
Due to insufficient anti-aircraft weapons, rebel units attempted to
nullify the government's air power by destroying landed helicopters and
aircraft on air bases.
[190] On 3 November, rebels launched an attack on the
Taftanaz air base.
[191]
On 18 November, rebels
took control of Base 46 in the
Aleppo Governorate,
one of the Syrian Army's largest bases in northern Syria, after weeks
of intense fighting. Defected General Mohammed Ahmed al-Faj, who
commanded the assault, stated that nearly 300 Syrian troops had been
killed and 60 had been captured, with rebels seizing large amounts of
heavy weapons, including tanks.
[192] On 22 November, rebels captured the
Mayadeen military base in the country's eastern
Deir ez-Zor Governorate. Activists said this gave the rebels control of a large amount of territory east of the base, stretching to the Iraqi border.
[193] On 29 November, at approximately 10:26
UTC, the Syrian Internet and phone service was shut off for a two-day period.
[194] Syrian government sources denied responsibility and blamed the blackout on
fiber optic lines near Damascus becoming exposed and damaged;
[195] Edward Snowden in August 2014 claimed that this Internet breakdown had been caused, though unintendedly, by hackers of the
NSA during an operation to intercept Internet communication in Syria.
[196]
A destroyed tank on a road in Aleppo.
In mid-December 2012, American officials said that the Syrian military had fired
Scud
ballistic missiles at rebel fighters inside Syria. Reportedly, six Scud
missiles were fired at the Sheikh Suleiman base north of Aleppo, which
rebel forces had occupied. It is unclear whether the Scuds hit the
intended target.
[197] The government denied this claim.
[198]
Later that month, a further Scud attack took place near Marea, a town
north of Aleppo near the Turkish border. The missile appeared to have
missed its target.
[197] That same month, the British
Daily Telegraph reported that the FSA had now penetrated into Latakia Governorate's coast through Turkey.
[199] In late December, rebel forces pushed further into Damascus, taking control of the adjoining
Yarmouk and Palestine refugee camps, pushing out pro-government
Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine-General Command fighters with the help of other factions.
[200] Rebel forces launched
an offensive in Hama governorate, later claiming to have forced army regulars to evacuate several towns and bases,
[201] and stating that "three-quarters of western rural Hama is under our control."
[202] Rebels also captured the town of Harem near the Turkish border in Idlib governorate, after weeks of heavy fighting.
[203]
On 11 January 2013, Islamist groups, including al-Nusra Front, took full control of the
Taftanaz
air base in the Idlib governorate, after weeks of fighting. The air
base was often used by the Syrian military to carry out helicopter raids
and deliver supplies. The rebels claimed to have seized helicopters,
tanks and multiple rocket launchers, before being forced to withdraw by a
government counter-attack. The leader of the al-Nusra Front said the
amount of weapons they took was a "game changer".
[204] On 11 February, Islamist rebels captured the town of
Al-Thawrah in
Ar-Raqqah Governorate and the nearby
Tabqa Dam, Syria's largest dam and a key source of
hydroelectricity.
[205][206] The next day, rebel forces took control of Jarrah air base, located 60 kilometres (37 mi) east of Aleppo.
[207] On 14 February, fighters from al-Nusra Front took control of Shadadeh, a town in
Al-Hasakah Governorate near the Iraqi border.
[208]
On 20 February, a
car bomb
exploded in Damascus near the Ba'ath Syrian Regional Branch
headquarters, killing at least 53 people and injuring more than 235.
[209] None of the groups claimed responsibility.
[210]
On 21 February, the FSA in Quasar began shelling Hezbollah positions in
Lebanon. Prior to this, Hezbollah had been shelling villages near
Quasar from within Lebanon. A 48-hour ultimatum was issued by a FSA
commander on 20 February, warning the militant group to stop the
attacks.
[211]
On 2 March, intense clashes between rebels and the Syrian Army
erupted in the city of Raqqa, with many reportedly killed on both sides.
[212] On the same day, Syrian troops regained several villages near Aleppo.
[213] By 3 March, rebels had overrun Raqqa's central prison, allowing them to free hundreds of prisoners, according to the SOHR.
[214] The SOHR also stated that rebel fighters were now in control of most of an
Aleppo police academy in
Khan al-Asal, and that over 200 rebels and government troops had been killed fighting for control of it.
[215]
By 6 March, the rebels had captured the city of Raqqa, effectively
making it the first provincial capital to be lost by the Assad
government. Residents of Raqqa toppled a bronze statue of his late
father
Hafez Assad in the centre of the city. The rebels also seized two top government officials.
[216]
On 18 March, the Syrian Air Force attacked rebel positions in Lebanon
for the first time. The attack occurred at the Wadi al-Khayl Valley
area, near the town of Arsal.
[217]
On 21 March, a suspected suicide bombing in the Iman Mosque in Mazraa
district killed as many as 41 people, including the pro-Assad Sunni
cleric, Sheikh
Mohammed al-Buti.
[218]
On 23 March, several rebel groups seized the 38th division air defense
base in southern Daraa governorate near a highway linking Damascus to
Jordan.
[219] On the next day, rebels captured a 25 km strip of land near the Jordanian border, which included the towns of
Muzrib, Abdin, and the al-Rai military checkpoint.
[220]
On 25 March, rebels launched one of their heaviest bombardments of
Central Damascus since the revolt began. Mortars reached Umayyad Square,
where the Ba'ath Party headquarters, Air Force Intelligence and state
television are located.
[221]
On 26 March, near the Syrian town of al-Qusayr, rebel commander Khaled
al Hamad, who commands the Al Farooq al-Mustakilla Brigade and is also
known by his nom de guerre Abu Sakkar, ate the heart and liver of a dead
soldier and said "I swear to God, you soldiers of Bashar, you dogs, we
will eat from your hearts and livers! O heroes of Bab Amr, you slaughter
the Alawites and take out their hearts to eat them!" in an apparent
attempt to increase sectarianism.
[222][223]
Video of the event emerged two months later and resulted in
considerable outrage, especially from Human Rights Watch which
classified the incident as a war crime. According to the BBC, it was one
of the most gruesome videos to emerge from the conflict to-date.
[224] On 29 March, rebels captured the town of
Da'el after fierce fighting. The town is located in
Daraa Governorate, along the highway connecting Damascus to Jordan.
[225] On 3 April, rebels captured a military base near the city of
Daraa.
[226]
Government and Hezbollah offensives (April – June 2013)
On 17 April, government forces breached a six-month rebel blockade in
Wadi al-Deif, near Idlib. Heavy fighting was reported around the town
of Babuleen after government troops attempt to secure control of a main
highway leading to Aleppo. The break in the siege also allowed
government forces to resupply two major military bases in the region
which had been relying on sporadic airdrops.
[227] On 18 April, the FSA took control of Al-Dab'a Air Base near the city of al-Qusayr.
[228]
The base was being used primarily to garrison ground troops. Meanwhile,
the Syrian Army re-captured the town of Abel. The SOHR said the loss of
the town will hamper rebel movements between al-Qusayr and Homs city.
The capture of the airport would have relieved the pressure on the
rebels in the area, but their loss of
Abel made the situation more complicated.
[229] The same day, rebels reportedly assassinated Ali Ballan, who was a government employee, in the Mazzeh district of Damascus.
[230] On 21 April, government forces
captured the town of Jdaidet al-Fadl, near Damascus.
[231]
In April, government and
Hezbollah forces launched
an offensive
to capture areas near al-Qusayr. On 21 April, pro-Assad forces captured
the towns of Burhaniya, Saqraja and al-Radwaniya near the Lebanese
border.
[232][233] By this point, eight villages had fallen to the government offensive in the area.
[234]
On 24 April, after five weeks of fighting, government troops re-took
control of the town of Otaiba, east of Damascus, which had been serving
as the main arms supply route from Jordan.
[235]
Meanwhile, in the north of the country, rebels took control of a
position on the edge of the strategic Mennagh Military airbase, on the
outskirts of Aleppo. This allowed them to enter the airbase after months
of besieging it.
[236]
On 2 May, government forces captured the town of
Qaysa
in a push north from the city's airport. Troops also retook the Wadi
al-Sayeh central district of Homs, driving a wedge between two rebel
strongholds.
[237] SOHR reported
a massacre
of over 100 people by the Syrian army in the coastal town of Al Bayda,
Baniyas. However, this could not be independently verified due to
movement restrictions on the ground.
[238]
Yet the multiple video images that residents said they had recorded –
particularly of small children, were so shocking that even some
government supporters rejected Syrian television's official version of
events, that the army had simply "crushed a number of terrorists."
[239] On 3 May, the Syrian army backed by the
Shabiha reportedly committed a massacre of civilians near the city of Baniyas. The
Syrian Observatory for Human Rights said that at least 50 people – and possibly as many as 100 – were killed and that dozens of villagers were still missing.
[240]
On 8 May, government forces captured the town of
Khirbet Ghazaleh,
situated along the highway to the Jordanian border. Over 1,000 rebel
fighters withdrew from the town due to the lack of reinforcements and
ammunition. The loss of the town also resulted in the reopening of the
government supply-route to the city of Daraa. The rebels continued to
withdraw from other towns so as to not face the Army's advance along the
highway.
[241]
On 11 May, the rebels managed to cut a newly build desert road used as
an Army supply route between central Syria and Aleppo's airport.
[242] On 12 May, government forces took control of Khirbet Ghazaleh and secured the highway near the town.
[243]
By mid-May, due to the recent Army gains in retaking strategically
important locations, military analysts pointed out that the government
would have a major advantage in any future peace talks. Analysts on both
sides credited the government advances to the restructuring of their
forces, which they filled with thousands of militia irregulars trained
partly by Hezbollah and Iranian advisers in counter-insurgency
operations.
[244]
The government's success was also credited to the shift by the Army
from trying to recapture the whole country to holding on to strategic
areas.
[245]
On 13 May, government forces captured the towns of Western Dumayna,
Haidariyeh, and Esh al-Warwar allowing them to block supplies to the
rebels in al-Qusayr.
[246][247] On 16 May, rebels stated that they recaptured the town of
Al-Qisa.
[248]
On 17 May, rebels captured four villages in Eastern Hama, including the
Alawite town of Tulaysiah. The villages were abandoned by its residents
before the rebels arrived.
[249] On 19 May, government forces captured the town of Halfaya in Hama governorate.
[250]
The Syrian army also launched its offensive against the town of Qusayr.
A military source reported that the Army entered Qusayr, capturing the
city center and the municipality building.
[251] One opposition activist denied this,
[252] but another confirmed the Army was in control of 60 percent of the city.
[253] During the day's fighting, Hezbollah commander Fadi al-Jazar was killed.
[254]
An opposition source said the attack was launched from the east and
the south and that Hezbollah fighters took control of the town hall
within a few hours. He added that the fighting was then concentrated in
the northern part of the city.
[255]
The attack appeared to surprise the rebels, who expected the army to
push by the north on several rebel-controlled villages before attacking
the city. The turning point of the offensive was reached when Hezbollah
fighters took control of the Al Tal area overlooking Qusayr. Several
rebels fighters accused some commanders from fleeing the Al tal area at
the last minute.
[256]
Meanwhile, SOHR reported that the Syrian army was at the area by the
western neighborhood of al-Quseir in order to lay siege on the city
itself.
[257] On 23 May, rebels captured a military base near the town of Nairab.
[258] By 29 May, government forces captured the al-Dabaa air base, north of al-Qusayr.
[259]
On 1 and 2 June, after heavy fighting, the Syrian Army recaptured three
of the Alawite villages that had been previously captured by the rebels
in Eastern Hama governorate.
[260] On 5 June, rebel forces withdrew fully from al-Qusayr.
[261] The following day, government forces captured the nearby village of Dabaa.
Za'atri camp for Syrian refugees in Jordan
On 6 June, rebels temporarily captured the
Quneitra border crossing which links the Israeli-occupied
Golan Heights
with Syria. However, the same day, government forces counter-attacked
with tanks and armoured personnel carriers, recapturing the crossing.
[262][263] On 7 June, Syrian troops backed by Hezbollah captured two villages north of al-Qusayr: Salhiyeh and Masoudiyeh.
[264] The next day, they captured the village of Buwaydah, the last rebel-held village in the al-Qusayr region.
[265] Between 7 and 14 June, Army troops, government militiamen, and Hezbollah fighters launched operations in
Aleppo Governorate.
Over a one-week period, government forces had advanced both in Aleppo
city and the countryside around the city. However, on 14 June, according
to an opposition activist, the tide had started reversing, after rebels
managed to halt an armoured reinforcement column from Aleppo city for
two government-held Shiite villages northwest of the city. Rebels
claimed they destroyed one tank and killed 20 government soldiers
northwest of the town of Maaret al-Arteek. Before the column was
stopped, government forces had captured the high ground at Maaret
al-Arteek, threatening rebel positions. Government forces also made some
advances in the southern part of Aleppo governorate, capturing the
village of Ain-Assan.
[266][267]
During the fighting in Aleppo city itself, on 13 June, government
forces managed to temporarily advance into the rebel-held Sakhour
district from two directions, but were soon repelled.
[268] Some described it as possibly a probing attack and not a full assault.
[269]
On 10 June, Shia pro-government fighters from the village of Hatla,
east of Deir al-Zour, attacked a nearby rebel position, killing four
rebels.
[270]
The next day, in retaliation for the attack, thousands of rebels
attacked and captured the village, killing 60 residents, fighters and
civilians, according to SOHR. 10 rebel fighters were killed during the
attack.
[270]
At dawn on 13 June, rebels seized an Army position on the northern edge
of the town of Morek, which is located on the north-south highway,
[271] in fighting that killed six soldiers and two rebels. Later in the day, the Army shelled the base and sent reinforcements.
[272][273] On 14 June, the Al Nusra front captured a military barracks near Idlib city.
[274]
On 15 June, the Syrian Army captured the Damascus suburb of Ahmadiyeh
near the city's airport. Rebels said fighting began after rebels entered
the town to use it as a position to launch mortars on the Damascus
airport. They added that fighting was ongoing.
[275][276] On 22 June, the Syrian Army captured the rebel stronghold town of
Talkalakh.
[277][278] Four days later, the Army captured the town of Al-Qariatayn, also in Homs governorate.
[279]
Continued fighting (July – October 2013)
On 28 June, rebel forces captured a major military checkpoint in the city of Daraa.
[280]
On 12 July FSA reported that one of its commanders, Kamal Hamami, had
been killed by Islamists a day before. The rebels declared that the
assassination by the
Islamic State of Iraq and Levant, was tantamount to a declaration of war.
[281] On 17 July, FSA forces took control of most of the southern city of
Nawa after seizing up to 40 army posts stationed in the city.
[282] On 18 July, Kurdish YPG forces secured control of the northern town of
Ras al-Ain, after days of fighting with the al-Nusra Front.
[283]
In the following three months, continued fighting between Kurdish and
mainly jihadist rebel forces led to the capture of two dozen towns and
villages in
Hasakah Governorate by Kurdish fighters,
[284] while the Jihadists made limited gains in Aleppo and Raqqah governorates after they turned on the Kurdish rebel group
Jabhat al-Akrad
over its relationship with the YPG. In Aleppo governorate, Islamists
massacred the Kurds leading to a mass migration of civilians to the town
of Afrin.
[285]
On 22 July, FSA fighters seized control of the western Aleppo suburb of
Khan al-Asal. The town was the last government stronghold in the western portion of Aleppo governorate.
[286] On 25 July, the Syrian army secured the town of
al-Sukhnah, after expelling the al-Nusra Front.
[287] On 27 July, after weeks of fighting and bombardment in Homs, the Syrian Army captured the historic
Khalid ibn al-Walid Mosque,
[288] and two days later, captured the district of Khaldiyeh.
[289]
On 4 August, around 10 rebel brigades, launched
a large-scale offensive on the government stronghold of
Latakia Governorate.
Initial attacks by 2,000 opposition members seized as many as 12
villages in the mountainous area. Between 4 and 5 August, 20 rebels and
32 government soldiers and militiamen had been killed in the clashes.
Hundreds of Alawite villagers fled to Latakia. By 5 August, rebel
fighters advanced to 20 kilometers from Qardaha, the home town of the
Assad family.
[290][291]
However, in mid-August, the military counter-attacked and recaptured
all of the territory previously lost to the rebels in the coastal region
during the offensive.
[292][293]
A Syrian security force source "told AFP the army still had to
recapture the Salma region, a strategic area along the border with
Turkey."
[294] According to a
Human Rights Watch
report 190 civilians were killed by rebel forces during the offensive,
including at least 67 being executed. Another 200 civilians, primarily
women and children, were taken hostage.
[295][296]
On 6 August, rebels captured
Menagh Military Airbase after a 10-month siege. The strategic airbase is located on the road between Aleppo city and the Turkish border.
[297][298] On 21 August
a chemical attack
took place in the Ghouta region of the Damascus countryside, leading to
thousands of casualties and several hundred dead in the opposition-held
stronghold. The attack was followed by a military offensive by
government forces into the area, which had been hotbeds of the
opposition.
[299] On 24 August, rebels captured the town of
Ariha. However, government forces recaptured Ariha on 3 September.
[300][301] On 26 August, rebel forces took over the town of
Khanasir in Aleppo governorate which was the government's last supply route for the city of Aleppo.
[302] On 8 September, rebels led by the al-Nusra Front
captured the Christian town of Maaloula, 43 km north of Damascus,
[303] The Syrian Army launched a counterattack a few days later, recapturing the town.
[304]
On 18 September, the
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
(ISIS) overran the FSA-held town of Azaz in the north. The fighting was
the most severe since tensions rose between militant factions in Syria
earlier in the year.
[305][306]
Soon after ISIS captured Azaz, a ceasefire was announced between the
rival rebel groups. However, in early October, more fighting erupted in
the town.
[307] On 20 September, Alawite militias including the NDF killed 15 civilians in the Sunni village of
Sheik Hadid
in Hama Governorate. The massacre occurred in retaliation for a rebel
capture of the village of Jalma, in Hama, which killed five soldiers,
along with the seizure of a military checkpoint which killed 16 soldiers
and 10 NDF militiamen.
[308][309]
In mid-September, the military captured the towns of Deir Salman and
Shebaa on the outskirts of Damascus. The Army also captured six villages
in eastern Homs.
[310] Fighting broke out in those towns again in October.
[311]
On 28 September, rebels seized the Ramtha border post in
Daraa Governorate on the Syria Jordan crossing after fighting which left 26 soldiers dead along with 7 foreign rebel fighters.
[312] On 3 October, AFP reported that Syria's army re-took the town of
Khanasir, which is located on a supply route linking central Syria to the city of Aleppo.
[313] On 7 October, the Syrian Army managed to reopen the supply route between Aleppo and Khanasir.
[314]
On 9 October, rebels seized the Hajanar guard post on the Jordanian
border after a month of fierce fighting. Rebels were now in control of a
swath of territory along the border from outside of Daraa to the edge
of Golan Heights.
[315]
The same day, Hezbollah and Iraqi Shiite fighters, backed up by
artillery, air-strikes and tanks, captured the town of Sheikh Omar, on
the southern outskirts of Damascus. Two days later, they also captured
the towns of al-Thiabiya and Husseiniya on the southern approaches to
Damascus. The capture of the three towns strengthened the government
hold on major supply lines and put more pressure on rebels under siege
in the Eastern Ghouta area.
[316][317] On 14 October, SOHR reported that rebels captured the Resefa and Sinaa districts of
Deir ez-Zor city, as well as Deir ez-Zor's military hospital.
[318]
Government and Hezbollah offensives (October – December 2013)
The Syrian Army along with its allies, Hezbollah and the
al-Abas brigade, launched an offensive on Damascus and Aleppo.
[319][320]
On 16 October, AFP reported that Syrian troops recaptured the town of
Bweida, south of Damascus. On 17 October, the Syrian government's head
of Military Intelligence in
Deir ez-Zor Governorate,
Jameh Jameh, was assassinated by rebels in Deir ez-Zor city. SOHR
reported that he had been shot by a rebel sniper during a battle with
rebel brigades.
[321]
On 24 October, the Syrian army retook control of the town of Hatetat
al-Turkman, located southeast of Damascus, along the Damascus
International Airport road.
[322]
On 26 October, Kurdish rebel fighters seized control of the strategic
Yarubiya border crossing between Syria and Iraq from Al Nusra in Al
Hasakah Governorate.
[323] Elsewhere, in Daraa Governorate, rebel fighters captured the town of
Tafas from government forces after weeks of clashes which left scores dead.
[324] On 1 November, the Syrian army retook control of the key city of
Al-Safira[325] and the next day, the Syrian Army and its allies recaptured the village of Aziziyeh on the northern outskirts of Al-Safira.
[326]
From early to mid-November, Syrian Army forces captured several towns
south of Damascus, including Hejeira and Sbeineh. Government forces also
recaptured the town of Tel Aran, southeast of Aleppo, and a military
base near Aleppo's international airport.
[327]
On 10 November, the Syrian army had taken full control of "Base 80", near Aleppo's airport.
[328] According to the SOHR, 63 rebels,
[329] and 32 soldiers were killed during the battle.
[329] One other report put the number of rebels killed between 60 and 80.
[330] Army units were backed-up by Hezbollah fighters and pro-government militias during the assault.
[329] The following day, government forces secured most of the area around the airport.
[331][332] On 13 November, government forces captured most of Hejeira.
[333] Rebels retreated from Hejeira to
Al-Hajar al-Aswad. However, their defenses in besieged districts closer to the heart of Damascus were still reportedly solid.
[334] On 15 November, the Syrian Army retook control of the city of Tell Hassel near Aleppo.
[335] On 18 November, the Syrian troops stormed the town of Babbila.
[336] On 19 November, government forces took full control of Qara.
[337] The same day, the Syrian army captured al-Duwayrinah.
[338]
On 23 November, al-Nusra Front and other Islamist rebels captured the
al-Omar oil field, Syria's largest oil field, in Deir al-Zor governorate
causing the government to rely almost entirely on imported oil.
[339][340] On 24 November, rebels captured the towns of Bahariya, Qasimiya, Abbadah, and Deir Salman in Damascus's countryside.
[341] On 28 November, the Syrian army recaptured Deir Attiyeh.
[342]
On 2 December, rebels led by the Free Syrian army recaptured the historic Christian town of
Ma'loula.
After the fighting, reports emerged that 12 nuns had been abducted by
the rebels. However, the FSA disputes this and said that the nuns had
been evacuated to the nearby rebel held town of
Yabrud due to the Army shelling.
[343][344] In early December, the Islamic Front seized control of Bab al-Hawa border crossing with Turkey, which had been in hands of FSA.
[345]
The groups also captured warehouses containing equipment delivered by
the U.S. In response, the U.S. and Britain said they halted all
non-lethal aid to the FSA, fearing that further supplies could fall in
hands of
al-Qaeda militants.
[346] On 10 December, the Army took full control of Nabek,
[347] with fighting continuing in its outskirts.
[216]
Fighting between ISIS and other rebel groups (January – March 2014)
Tension between moderate rebel forces and ISIS had been high since ISIS captured the border town of
Azaz from FSA forces on 18 September 2013.
[348] Conflict was renewed over
Azaz in early October
[349] and in late November ISIS captured the border town of
Atme from an FSA brigade.
[350] On 3 January 2014, the Army of the Mujahideen, the Free Syrian Army and the Islamic Front launched an offensive against
ISIS
in Aleppo and Idlib governorates. A spokesman for the rebels said that
rebels attacked ISIS in up to 80% of all ISIS held villages in Idlib and
65% of those in Aleppo.
[351]
By 6 January, opposition rebels managed to expel ISIS forces from the
city of Raqqa, ISIS's largest stronghold and capital of the Raqqa
Governorate.
[352] On 8 January, opposition rebels expelled most ISIS forces from the city of Aleppo, however ISIS reinforcements from the
Deir ez-Zor Governorate managed to retake several neighborhoods of the city of Raqqa.
[353][354]
By mid January ISIS retook the entire city of Raqqa, while rebels
expelled ISIS fighters fully from Aleppo city and the villages west of
it.
On 29 January, Turkish aircraft near the border fired on an ISIS
convoy inside the Aleppo Provence of Syria, killing 11 ISIS fighters and
1 ISIS emir.
[355][356] In late January it was confirmed that rebels had assassinated ISIS's second in command,
Haji Bakr, who was al-Qaeda's military council head and a former military officer in Saddam Hussein's army.
[357]
By mid-February, the Al-Nusra Front joined the battle in support of
rebel forces, and expelled ISIS from the Deir Ezzor Governorate.
[358] By March, the ISIS forces fully retreated from the Idlib Governorate.
[359][360]
On 4 March, ISIS retreated from the border town of Azaz and other
nearby villages, choosing instead to consolidate around Raqqa in an
anticipation of an escalation of fighting with Al Nusra.
[361]
Continued government and Hezbollah offensive (March 2014)
On 4 March, the
Syrian army took control of Sahel in the Qalamoun region.
[362] On 8 March, government forces took over Zara, in Homs Governorate, further blocking rebel supply routes from Lebanon.
[363] On 11 March, Government forces and
Hezbollah took control of the Rima Farms region, directly facing Yabrud.
[364] On 16 March, Hezbollah and government forces captured
Yabrud, after Free Syrian Army fighters made an unexpected withdrawal, leaving the Al Nusra Front to fight in the city on its own.
[365]
On 18 March, Israel used artillery against Syrian Army base, after four
of its soldiers had been wounded by a roadside bomb while patrolling
Golan Heights.
[366]
On 19 March, the Syrian army captured Ras al-Ain near
Yabrud,
after two days of fighting and al-Husn in Homs Governorate, while
rebels in the Daraa Governorate captured Daraa prison, and freed
hundreds of detainees.
[367][368][369] On 20 March, the
Syrian army took control of the
Krak des Chevaliers in al-Husn.
[369] On 29 March, Syrian army took control of the villages of
Flitah and Ras Maara near the border with Lebanon.
[370]
Continued fighting (March – May 2014)
On 22 March, rebels took control of the Kesab border post in the Latakia Governorate.
[371] By 23 March, rebels had taken most of Khan Sheikhoun in Hama.
[372] During clashes near the rebel-controlled Kesab border post in Latakia, Hilal Al Assad, NDF leader in Latakia and one of
Bashar Al Assad's cousins was killed by rebel fighters.
[373][374] On 4 April, rebels captured the town of Babulin, Idlib.
[375] On 9 April, the Syrian army took control of
Rankous in the Qalamoun region.
[376]
On 12 April, rebels in Aleppo stormed the government-held Ramouseh
industrial district in an attempt to cut the Army supply route between
the airport and a large Army base. The rebels also took the Rashidin
neighbourhood and parts of the Jamiat al-Zahra district.
[377] On 26 April, the Syrian army took control of
Al-Zabadani.
[378] According to SOHR, rebels took control of Tell Ahrmar, Quneitra.
[379] Rebels in Daraa also took over Brigade 61 Base and the 74th battalion.
[380]
On 26 April, the FSA announced they had begun an offensive against
ISIS in the Raqqa Governorate, and had seized five towns west of Raqqa
city.
[381] On 29 April, activists said that the Syrian army captured Tal Buraq near the town of Mashara in Quneitra without any clashes.
[382]
On 7 May, a truce went into effect in the city of Homs, SOHR reported.
The terms of the agreement include safe evacuation of Islamist fighters
from the city, which would then fall under government control, in
exchange for release of prisoners and safe passage of humanitarian aid
for Nubul and Zahraa, two Shiite enclaves besieged by the rebels.
[383] On 18 May, the head of Syria's Air Defense, General
Hussein Ishaq,
died of wounds sustained during a rebel attack on an air defense base
near Mleiha the previous day. In Hama governorate, rebel forces took
control of the town of Tel Malah, killing 34 pro-Assad fighters at an
army post near the town. Its seizure marked the third time rebels have
taken control of the town.
[384][385]
Presidential election (June 2014)
Syria held a presidential election in government-held areas on 3 June
2014. For the first time in the history of Syria more than one person
was allowed to stand as a presidential candidate.
[386] More than 9,000 polling stations were set up in government-held areas.
[387][388] According to the
Supreme Constitutional Court of Syria, 11.63 million Syrians voted (the turnout was 73.42%).
[389] President
Bashar al-Assad won the election with 88.7% of the votes. As for Assad's challengers,
Hassan al-Nouri received 4.3% of the votes and
Maher Hajjar received 3.2%.
[390] Allies of Assad from more than 30 countries were invited by the Syrian government to follow the presidential election,
[391] including Bolivia, Brazil, Cuba, Ecuador, India, Iran, Iraq, Nicaragua, Russia, South Africa and Venezuela.
[392][393] The Iranian official
Alaeddin Boroujerdi read a statement by the group saying the election were "free, fair and transparent".
[394] The
Gulf Cooperation Council, the
European Union and the
United States all dismissed the election as illegitimate and a farce.
[395][396][397][398]
State employees were told to vote or face interrogation.
[399] On the ground there were no independent monitors stationed at the polling stations.
[400][401][402]
It is noted by analysts that as few as 6 million eligible voters remained in Syria.
[403][404] Due to rebel, Kurdish and ISIS control of Syrian territories there was no voting in roughly 60% of the country.
[405][406]
ISIL offensives and U.S. airstrikes (June 2014 – January 2015)
Starting on 5 June,
ISIL seized swathes of territory in
Iraq in addition to heavy weapons and equipment from the
Iraqi Army, some of which they brought into Syria. Government airstrikes targeted ISIL bases in
Ar-Raqqah and
Al-Hasakah in coordination with an Iraqi Army counteroffensive.
[407] On 14 June, government forces retook the town of
Kessab in northern
Latakia Governorate, while rebels took over Tall al-Gomo near the town of
Nawa in the
Daraa Governorate, as well as reentering the
Qalamoun area.
[408][409]
According to the
Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, on 17 July ISIL took control of the
Shaar oil field,
killing 90 pro-government forces while losing 21 fighters. In addition,
270 guards and government-aligned fighters were missing. About 30
government persons managed to escape to the nearby Hajjar field.
[410] On 20 July, the Syrian Army secured the field, although fighting continued in its outskirts.
[411] On 25 July, the Islamic State took control of the Division 17 base near Raqqah.
[412]
On 7 August, ISIL took the Brigade 93 base in Raqqah using weapons captured from their offensive in Iraq. Multiple
suicide bombs also went off before the base was stormed.
[413] On 13 August, ISIL forces took the towns of
Akhtarin and Turkmanbareh from rebels in
Aleppo. ISIL forces also took a handful of nearby villages. The other towns seized include Masoudiyeh,
Dabiq and Ghouz.
On 14 August, the
Free Syrian Army commander Sharif As-Safouri admitted working with
Israel and receiving
anti-tank weapons from Israel and FSA soldiers also received medical treatment inside Israel.
[414] On 14 August, the
Syrian Army as well as
Hezbollah militias retook the town of Mleiha in
Rif Dimashq Governorate.
The Supreme Military Council of the FSA denied claims of Mleiha's
seizure, rather the rebels have redeployed from recent advances to other
defensive lines.
[415] Mleiha has been held by the
Islamic Front. Rebels had used the town to fire mortars on government held areas inside Damascus.
[416][417]
Meanwhile, ISIL forces in Raqqah were launching a siege on
Tabqa airbase, the Syrian government's last military base in Raqqah. Kuwaires airbase in
Aleppo also came under fierce attack by ISIL.
[418][419] On 16 August, there were reports that 22 people were killed in the village of
Daraa by a
car bomb
outside a mosque. The bomb was thought to be detonated by ISIS. Also on
16 August, the Islamic State seized the village of Beden in the Aleppo
Governorate from rebels.
[420][421]
On 17 August, SOHR said that in the past two weeks ISIL jihadists killed over 700 tribal members in oil-rich
Deir ez-Zor Governorate.
[422]
On 19 August, a senior figure in ISIL who had prepared planned car
and suicide bombs across Syria, Lebanon and Iraq was killed. Some
reports said that he was killed by Hezbollah fighters. There were also
several reports that he was killed by the Syrian Army in the Qalamoun
region, near the border with
Lebanon.
[423][424][425]
On 19 August, American journalist
James Foley
was executed by ISIL, who claimed it was in retaliation for the United
States operations in Iraq. Foley was kidnapped in Syria in November 2012
by
Shabiha militia.
[426] ISIL also threatened to execute
Steven Sotloff, who was kidnapped at the Syrian-Turkish border in August 2013.
[427] There are reports ISIS captured a Japanese national, two Italian nationals, and a Danish national as well.
[428] At least 70 journalists have been killed covering the Syrian war, and more than 80 kidnapped, according to the
Committee to Protect Journalists.
[429]
On 22 August, the
al-Nusra Front released a video of captured Lebanese soldiers and demanded that Hezbollah withdraw from Syria under threat of their execution.
[430]
On 23 August, the Tabqa airbase was no longer encircled by ISIL
fighters and the Syrian Army had taken back the M-42 Highway from ISIL
fighters, which leads to the city of
Salamiyah in the
Hama Governorate.
[431] Also in Raqqah, the Syrian Army took control of the town of Al-Ejeil.
[432][433]
ISIL reportedly sent reinforcements from Iraq to the governorate of
Raqqah. The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights said at least 400 ISIL
fighters had also been wounded in the previous five days in clashes with
the Syrian Army and
National Defence Force in Raqqah alone.
[432][434] At the same time, Several senior
UK and
US figures urged
Turkey to stop allowing ISIL to cross the border to Syria and Iraq.
[435]
On the following day, the Islamic State seized Tabqa airbase from government forces.
[436] The battle for the base left 346 ISIL fighters and 195 soldiers dead.
[437]
Prisoners taken by ISIL forces were executed and a video from the mass
killing was posted on YouTube. The death toll varied from 120 to 250.
[438]
On 26 August, the Syrian Air Force carried out airstrikes against
ISIL targets in the Governorate of Deir ez-Zor. This was the first time
the Syrian army attacked them in
Deir ez-Zor
as the Syrian Army pulled out of Raqqah and shifted to Deir ez-Zor in a
bid to seize its oil and natural gas resources as well as strategically
splitting ISIL territories.
[439][440]
American jets began bombing ISIL in Syria on 23 September 2014,
raising U.S. involvement in the war-torn country. At least 20 targets in
and around Raqqa were hit, the opposition group Syrian Observatory for
Human Rights said. Foreign partners participating in the strikes with
the United States were Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates,
Qatar and Jordan. The US and "partner nation forces" began striking ISIL
targets using fighters, bombers and Tomahawk missiles, Pentagon
spokesman Rear Adm. John Kirby said.
[441]
US aircraft include
B-1 bombers,
F-16s,
F-18s and
Predator drones, with F-18s flying missions off the
USS George H.W. Bush (CVN-77) in the Persian Gulf.
Tomahawk missiles were fired from the destroyer
USS Arleigh Burke (DDG-51) in the
Red Sea.
Syria's Foreign Ministry told the Associated Press that the US informed
Syria's envoy to the U.N. that "strikes will be launched against the
terrorist group in Raqqa".
[442]
The United States informed the Free Syrian Army beforehand of the
impending airstrikes, and the rebels said that weapons transfers to the
Free Syrian Army had begun.
[443]
The United States also attacked a specific faction of Al-Nusra called the
Khorasan Group, who according to the United States had training camps and plans for attacking the United States in the future.
[444]
For its part, Turkey launched an official request to the UN for a no-fly zone over Syria.
[445]
The same day, Israel shot down a Syrian warplane after it entered the Golan area from Quneitra.
[446]
By 3 October, ISIL forces were
heavily shelling the city of Kobane and were within a kilometer of the town.
[447]
Within 36 hours from 21 October, the Syrian air force carried out
over 200 airstrikes on rebel-held areas across Syria and US and Arab
jets attacked IS positions around Kobane. Syrian Information Minister
Omran al-Zoubi said the YPG forces in Kobane had been provided with military and logistical support.
[448][449] Syria reported that its air force had destroyed two fighter jets being operated by IS.
[450]
By 26 January, the Kurdish YPG forced ISIL forces in Kobanî to retreat,
[451] thus fully recapturing the city.
[452] The U.S. confirmed that the city had been cleared of ISIL forces on 27 January,
[453] and ISIL admitted defeat in Kobanî city three days later, although they vowed to return.
[454]
The Southern Front (October 2014 – February 2015)
In February 2014, the
Southern Front of the Free Syrian Army formed in southern Syria. Six months later, they started a string of victories in Daraa and Quneitra during the
2014 Quneitra offensive, the
Daraa offensive (October 2014), the
Battle of Al-Shaykh Maskin, the
Battle of Bosra (2015) and the
Battle of Nasib Border Crossing. A government counter-offensive (the
2015 Southern Syria offensive) during this period, that included the
IRGC and
Hezbollah, recaptured 15 towns, villages and hills,
[455][456][457] but the operation slowed soon after
[458] and stalled.
[459]
Since early 2015, opposition military operations rooms based in Jordan and Turkey began increasing cooperation,
[460]
with Saudi Arabia and Qatar also reportedly agreeing upon the necessity
to unite opposition factions against the Syrian government.
[461]
Northern Al-Nusra Front and Islamist takeover (October 2014 – March 2015)
In late October 2014, a conflict erupted between the Al-Nusra Front on one side and the western-backed
SRF and
Hazzm Movement on the other (
Al-Nusra Front–SRF/Hazzm Movement conflict). Al-Nusra was reportedly reinforced by ISIL. By the end of February 2015, Al-Nusra defeated both groups, captured the entire
Zawiya Mountain region in Idlib province and several towns and military bases in other governorates, and seized weapons supplied by the
CIA to the two moderate groups.
[462][463] The significant amount of weapons seized included a small number of
BGM-71
anti-tank missiles that were identical to weapons systems al-Nusra
Front had previously captured from government stockpiles such as French
MILANs, Chinese
HJ-8s and Russian
9K111 Fagots.
[464] Reuters reported that this represented al-Nusra crushing pro-Western rebels in the north of the country.
[465]
According to FSA commanders in northern Syria however, the elimination
of Harakat Hazm and the SRF was a welcome development due to the leaders
of those factions allegedly involved in corruption.
[466] The Western-backed 30th Division of the FSA remained active elsewhere in Idlib.
[467]
By 24 March, the Al-Nusra Front dominated most of Idlib province, except for the government-held provincial capital,
Idlib, which they had encircled on three sides along with its Islamist allies.
[468] On 28 March, a joint coalition of Islamist forces, the
Army of Conquest, captured Idlib.
[469][470][471] This left the north largely taken over by
Ahrar ash-Sham,
Al-Nusra Front and other Islamist rebels, with the south of the country
becoming the last significant foothold for the mainstream, non-jihadist
opposition fighters.
[472]
Army of Conquest advances in Idlib (April 2014 – June 2015)
On 22 April,
a new rebel offensive was launched in the north-west of Syria and by 25 April, the rebel coalition
Army of Conquest had captured the city of
Jisr al-Shughur.
[473] At the end of the following month, the rebels also seized seized the
Al-Mastumah military base,
[474] and
Ariha, leaving government forces in control of tiny pockets of Idlib, including the Abu Dhuhur military airport.
[475]
In addition, according to Charles Lister (Brookings Doha Center), the
Army of Conquest coalition was a broad opposition effort to ensure that
the Al-Qaeda-affiliated Al-Nusra Front was contained, with the rearguard
involvement of Western-backed factions being regarded as crucial.
[466]
Rebel advances led to government and Hezbollah morale plunging dramatically.
[476]
In north-west Syria these losses were countered by a Hezbollah-led
offensive in the Qalamoun mountains north of Damascus, on the border
with Lebanon, that gave Hezbollah effective control of the entire area.
[477]
Resurgent ISIL advance (May 2015)
On 21 May, ISIL took control of
Palmyra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, after eight days of fighting.
[478] The jihadists also captured the nearby towns of Al-Sukhnah and Amiriya, as well as several oil fields.
[479]
Following the capture of Palmyra, ISIL conducted mass executions in the
area, killing an estimated 217–329 government civilian supporters and
soldiers, according to opposition activists.
[480][481][482] Government sources put the number of killed at 400–450.
[483]
By early June, ISIL reached the town of Hassia, which lays on the
main road from Damascus to Homs and Latakia, and reportedly took up
positions to the west of it, creating a potential disaster for the
government and raising the threat of Lebanon being sucked further into
the war.
[484]
Advanced weaponry and tactics
Chemical weapons
A UN fact-finding mission
was requested by member states to investigate 16 alleged chemical
weapons attacks. Seven of them have been investigated (nine were dropped
for lack of "sufficient or credible information") and in four cases the
UN inspectors confirmed use of
sarin gas. The reports, however, did not blame any party of using chemical weapons.
[485]
Many countries, including the United States and the European Union have
accused the Syrian government of conducting several chemical attacks,
the most serious of them being the
2013 Ghouta attacks. Following this incident and international pressure, the
destruction of Syria's chemical weapons began. In 2015 the UN mission disclosed previously undeclared traces of sarin compounds
[disputed – discuss] in a "military research site".
[486]
Cluster bombs
The Syrian army began using
cluster bombs
in September 2012. Steve Goose, director of the Arms division at Human
Rights Watch said "Syria is expanding its relentless use of cluster
munitions, a banned weapon, and civilians are paying the price with
their lives and limbs", "The initial toll is only the beginning because
cluster munitions often leave unexploded bomblets that kill and maim
long afterward."
[487]
Scud missile attacks
In December 2012, the Syrian government began using
Scud missiles on rebel-held towns, primarily targeting Aleppo.
[488] On 19 February, four Scud missiles were fired, three landed in Aleppo city and one on
Tell Rifaat town, Aleppo governorate. Between December and February, at least 40 Scud missile landings were reported.
[489] Altogether, Scud missiles killed 141 people in the month of February.
[490] The United States condemned the Scud missile attacks.
[491] On 1 March, a Scud missile landed in Iraq. It is believed that the intention was to hit the Deir Ezzor governorate.
[492] On 29 March, a Scud missile landed on
Hretan, Aleppo, killing 20 and injuring 50.
[493] On 28 April, a Scud missile landed on Tell Rifaat, killing four, two of them women and two of them children, SOHR reported.
[494] On 3 June, a surface to surface missile, not confirmed as a Scud, hit the village of
Kafr Hamrah around midnight killing 26 people including six women and eight children according to
SOHR.
[495]
Suicide bombings
Rebel suicide bombings
began in December 2011; the Al-Nusra Front has claimed responsibility for 57 out of 70 similar attacks through April 2013.
[75][496] The bombings have claimed numerous civilian casualties,
[497] including 47 mainly Alawite children killed in Homs on 1 October 2014.
[498]
Barrel bombs
Main article:
Barrel bomb
A barrel bomb is a type of
improvised explosive device used by the Syrian Air Force. Typically, a barrel is filled with a large amount of TNT, and possibly
shrapnel (such as nails) and oil, and dropped from a helicopter. The resulting detonation can be devastating.
[499][500][501]
Thermobaric weapons
Thermobaric weapons,
also known as "fuel-air bombs", have been used by the government side
during the Syrian civil war. Since 2012, rebels have said that the
Syrian Air Force (government forces) is using thermobaric weapons
against residential areas occupied by the rebel fighters, such as during
the
Battle of Aleppo and also in
Kafr Batna.
[502][503]
A panel of United Nations human rights investigators reported that the
Syrian government used thermobaric bombs against the strategic town of
Qusayr in March 2013.
[504] In August 2013, the BBC reported on the use of napalm-like incendiary bombs on a school in northern Syria.
[505]
Belligerents
Syrian government and affiliated parties
Syrian Armed Forces
Two destroyed Syrian Army tanks in Azaz, August 2012
Before the uprising and war broke out, the force of the Syrian Armed
Forces was estimated at 325,000 regular troops, of which 220,000 were
'army troops' and the rest in the navy, air force and air defenses.
There were also approximately 280,000–300,000 reservists. Since June
2011, defections of soldiers have been reported. By July 2012, the
Syrian Observatory for Human Rights
estimated that tens of thousands of soldiers have defected, and a
Turkish official estimated that 60,000 soldiers have defected.
National Defense Force
The Syrian NDF was formed out of pro-government militias. They
receive their salaries, and their military equipment from the
government,
[506][507] and numbers around 100,000.
[508][509]
The force acts in an infantry role, directly fighting against rebels on
the ground and running counter-insurgency operations in coordination
with the army, which provides them logistical and artillery support. The
force has a 500-strong women's wing called "
Lionesses of National Defense" which operates checkpoints.
[510] NDF soldiers are allowed to take
loot from battlefields, which can then be sold for extra money.
[506]
Shabiha
The
Shabiha are unofficial pro-government militias drawn largely from Assad's
Alawite minority group. Since the uprising, the Syrian government has frequently used
shabiha to break up protests and enforce laws in restive neighborhoods.
[511] As the protests escalated into an armed conflict, the opposition started using the term
shabiha to describe any civilian Assad supporter taking part in the government's crackdown on the uprising.
[512] The opposition blames the
shabiha for the many violent excesses committed against anti-government protesters and opposition sympathizers,
[512] as well as looting and destruction.
[513][514] In December 2012, the
shabiha were designated a terrorist organization by the United States.
[515]
Bassel al-Assad is reported to have created the
shabiha in the 1980s for government use in times of crisis.
[516] Shabiha
have been described as "a notorious Alawite paramilitary, who are
accused of acting as unofficial enforcers for Assad's regime";
[517] "gunmen loyal to Assad",
[518]
and, according to the Qatar-based Arab Center for Research and Policy
Studies, "semi-criminal gangs comprised of thugs close to the regime".
[518] Despite the group's image as an Alawite militia, some
shabiha operating in Aleppo have been reported to be Sunnis.
[519] In 2012, the Assad government created a more organized official militia known as the
Jaysh al-Sha'bi, allegedly with help from Iran and Hezbollah. As with the
shabiha, the vast majority of Jaysh al-Sha'bi members are Alawite and Shi'ite volunteers.
[520][521]
Hezbollah
General Secretary
Hassan Nasrallah
denied Hezbollah had been fighting on behalf of the Syrian government,
stating in a 12 October 2012 speech that "right from the start the
Syrian opposition has been telling the media that Hezbollah sent 3,000
fighters to Syria, which we have denied".
[522] However, according to the Lebanese
Daily Star
newspaper, Nasrallah said in the same speech that Hezbollah fighters
helped the Syrian government "retain control of some 23 strategically
located villages [in Syria] inhabited by Shiites of Lebanese
citizenship". Nasrallah said that Hezbollah fighters have died in Syria
doing their "jihadist duties".
[523] In 2012, Hezbollah fighters crossed the border from Lebanon and took over eight villages in the
Al-Qusayr District of Syria.
[524] The former secretary general of Hezbollah, Sheikh
Subhi al-Tufayli, confirmed in February 2013 that Hezbollah was fighting for the Syrian army.
[525]
On 12 May, Hezbollah, with the Syrian army, attempted to retake part of
Qusayr.
[253] By the end of the day, 60 percent of the city, including the municipal office building, were under pro-Assad forces.
[253]
In Lebanon, there have been "a recent increase in the funerals of
Hezbollah fighters" and "Syrian rebels have shelled Hezbollah-controlled
areas."
[253] As of 14 May, Hezbollah fighters were reported to be fighting alongside the Syrian army, particularly in the
Homs Governorate.
[526] Hassan Nasrallah has called on Shiites and Hezbollah to protect the shrine of Sayida Zeinab.
[526]
President Bashar al-Assad denied in May 2013 that there were foreign
fighters, Arab or otherwise, fighting for the government in Syria.
[527]
On 25 May, Nasrallah announced that Hezbollah was fighting in the
Syria against Islamic extremists and "pledged that his group will not
allow Syrian militants to control areas that border Lebanon".
[528] He confirmed that Hezbollah was fighting in the strategic Syrian town of Qusayr on the same side as
Assad's forces.
[74] In the televised address, he said, "If Syria falls in the hands of America, Israel and the
takfiris, the people of our region will go into a dark period."
[74]
According to independent analysts, by the beginning of 2014,
approximately 500 Hezbollah fighters had died in the Syrian conflict.
[529]
Iran
Since the start of the civil war, Iran has expressed its support for
the Syrian government and has provided it with financial, technical, and
military support, including training and some combat troops.
[530] Iran and
Syria are
close strategic allies. Iran sees the survival of the Syrian government as being crucial to its regional interests.
[531][532] Iran's
supreme leader,
Ali Khamenei, was reported in September 2011 to be vocally in favor of the Syrian government.
[533] In the
civil uprising phase of the Syrian civil war, Iran provided Syria with technical support based on Iran's capabilities developed following the
2009–2010 Iranian election protests.
[533] As the uprising developed into the
Syrian civil war,
there were increasing reports of Iranian military support, and of
Iranian training of NDF (National Defence Forces) both in Syria, and in
Iran.
[534]
Iranian security and intelligence services are advising and assisting
the Syrian military to preserve Bashar al-Assad's hold on power.
[531] Those efforts include training, technical support, combat troops.
[530][531] By December 2013 Iran was thought to have approximately 10,000 operatives in Syria.
[532] Lebanese
Hezbollah fighters backed by Tehran has taken direct combat roles since 2012.
[532][535]
In the summer of 2013, Iran and Hezbollah provided important
battlefield support for Assad, allowing it to make advances on the
opposition.
[535] In 2014, coinciding with the
peace talks at Geneva II, Iran has stepped up support for Syrian President Assad.
[532][535] Syrian Minister of Finance and Economy announced that the "Iranian government has given more than 15 billion dollars" to Syria.
[536] Iranian Revolutionary Guards Corps Quds Force commander
Qasem Suleimani
is in charge of Syrian President Assad's security portfolio and has
overseen the arming and training of thousands of pro-government Shi'ite
fighters.
[149][537]
Syrian Opposition
Syrian National Coalition
On 11 November 2012 in Doha, the National Council and other opposition forces united as the
National Coalition for Syrian Revolutionary and Opposition Forces.
[538] The following day, it was recognized as the legitimate government of Syria by numerous
Persian Gulf
states. Delegates to the Coalition's leadership council are to include
women and representatives of religious and ethnic minorities, including
Alawites. The military council will reportedly include the Free Syrian
Army.
[539] The main aims of the National Coalition are replacing the
Bashar al-Assad government and "its symbols and pillars of support", "dismantling the security services", unifying and supporting the
Free Syrian Army,
refusing dialogue and negotiation with the al-Assad government, and
"holding accountable those responsible for killing Syrians, destroying
[Syria], and displacing [Syrians]".
[540]
Free Syrian Army
Free Syrian Army fighters being transported by pick up truck
The formation of the Free Syrian Army (FSA) was announced on 29 July 2011 by a group of defecting
Syrian Army
officers. In a video, the men called upon Syrian soldiers and officers
to defect to their ranks, and said the purpose of the Free Syrian Army
was to defend civilian protesters from violence by the state, and "to
bring this [Syrian] regime down".
[541]
Many Syrian soldiers subsequently deserted to join the FSA.
[542] By December 2011, the estimated number of soldiers who had defected to the FSA was ranging from 1,000 to over 25,000.
[543]
The FSA functions more as an umbrella organization than a traditional
military chain of command, and was first "headquartered" in Turkey, but
moved its command headquarters to northern Syria in September 2012.
In March 2012, two reporters of
The New York Times witnessed an FSA attack with a
roadside bomb and AK-47 rifles on a column of armored Syrian tanks in
Saraqib in
Idlib Governorate,
and learned that FSA had a stock of able, trained soldiers and
ex-officers, organized to some extent, but were without the weapons to
put up a realistic fight.
[544]
In April 2013, the
US announced it would transfer $123 million in nonlethal aid to Syrian rebels through defected general
Salim Idriss, leader of the FSA.
[545]
In May 2013,
Salim Idriss,
the FSA leader, acknowledged that "the rebels" were badly fragmented
and lacked the military skill needed to topple the government of
President Bashar al-Assad. Idriss said he was working on a countrywide
command structure, but that a lack of material support was hurting that
effort. "Now it is very important for them to be unified. But unifying
them in a manner to work like a regular army is still difficult", Idriss
said. He acknowledged common operations with Islamist group
Ahrar ash-Sham but denied any cooperation with Islamist group
al-Nusra Front.
[545]
Abu Yusaf, a commander of the
Islamic State
(IS), said in August 2014 that many of the FSA members who had been
trained by United States’ and Turkish and Arab military officers were
now actually joining IS.
[546]
On the contrary to the ISIS commander's claims, by September 2014 the
Free Syrian Army was joining an alliance and a common front with Kurdish
militias including the YPG to fight ISIS.
[547][548]
Syrian National Council
Formed on 23 August 2011, the National Council is a coalition of
anti-government groups, based in Turkey. The National Council seeks the
end of Bashar al-Assad's rule and the establishment of a modern, civil,
democratic state. SNC has links with the
Free Syrian Army. In November 2012, the council agreed to unify with several other opposition groups to form the
Syrian National Coalition. The SNC has 22 out of 60 seats of the Syrian National Coalition.
[549]
Islamic Front
The
Islamic Front (
Arabic:
الجبهة الإسلامية,
al-Jabhat al-Islāmiyyah) is a merger of seven rebel groups involved in the
Syrian civil war[13] that was announced on 22 November 2013.
[550] The group has between 40,000
[551] and 60,000 fighters. An anonymous spokesman for the group has stated that it will not have ties with the
Syrian National Coalition,
[552] though a member of the political bureau of the group, Ahmad Musa, has stated that he hopes for recognition from the
Syrian National Council in cooperation for what he suggested "the Syrian people want. They want a revolution and not politics and foreign agendas."
[553] The group is widely seen as backed and armed by
Saudi Arabia.
[554][555][556]
Salafist factions
In September 2013, US Secretary of State
John Kerry stated that extremist groups make up 15–25% of rebel forces.
[557] According to
Charles Lister, about 12% of rebels are part of groups linked to
al-Qaeda, 18% belong to
Ahrar ash-Sham, and 9% belong to
Suqour al-Sham Brigade.
[558][559] These numbers contrast with a report by
Jane's Information Group, a defence outlet, claiming almost half of all rebels being affiliated to Islamist groups.
[560] Foreign fighters have joined the conflict in opposition to Assad. While most of them are jihadists, some individuals, such as
Mahdi al-Harati, have joined to support the Syrian opposition.
[561]
The
ICSR
estimates that 2,000–5,500 foreign fighters have gone to Syria since
the beginning of the protests, about 7–11 percent of whom came from
Europe. It is also estimated that the number of foreign fighters does
not exceed 10 percent of the opposition armed forces.
[562] Another estimate puts the number of foreign jihadis at 15,000 by early 2014
[563]), The
European Commission
expressed concerns that some of the fighters might use their skills
obtained in Syria to commit acts of terrorism back in Europe in the
future.
[564]
Islamic campaign in support of Syrian opposition
In October 2012, various Iraqi religious groups join the conflict in
Syria on both sides. Radical Sunnis from Iraq, have traveled to Syria to
fight against President
Bashar al-Assad and the Syrian government.
[565] Also, Shiites from Iraq, in
Babil Province and
Diyala Province, have traveled to
Damascus from
Tehran, or from the Shiite Islamic holy city of
Najaf, Iraq to protect
Sayyida Zeinab, an important mosque and shrine of
Shia Islam in Damascus.
[565]
In September 2013, leaders of 13 powerful rebel brigades rejected
Syrian National Coalition and called Sharia law "the sole source of
legislation". In a statement they declared that "the coalition and the
putative government headed by Ahmad Tomeh does not represent or
recognize us". Among the signatory rebel groups were
Al-Nusra Front,
Ahrar ash-Sham and
Al-Tawheed.
[566] In November 2013, seven Islamist groups combined to form the
Islamic Front.
Al-Nusra Front
Main article:
Al-Nusra Front
The al-Nusra Front, being the biggest
jihadist group in Syria, is often considered to be the most aggressive and violent part of the opposition.
[567] Being responsible for over 50
suicide bombings, including several deadly explosions in Damascus in
2011 and
2012,
it is recognized as a terrorist organization by Syrian government and
was designated as such by United States in December 2012.
[75] In April 2013, the leader of the
Islamic state of Iraq released an audio statement announcing that al-Nusra Front is its branch in Syria.
[568]
The leader of al-Nusra, Abu Mohammad al-Golani, said that the group
will not merge with the Islamic State of Iraq, but still maintain
allegiance to
Ayman al-Zawahiri, the leader of
al-Qaeda.
[569]
The relationship between the Al-Nusra Front and the indigenous Syrian
opposition is tense, even though al-Nusra Front has fought alongside
the FSA in several battles and some FSA fighters defected to the
al-Nusra Front.
[570] The Mujahideen's strict religious views and willingness to impose
sharia law disturbed many Syrians.
[571]
Some rebel commanders have accused foreign jihadists of "stealing the
revolution", robbing Syrian factories and displaying religious
intolerance.
[572] Al-Nusra Front has been accused of mistreating religious and ethnic minorities since their formation.
[573] The estimated manpower of al-Nusra Front is approximately 6,000–10,000 people, including many foreign fighters.
[574]
On 10 March 2014, Al Nusra released 13 Christian nuns captured from
Malouula, Damascus, in exchange for the release of 150 women from the
Syrian government's prisons. The nuns reported that they were treated
well by Al Nusra during their captivity, adding that they "were giving
us everything we asked for" and that "no one bothered us".
[575]
Syrian Kurds
Kurds showing their support for the PYD in Afrin during the conflict
Kurds – mostly
Sunni Muslims, with a small minority of
Yezidis
– represented 10% of Syria's population at the start of the uprising in
2011. They had suffered from decades of discrimination and neglect,
being deprived of basic civil, cultural, economic, and social rights.
[576]:7
When protests began, Assad's government finally granted citizenship to
an estimated 200,000 stateless Kurds, in an effort to try and neutralize
potential Kurdish opposition.
[577]
This concession, combined with Turkish endorsement of the opposition
and Kurdish under-representation in the Syrian National Council, has
resulted in Kurds participating in the civil war in smaller numbers than
their Syrian Arab Sunni counterparts.
[577] Consequently, violence and state repression in Kurdish areas has been less severe.
[577] In terms of a post-Assad Syria, Kurds reportedly desire a degree of autonomy within a decentralized state.
[578]
Since the outset of the civil war, most Kurdish political parties organised themselves into the
National Coordination Committee for Democratic Change (NCC), holding a more moderate stance regarding the Assad government. However, in October 2011, all but the
Democratic Union Party (PYD) left the NCC to form their own umbrella organisation, the
Kurdish National Council.
The Syrian Kurdish
People's Protection Units (YPG), first entered this Syrian Civil War as belligerent in July 2012, by capturing a town,
Kobanê, that until then was under control of the Syrian Assad-government (see
Syrian Kurdistan campaign (2012–present)).
The conflict between the Kurdish People's Protection Units (YPG) and
Islamists groups such as al-Nusra Front have escalated since a group of
Kurds expelled Islamists from the border town of Ras al-Ain.
[579]
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL)
Called Dā'ash or the
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (abbrv. ISIL or ISIS [Islamic State of Iraq and Syria] or
Islamic State)
made rapid military gains in Northern Syria starting in April 2013 and
as of Mid 2014 controls large parts of that region, where the
Syrian Observatory for Human Rights describes it as "the strongest group".
[580] It has imposed strict
Sharia law over land that it controls. The group was, until 2014, affiliated with
al-Qaeda, led by the Iraqi fighter
Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi,
and has an estimated 7,000 fighters in Syria, including many
non-Syrians. It has been praised as less corrupt than other militia
groups, and criticized for abusing human rights
[581]
and for not tolerating non-Islamist militia groups, foreign journalists
or aid workers, whose members it has expelled, imprisoned.
[582]
or executed. According to Michael Weiss, ISIL has not been targeted by
the Syrian government "with quite the same gusto" as other rebel
factions.
[149]
In summer 2014 the ISIL controlled a third of Syria. It established
itself as the dominant force of Syrian opposition, defeating Jabhat
al-Nusra in Deir Ezzor governorate and claiming control over most of
Syria's oil and gas production.
[76]
The Syrian government did not begin to fight ISIL until June 2014
despite its having a presence in Syria since April 2013, according to
Kurdish officials.
[583]
ISIL has recruited more than 6,300 fighters in July 2014 alone.
[584]
In September 2014, reportedly some Syrian rebels and ISIL signed a
"non-aggression" agreement in a suburb of Damascus, citing inability to
deal with both ISIL and the Syrian army's attacks at once.
[585] Some Syrian rebels have, however, decried the news on the "non-aggression" pact.
Reporting, censoring and propaganda
Reporting on this war is difficult and dangerous: journalists are
being attacked, detained, reportedly tortured, over hundred reportedly
killed already by October 2012. Technical facilities (internet,
telephone etc.) are being sabotaged by the Syrian government. Both sides
in this war try to disqualify their opponent by framing or indicating
them with negative labels and terms ("terrorists", "propaganda",
"biased", "foreign conspiracy"), or by presenting false evidence.
[586]
International reaction
The
Arab League,
European Union, the United Nations,
[587]
and many Western governments quickly condemned the Syrian government's
violent response to the protests, and expressed support for the
protesters' right to exercise
free speech.
[588]
Initially, many Middle Eastern governments expressed support for Assad,
but as the death toll mounted they switched to a more balanced
approach, criticizing violence from both government and protesters. Both
the Arab League and the
Organisation of Islamic Cooperation suspended Syria's membership. Russia and China vetoed Western-drafted
United Nations Security Council
resolutions in 2011 and 2012, which would have threatened the Syrian
government with targeted sanctions if it continued military actions
against protestors.
[589] The United Nations prepared an
international peace conference in Geneva on 22 January 2014, in which both the Syrian government and opposition have promised to participate.
[citation needed]
Humanitarian help
The international humanitarian response to the conflict in Syria is coordinated by the
United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA) in accordance with
General Assembly Resolution 46/182.
[590] The primary framework for this coordination is the Syria Humanitarian Assistance Response Plan (SHARP) which appealed for
USD $1.41 billion to meet the humanitarian needs of Syrians affected by the conflict.
[591] Official United Nations data on the humanitarian situation and response is available at
http://syria.unocha.org/;
an official website managed by UNOCHA Syria (Amman). UNICEF is also
working alongside these organizations to provide vaccinations and care
packages to those in need. It has launched a vaccination campaign to
eradicate polio from the region, as 17 cases have come up since the war
broke over three years ago.
US non-lethal aid to Syrian opposition forces, May 2013
Financial information on the response to the SHARP, as well as
assistance to refugees and for cross-border operations, can be found on
UNOCHA's Financial Tracking Service. As at 18 September 2013, the top
ten donors to Syria were: United States, European Commission, Kuwait,
United Kingdom, Germany, Canada, Japan, Australia, Saudi Arabia, and
Denmark.
[592] USAID
and other government agencies in US delivered nearly $385 million of
aid items to Syria in 2012 and 2013. The United States is providing food
aid, medical supplies, emergency and basic health care, shelter
materials, clean water, hygiene education and supplies, and other relief
supplies.
[593] Islamic Relief has stocked 30 hospitals and sent hundreds of thousands of medical and food parcels.
[594]
Other countries in the region have also contributed various levels of
aid. Iran has been exporting between 500 and 800 tonnes of flour daily
to Syria.
[595] Israel has provided treatment to 750 Syrians in a field hospital located in
Golan Heights. Rebels say that 250 of their fighters received medical treatment there.
[596] On 26 April 2013, a humanitarian convoy, inspired by
Gaza Flotilla, departed from Turkey to Syria. Called
Hayat ("Life"), it is set to deliver aid items to
IDPs
inside Syria and refugees in neighboring countries: Turkey, Lebanon,
Jordan, Iraq, and Egypt. Syrian refugees make up one quarter of
Lebanon's population, mostly consisting of women and children.
[597]
The
World Health Organization
has reported that 35% of the country's hospitals are out of service
and, depending upon the region, up to 70% of health care professionals
have fled. Cases of
diarrhoea and
hepatitis A
have increased by more than twofold since the beginning of 2013. Due to
fighting, the normal vaccination programs cannot be undertaken. The
displaced refugees may also pose a risk to countries to which they have
fled.
[598]
Foreign involvement
Map of countries surrounding Syria (red) with military involvement.
Syria
Countries that support the rebels
Countries that support the Syrian government
Countries that have groups that support the Syrian government with military force
Both the Syrian government and the opposition have received support,
militarily and diplomatically, from foreign countries leading the
conflict to often be described as a
proxy war. The major parties supporting the Syrian Government are
Iran and Hezbollah.
Both of these are involved in the war politically and logistically by
providing military equipment, training and battle troops. The Syrian
government has also received arms from Russia and
SIGINT support directly from
GRU,
[599] in addition to significant political
support from Russia.
[600] However, recent developments have led Russia to realize that there has been a "turning point" against Assad.
[601]
The main Syrian opposition body – the Syrian coalition – receives political, logistic and military support from the
United States, Britain and France.
[602][603][604] Some Syrian rebels get
training from the CIA at bases in
Qatar,
Jordan and
Saudi Arabia.
[605][606][607] The Syrian coalition also receives logistic and political support from Sunni states, most notably
Turkey,
Qatar and Saudi Arabia; all the three major supporting states however
have not contributed any troops for direct involvement in the war,
though Turkey was involved in border incidents with the Syrian Army. The
Financial Times and
The Independent reported that
Qatar had funded the Syrian rebellion by as much as $3 billion.
[608][609] It reported that Qatar was offering refugee packages of about $50,000 a year to defectors and family.
[609] Saudi Arabia has emerged as the main group to finance and arm the rebels.
[610]
French television France 24 reported that the
Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant, with perhaps 3,000 foreign jihadists among its ranks,
[611] "receives private donations from the
Gulf states."
[612] As of 2015, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and Turkey are openly backing the
Army of Conquest, an umbrella rebel group that reportedly includes an
al-Qaeda linked
al-Nusra Front and another
Salafi coalition known as
Ahrar ash-Sham, and
Faylaq Al-Sham, a coalition of
Muslim Brotherhood-linked rebel groups.
[613][614][615] The major Syrian Kurdish opposition group, the PYD, was reported to get logistic and training support from
Iraqi Kurdistan.
On 21 August 2014, two days after US photojournalist
James Foley was beheaded, the
U.S. military admitted a covert rescue attempt involving dozens of
US Special Operations forces
had been made to rescue Americans and other foreigners held captive in
Syria by ISIL militants. The rescue attempt is the first known US
military ground action inside Syria. The resultant gunfight resulted in
one US soldier being injured. The rescue was unsuccessful as the
captives were not in the location targeted.
On 11 September 2014 Congress expressed support to give President
Obama the $500 million he wants to arm and train moderate Syrian rebels.
The question of whether the president has authority to continue
airstrikes beyond the 60-day window granted by the War Powers Resolution
remained unresolved.
[616]
On 12 September, US Secretary of State John Kerry met Turkish leaders
to secure backing for US-led action against ISIL, but Ankara showed
reluctance to play a frontline role. Kerry stated that it was "not
appropriate" for Iran to join talks on confronting ISIL.
[617]
The plans revealed in September also involve Iraq in targeting ISIL.
US warplanes have launched 158 strikes in Iraq over the past five weeks
while emphasizing a relatively narrow set of targets. The Pentagon's
press secretary, John Kirby, said the air campaign in Iraq, which began 8
Aug., will enter a more aggressive phase.
[618]
Impact
Deaths
Total deaths over the course of the conflict in Syria (18 March 2011 – 18 October 2013)
Estimates of deaths in the conflict vary widely, with figures, per opposition activist groups, ranging from 131,235 and 300,518.
[53][619][620][621] On 2 January 2013, the United Nations stated that 60,000 had been killed since the civil war began, with UN
High Commissioner for Human Rights Navi Pillay saying "The number of casualties is much higher than we expected, and is truly shocking."
[622] Four months later, the UN's updated figure for the death toll had reached 80,000.
[623]
On 13 June, the UN released an updated figure of people killed since
fighting began, the figure being exactly 92,901, for up to the end of
April 2013.
Navi Pillay,
UN high commissioner for human rights, stated that: "This is most
likely a minimum casualty figure." The real toll was guessed to be over
100,000.
[624][625]
Some areas of the country have been affected disproportionately by the
war; by some estimates, as many as a third of all deaths have occurred
in the city of
Homs.
[626]
One problem has been determining the number of "armed combatants" who
have died, due to some sources counting rebel fighters who were not
government defectors as civilians.
[627]
At least half of those confirmed killed have been estimated to be
combatants from both sides, including 52,290 government fighters and
29,080 rebels, with an additional 50,000 unconfirmed combatant deaths.
[53] In addition,
UNICEF reported that over 500 children had been killed by early February 2012,
[628] and another 400 children have been reportedly arrested and tortured in Syrian prisons;
[629]
both of these claims have been contested by the Syrian government.
Additionally, over 600 detainees and political prisoners are known to
have died under torture.
[630] In mid-October 2012, the opposition activist group
SOHR reported the number of children killed in the conflict had risen to 2,300,
[631] and in March 2013, opposition sources stated that over 5,000 children had been killed.
[619] In January 2014,
a report was released detailing the systematic killing of more than 11,000 detainees of the Syrian government.
[632]
On 20 August 2014, a new U.N. study concludes at least 191,369 people have died in Syrian conflict.
[633]
Illness
Once-rare infectious diseases have spread in rebel held areas,
primarily affecting children, brought on by the collapse of sanitation
and deteriorating living conditions. These include
measles,
typhoid,
hepatitis,
dysentery,
tuberculosis,
diphtheria,
whooping cough,
leishmaniasis, (a disfiguring parasitic skin disease). Of particular concern is the contagious and crippling
Poliomyelitis
which as of late 2013 doctors and international public health agencies
report more than 90 cases of. Critics of the government complain that it
has brought on the spread of disease by cutting off vaccination,
sanitation and safe-water services to "areas considered politically
unsympathetic" even before the uprising.
[634]
Refugees
Syrian refugees in Lebanon living in cramped quarters (6 August 2012).
The violence in Syria has caused millions to flee their homes. As of
March 2015, Al-Jazeera estimates 10.9 million Syrians, or almost half
the population, have been displaced.
[635] 3.8 million have been made refugees.
[635][636] As of 2013, 1 in 3 of Syrian refugees (about 667,000 people) sought safety in tiny
Lebanon (normally 4.8 million population).
[637]
Others have fled to Jordan, Turkey, and Iraq. Turkey has accepted
+1.700.000 (2015) Syrian refugees, half of whom are spread around a
cities and dozen camps placed under the direct authority of the Turkish
Government. Satellite images confirmed that the first Syrian camps
appeared in Turkey in July 2011, shortly after the towns of Deraa, Homs,
and Hama were besieged.
[638] In September 2014, the UN stated that the number of Syrian refugees had exceeded 3 million.
[639] According to the
Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs,
Sunnis are leaving for Lebanon and undermining Hezbollah's status. The
fleeing Syrian refugees has caused the "Jordan is Palestine" threat to
be diminished due to the onslaught of new refugees in Jordan.
Additionally, "the West Bank is undergoing emigration pressures which
will certainly be copied in Gaza if emigration is allowed".
[640] Greek Catholic Patriarch
Gregorios III Laham claims more than 450,000
Syrian Christians have been displaced by the conflict.
[641]
Human rights violations
According to various human rights organizations and United Nations,
human rights violations have been committed by both the government and
the rebels, with the 'vast majority of the abuses having been committed
by the Syrian government'.
[642][643][644][645] The U.N.
commission
investigating human rights abuses in Syria confirms at least 9
intentional mass killings in the period 2012 to mid-July 2013,
identifying the perpetrator as Syrian government and its supporters in
eight cases, and the opposition in one.
[646][647]
Syria's civil war victims
By late November 2013, according to the
Euro-Mediterranean Human Rights Network
(EMHRN) report entitled "Violence against Women, Bleeding Wound in the
Syrian Conflict", approximately 6,000 women have been raped (including
gang-rape) since the start of the conflict - with figures likely to be
much higher given that most cases go unreported.
[648][649][650]
According to three international lawyers,
[651]
Syrian government officials could face war crimes charges in the light
of a huge cache of evidence smuggled out of the country showing the
"systematic killing" of about
11,000 detainees.
Most of the victims were young men and many corpses were emaciated,
bloodstained and bore signs of torture. Some had no eyes; others showed
signs of strangulation or electrocution.
[652]
Experts say this evidence is more detailed and on a far larger scale
than anything else that has yet emerged from the 34-month crisis.
[653][654]
On 30 January 2014, Human Rights Watch released a report detailing,
between June 2012 and July 2013, government forces razing to the ground
seven anti-government districts in the cities of Damascus and Hama,
equating to an area the size of 200 football fields. Witnesses spoke of
explosives and bulldozers being used to knock down buildings.
[655] Satellite imagery
was provided as part of the report and the destruction was
characterized as collective punishment against residents of rebel-held
areas.
[656]
UN reported also that
"siege
warfare is employed in a context of egregious human rights and
international humanitarian law violations. The warring parties do not
fear being held accountable for their acts." Armed forces of both
sides of the conflict blocked access of humanitarian convoys,
confiscated food, cut off water supplies and targeted farmers working
their fields. The report pointed to four places besieged by the
government forces: Muadamiyah, Daraya, Yarmouk camp and Old City of
Homs, as well as two areas under siege of rebel groups: Aleppo and Hama.
[657][658] In
Yarmouk Camp
20,000 residents are facing death by starvation due to blockade by the
Syrian government forces and fighting between the army and
Jabhat al-Nusra, which prevents food distribution by UNRWA.
[657][659]
The UN further stated that government sieges have left more than
250,000 subjected to relentless shelling and bombardment. "They are
denied humanitarian aid, food and such basic necessities as medical
care, and must choose between surrender and starvation,” the members of
the UN Commission of Inquiry said.
[660]
ISIS forces have been accused by UN of using public executions, amputations and lashings in a campaign to instill fear.
"Forces
of the Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham have committed torture,
murder, acts tantamount to enforced disappearance and forced
displacement as part of attacks on the civilian population in Aleppo and
Raqqa governorates, amounting to crimes against humanity", said the report from 27 August 2014.
[661]
Enforced disappearances and arbitrary detentions have also been a feature since the Syrian uprising began.
[662]
Threats against Syrian sects and minorities
Map of Syria's ethno-religious composition in 1976
The successive governments of Hafez and Bashar al-Assad have been closely associated with the country's minority
Alawite religious group,
[663] an offshoot of Shia, whereas the majority of the population, and most of the opposition, is
Sunni. Alawites started to be threatened and attacked by dominantly Sunni rebel fighting groups like the
Al-Nusra Front and the
FSA since December 2012 (see
Sectarianism and minorities in the Syrian Civil War#Alawites).
Many
Syrian Christians reported to have fled after they were targeted by the anti-government rebels.
[664][665] (See:
Sectarianism and minorities in the Syrian Civil War#Christians.)
Economy
By July 2013, the Syrian economy had shrunk 45 percent since the
start of the conflict. Unemployment increased fivefold, the value of the
Syrian currency decreased to one-sixth its pre-war value, and the
public sector lost USD $15 billion.
[666][667] By the end of 2013, the UN estimated total economic damage of the Syrian civil war at $143 billion.
[668] The total economic loss from the Syrian Civil War will reach $237 billion by the end of 2015, according to the
United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia, with the Syrian opposition's capture of
Nasib border crossing costing the government a further $500–$700 million a year on top of this.
[669]
Crime wave
Doctors and medical staff treating injured rebel fighters and civilians in Aleppo
As the conflict has expanded across Syria, many cities have been
engulfed in a wave of crime as fighting caused the disintegration of
much of the civilian state, and many police stations stopped
functioning. Rates of theft increased, with criminals looting houses and
stores. Rates of kidnappings increased as well. Rebel fighters were
seen stealing cars and, in one instance, destroying a restaurant in
Aleppo where Syrian soldiers had been seen eating.
[670]
By July 2012, the human rights group
Women Under Siege had documented over 100 cases of rape and
sexual assault
during the conflict, with many of these crimes believed to have been
perpetrated by the Shabiha and other pro-government militias. Victims
included men, women, and children, with about 80% of the known victims
being women and girls.
[671]
Local
National Defence Forces
commanders often engaged "in war profiteering through protection
rackets, looting, and organized crime". NDF members were also implicated
in "waves of murders, robberies, thefts, kidnappings, and extortions
throughout regime-held parts of Syria since the formation of the
organization in 2013", as reported by the Institute for the Study of
War.
[672]
Criminal networks have been used by both the government and the
opposition during the conflict. Facing international sanctions, the
Syrian government relied on criminal organizations to smuggle goods and
money in and out of the country. The economic downturn caused by the
conflict and sanctions also led to lower wages for Shabiha members. In
response, some Shabiha members began stealing civilian properties and
engaging in kidnappings.
[511]
Rebel forces sometimes rely on criminal networks to obtain weapons
and supplies. Black market weapon prices in Syria's neighboring
countries have significantly increased since the start of the conflict.
To generate funds to purchase arms, some rebel groups have turned
towards extortion, theft, and kidnapping.
[511]
Cultural heritage
As of March 2015, the war has affected 290 heritage sites, severely
damaged 104, and completely destroyed 24. Five of the six UNESCO
World Heritage Sites in Syria have been damaged.
[635] Destruction of antiquities has been caused by
shelling, army entrenchment, and
looting at various
tells, museums, and monuments.
[673] A group called
Syrian Archaeological Heritage Under Threat
is monitoring and recording the destruction in an attempt to create a
list of heritage sites damaged during the war and to gain global support
for the protection and preservation of
Syrian archaeology and architecture.
[674]
UNESCO listed all six Syria's
World Heritage sites as endangered but direct assessment of damage is not possible. It is known that the
Old City of Aleppo was heavily damaged during battles being fought within the district, while
Palmyra and
Crac des Chevaliers
suffered minor damage. Illegal digging is considered a grave danger,
and hundreds of Syrian antiquities, including some from Palmyra,
appeared in Lebanon. Three archeological museums are known to have been
looted; in Raqqa some artifacts seem to have been destroyed by foreign
Islamists due to religious objections.
[675]
The war has produced its own particular artwork. A late Summer 2013 exhibition in London at the
P21 Gallery was able to show some of this work.
[676]
Spillover
With porous borders with most of its neighbors, the fighting has
spilled over them, causing fears of a regional war. In June 2014,
members of the
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) crossed the border from Syria into northern
Iraq, and have
taken control of large swaths of Iraqi territory as the
Iraqi Army abandoned its positions. The Syrian Civil War has led to incidents of sectarian violence in
northern Lebanon between supporters and opponents of the Syrian government, and armed clashes between Sunnis and Alawites in
Tripoli.
[677] Fighting between rebels and government forces has spilled into Lebanon on several occasions.
The fight between ISIL and the Kurds in the town of Kobani on the
Turkish border has led to rioting throughout Turkey and to brief
occupations of a number of parliament buildings in Western Europe.
[678]
See also
References

 Iran
Iran Russia[2][3]
Russia[2][3] North Korea[4]
North Korea[4] Opposition
(SRCC)Supported by:
Opposition
(SRCC)Supported by: Qatar
Qatar Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Turkey[5][6]
Turkey[5][6] United States[7]
United States[7] France[8]
France[8] Libya[Ω][9]
Libya[Ω][9] al-Nusra Front
al-Nusra Front Peshmerga Allied militias
Peshmerga Allied militias CJTF–OIR
CJTF–OIR Bashar al-Assad
Bashar al-Assad Maher al-Assad
Maher al-Assad Fahd Jassem al-Freij
Fahd Jassem al-Freij Dawoud Rajiha †
Dawoud Rajiha † Assef Shawkat †
Assef Shawkat † Ali Abdullah Ayyoub
Ali Abdullah Ayyoub Issam Hallaq
Issam Hallaq Ghassan Ismail
Ghassan Ismail Mohammad al-Shaar (WIA)
Mohammad al-Shaar (WIA) Suheil Al Hassan
Suheil Al HassanHassan Nasrallah
 Qasem Soleimani
Qasem Soleimani Ahmed Jibril
Ahmed Jibril Abdul-Ilah al-Bashir[10]
Abdul-Ilah al-Bashir[10] Salim Idris
Salim Idris Abdul Jabbar al-Oqaidi
Abdul Jabbar al-Oqaidi Jamal Maarouf
Jamal Maarouf Riad al-Asaad (WIA)[11]
Riad al-Asaad (WIA)[11] Mustafa Al-Sheikh[12]
Mustafa Al-Sheikh[12] Ahmed Issa al-Sheikh[13]
Ahmed Issa al-Sheikh[13] Abu Omar Hureitan[13]
Abu Omar Hureitan[13] Zahran Alloush
Zahran Alloush Hassan Aboud †[14]
Hassan Aboud †[14] Abdul Qader Saleh †[15]
Abdul Qader Saleh †[15] Abu Mohammad al-Julani
Abu Mohammad al-Julani Sami al-Oraydi
Sami al-Oraydi Abu Humam al-Shami †
Abu Humam al-Shami † Abu Firas al-Suri
Abu Firas al-Suri Abu Maria Al-Qahtani
Abu Maria Al-Qahtani Abu Muhammed al Ansari †
Abu Muhammed al Ansari † Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi[22]
Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi[22] Abu Ala al-Afri
Abu Ala al-Afri Abu Ali al-Anbari
Abu Ali al-Anbari Abu Suleiman al-Naser
Abu Suleiman al-Naser Abu Omar al-Shishani
Abu Omar al-Shishani Abu Mohammad al-Adnani
Abu Mohammad al-Adnani Abu Ayman al-Iraqi
Abu Ayman al-Iraqi Haji Bakr ("Haji Bakr") †[26]
Haji Bakr ("Haji Bakr") †[26] Abu Khattab al-Kurdi †
Abu Khattab al-Kurdi † Salih Muslim Muhammad
Salih Muslim Muhammad Sipan Hemo
Sipan Hemo Masoud Barzani
Masoud Barzani


























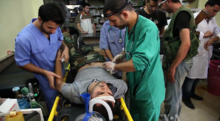
No comments:
Post a Comment